Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCLs) are rare lysosomal storage disorders characterized by progressive mental retardation and motor developmental regression and myoclonic seizures. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been suggested to be used in the treatment of lysosomal disorders and brain damage caused by a deficiency of soluble lysosomal enzymes. There are no previous reports on treating NCLs with HSCT in China.
Material and methodNCL pediatric patients who underwent allo-HSCT at Affiliated Children's Hospital of Capital Institute of Pediatrics were involved. A combination of medical histories, clinical features, and genetic analyses was used for the diagnosis of all patients. The written consent form for allo-HSCT was attained from the patient's guardian, which was then reviewed and approved by the ethics committee before the procedure.
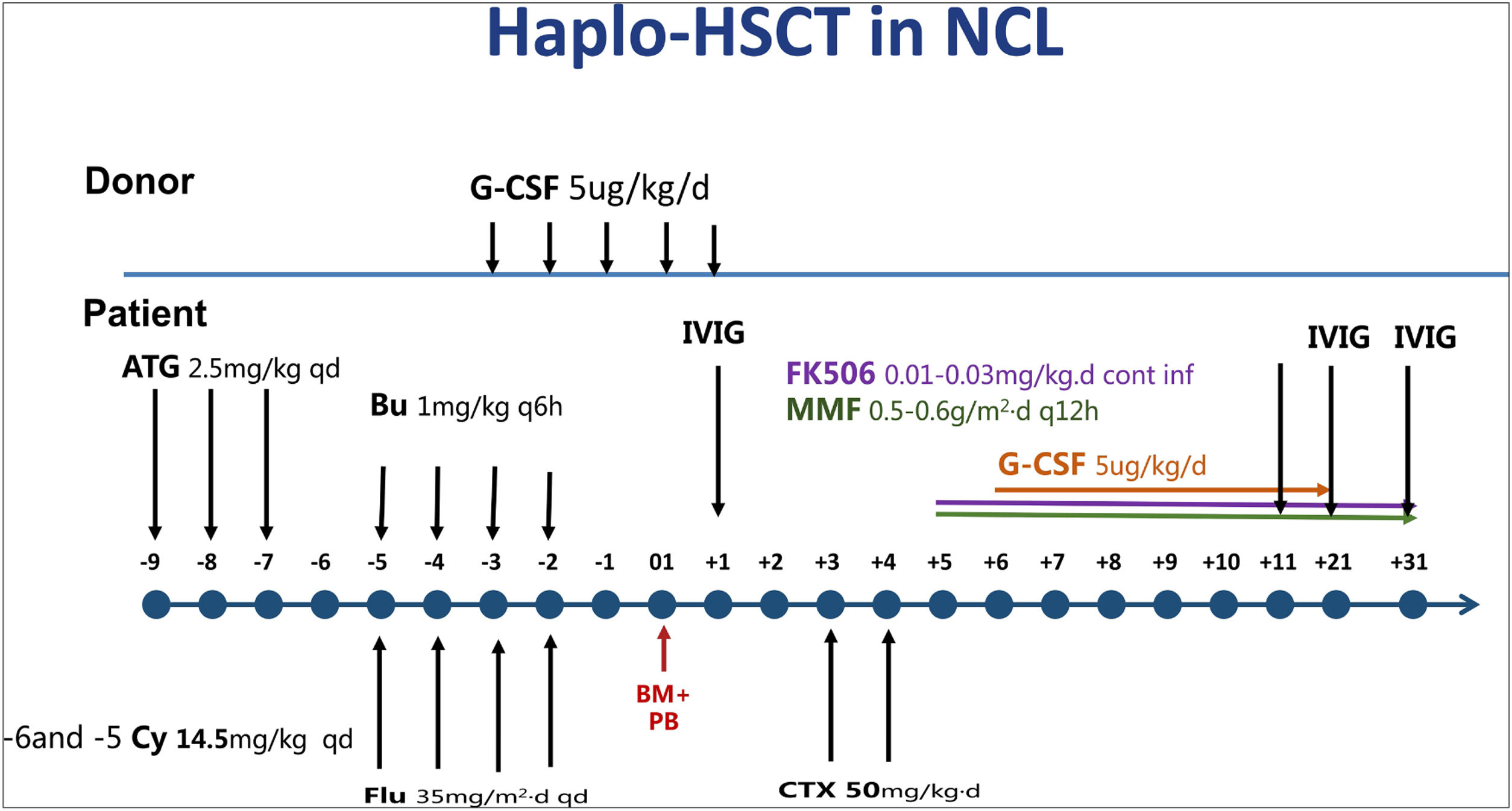
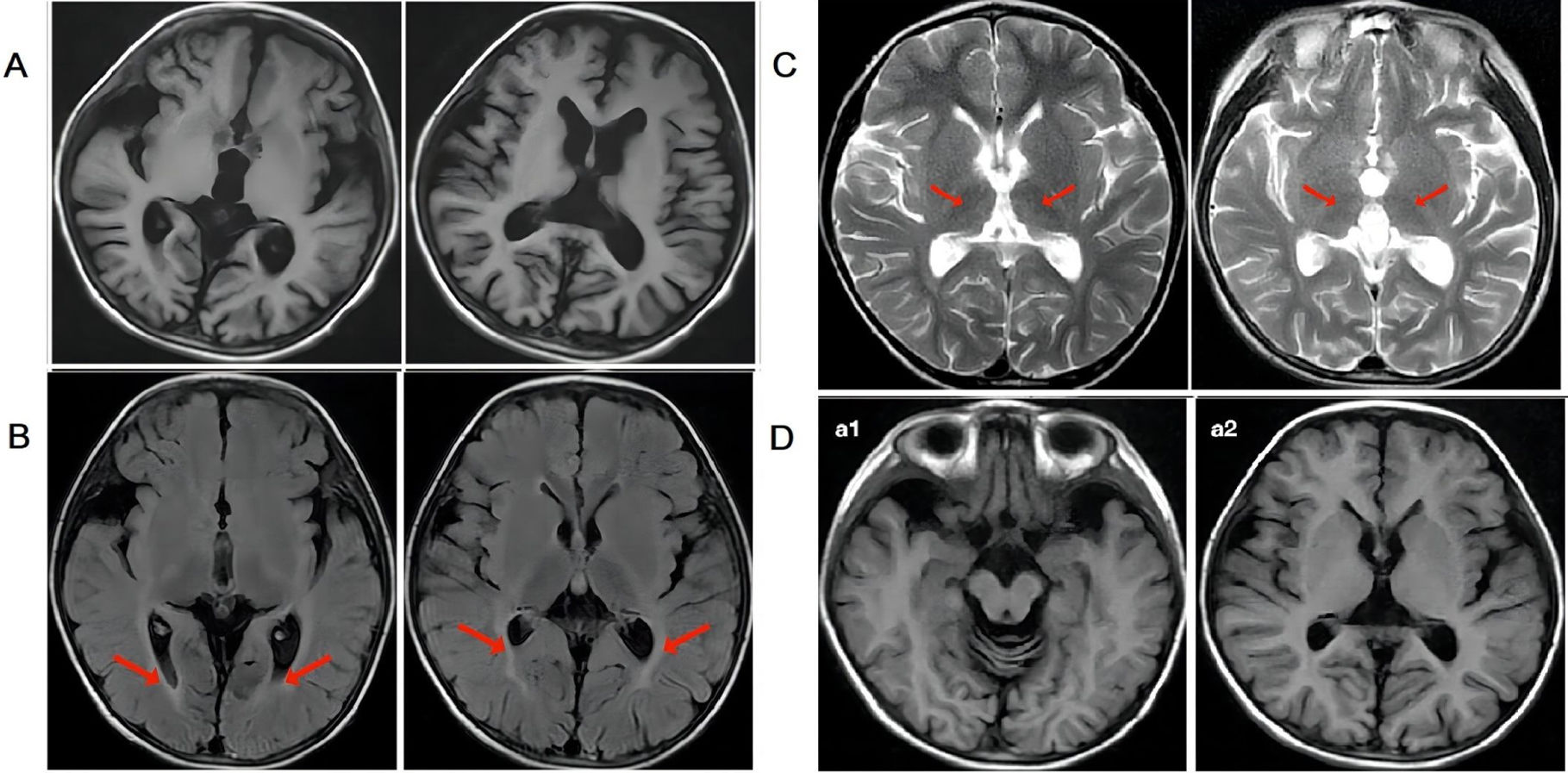
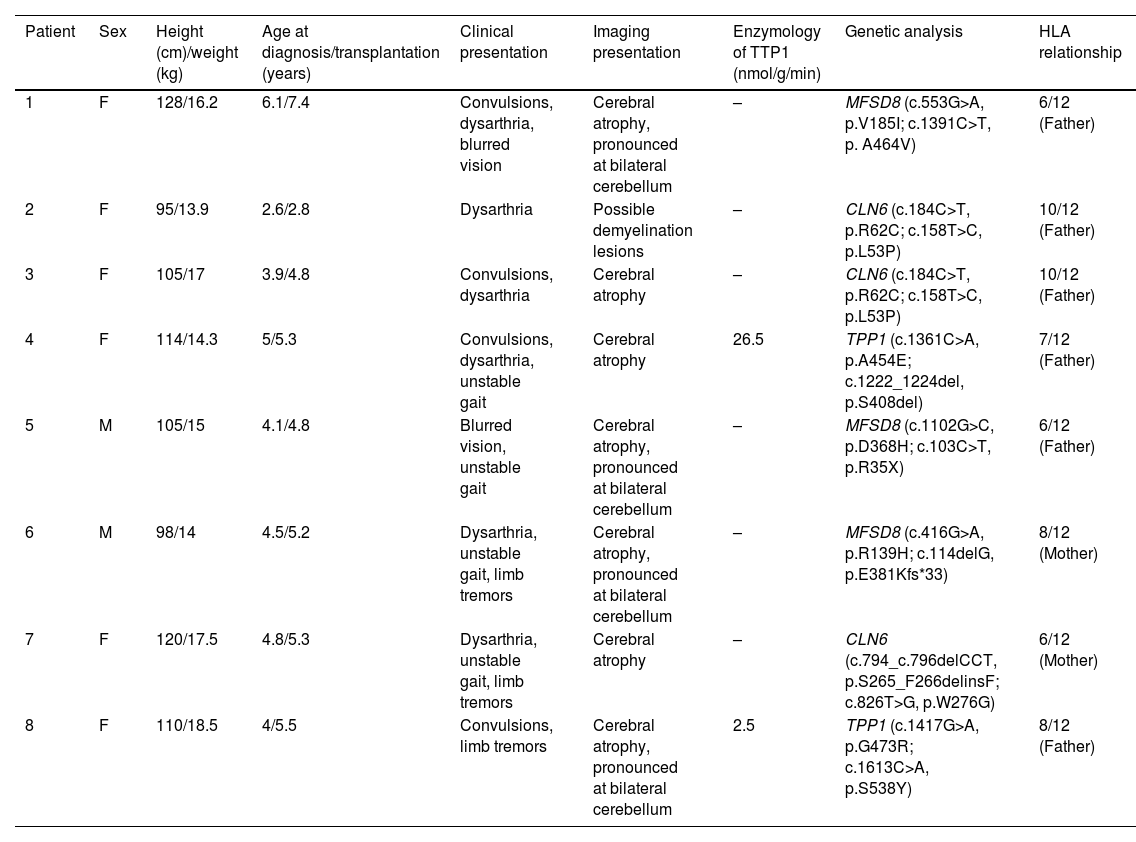
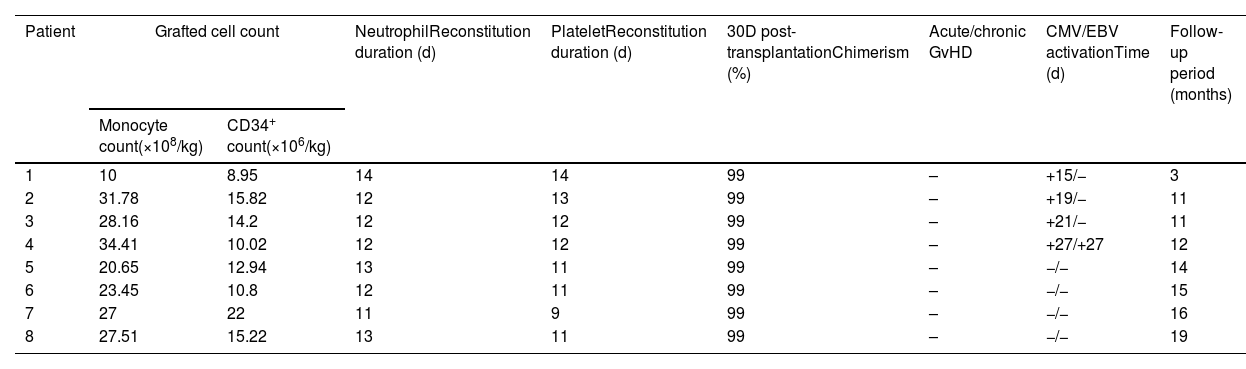
