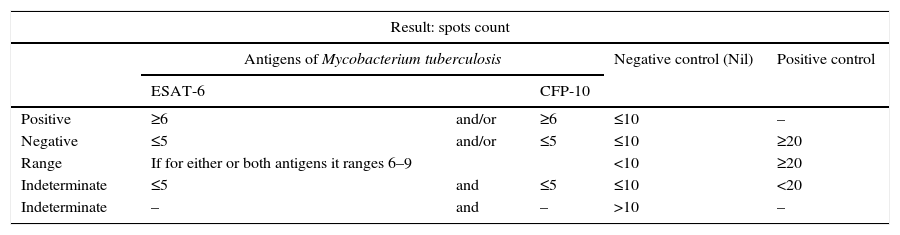
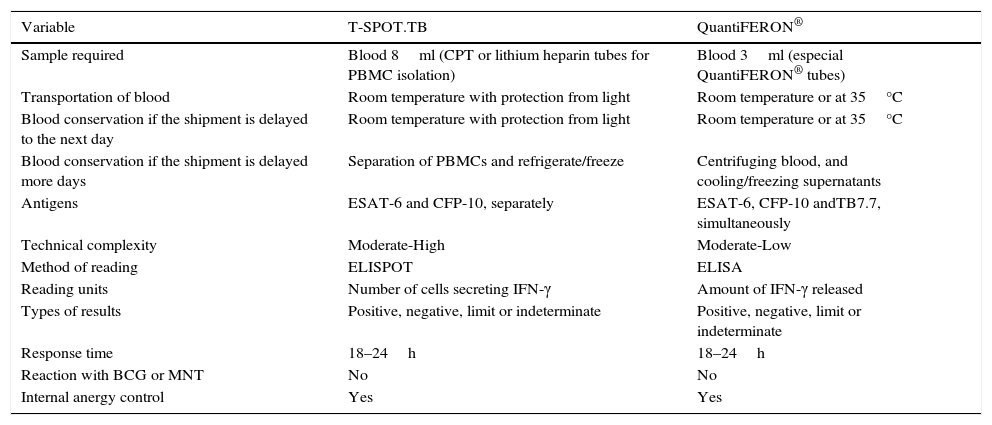
Tuberculosis remains one of the communicable diseases that cause increased morbidity and mortality worldwide. With an incidence rate of 13.04 per 100,000 population, Spain ranks third among the most affected European countries. These data show a tendency to decrease meaning that it may go unnoticed with the potential to miss the appropriate preventive measures in a suspected case. In centers where patients are treated with tuberculosis, health care worker presents risk of transmission. This risk is higher in some areas or work units. The occupational health physicians’ services, which monitorize the health of health care workers, use different strategies in order to prevent and detect tuberculosis infection. The national guidelines include the tuberculin skin test as a screening test for tuberculosis infection with mention of new diagnostic tests based on the in vitro detection of gamma interferon (IGRA) for certain cases. The purpose of this guide is to establish common criteria for IGRA tests, as a supplementary aid to the tuberculin skin test in health care workers, from the evidence available today. Recommendations for its use have been adapted to the different situations faced by the professionals involved in monitoring the health of health workers.
La tuberculosis continúa siendo una de las enfermedades transmisibles causantes de mayor morbimortalidad en el mundo. España con una tasa de incidencia de 13.04 por 100.000 habitantes ocupa el tercer lugar entre los países europeos más afectados. Estos datos muestran una tendencia a su disminución, pudiendo pasar desapercibida y hacer que no se realicen las medidas de prevención adecuadas ante un enfermo sospechoso. El personal sanitario que trabaja en un centro donde se atiende a pacientes con tuberculosis presenta riesgo de transmisión, siendo este riesgo superior en determinadas áreas o unidades de trabajo. Desde los Servicios de Prevención de Riesgos Laborales, encargados de vigilar la salud de los trabajadores sanitarios, se elaboran diferentes estrategias de abordaje con el objetivo de evitar la infección en estos trabajadores y detectar la infección tuberculosa reciente. Las guías nacionales existentes hasta la actualidad incluyen la prueba de la tuberculina como prueba de cribado de la infección tuberculosa, con referencia a las nuevas pruebas diagnósticas basadas en la detección in vitro de interferón-gamma (IGRA) para determinados casos. El objetivo de la presente guía ha sido consensuar y establecer unos criterios comunes para incluir las pruebas IGRA, como una ayuda complementaria a la prueba de la tuberculina en el personal sanitario, a partir de la evidencia disponible en la actualidad. Las recomendaciones de su utilización se han adaptado a las diferentes situaciones en que se pueden encontrar los profesionales que participan en la vigilancia de la salud de los trabajadores sanitarios.