ResultsFrom January 2018 to May 2019, the haplo-HSCT followed by PT/Cy on eight NCL pediatric patients was performed. The median age was 4.5 years (ranging from 2.8 to 7 years). The donors were their haploidentical HLA-matched parents, as no identically matched donors were found. The median nucleated cell count was 25.37 (10–34.41)×108/kg, and the median CD34+ count was 13.7 (8.95–22)×106/kg. Neutrophil reconstitution occurred 12 days (11–14 days) after transplantation, and the median platelet reconstitution time was 12 days (9–14 days) after transplantation. All patients achieved full donor chimerism and did not develop Grade II–IV acute GvHD or chronic GvHD after transplantation. The median follow-up period was 2.2 (1.5–2.6) years. All patients are still alive at present and develop no severe transplantation-related complications. The mental motor disorders, myoclonic seizures, and vision loss of all patients continued to progress. However, the progression slowed at 12 months after transplantation.
ConclusionThis study demonstrated that it is safe and efficacious to treat NCLs with haplo-HSCT. Transplantation should be performed at an early stage for the survival quality of pediatric patients.
Las lipofuscinosis neuronales ceroides (NCL) son trastornos raros del almacenamiento lisosomal caracterizados por retraso mental progresivo y regresión del desarrollo motor y convulsiones mioclónicas. Se ha sugerido que el trasplante de células madre hematopoyéticas (HSCT) se utilice en el tratamiento de trastornos lisosomales y daño cerebral causado por una deficiencia de enzimas lisosomales solubles. No hay informes previos sobre el tratamiento de NCL con HSCT en China.
Material y métodoPacientes pediátricos de NCL que se sometieron a alo-TCMH en el Hospital de Niños Afiliado del Instituto Capital de Pediatría involucrados. Se utilizó una combinación de historias clínicas, características clínicas y análisis genéticos para el diagnóstico de todos los pacientes. El formulario de consentimiento por escrito para el allo-TCMH se obtuvo del tutor del paciente, que luego fue revisado y aprobado por el comité de ética antes del procedimiento.
ResultadosDe enero de 2018 a mayo de 2019, se realizó el haplo-HSCT seguido de TP/Cy en 8 pacientes pediátricos con NCL. La mediana de edad fue de 4,5 años (variando de 2,8 a 7 años). Los donantes eran sus padres haploidénticos compatibles con HLA, ya que no se encontraron donantes idénticos. La mediana del recuento de células nucleadas fue de 25,37 (10–34,41)×108/kg, y la mediana del recuento de CD34+ fue de 13,7 (8,95-22)×106/kg. La reconstitución de neutrófilos ocurrió 12 días (11-14 días) después del trasplante, y el tiempo medio de reconstitución plaquetaria fue de 12 días (9-14 días) después del trasplante. Todos los pacientes alcanzaron quimerismo total del donante y no desarrollaron EICH aguda de grado II-IV o EICH crónica después del trasplante. La mediana del período de seguimiento fue de 2,2 (1,5–2,6) años. Todos los pacientes siguen vivos en la actualidad y no desarrollan complicaciones graves relacionadas con el trasplante. Los trastornos mentales motores, las convulsiones mioclónicas y la pérdida de visión de todos los pacientes continuaron progresando. Sin embargo, la progresión se ralentizó a los 12 meses después del trasplante.
ConclusiónEste estudio demostró que es seguro y eficaz tratar las NCL con haplo-TCMH. El trasplante debe realizarse en una etapa temprana para la calidad de supervivencia de los pacientes pediátricos.