Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) reactivation have been described in patients with invasive mechanical ventilation and recently in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) secondary to COVID-19 with higher rates of reactivation than were detected previously in critical care, and although the diagnosis of HSV-1 pneumonia is not easy, its presence is associate with an increase in morbidity and mortality. The objective of this study is to determinate if the identification of HSV-1 in lower airway of patients with ARDS secondary to COVID-19 have influence in clinical outcome and mortality.
MethodTwo hundred twenty-four admitted patients in intensive care unit (ICU) of Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Toledo diagnosed of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) were reviewed and were selected those with mechanical ventilation who had undergone (BAL). It was registered all results of HSV-1 PCR (negative and positive).
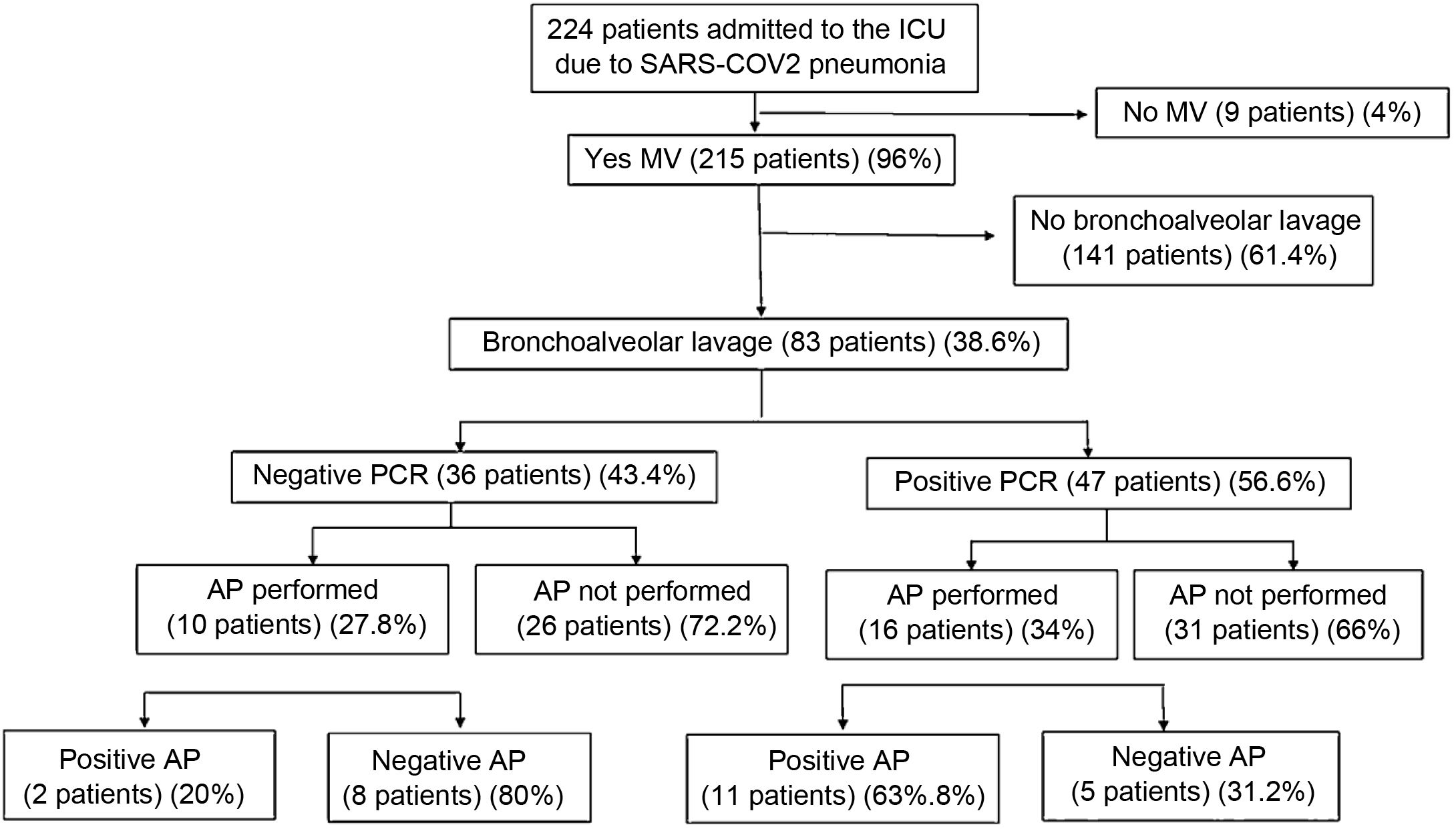
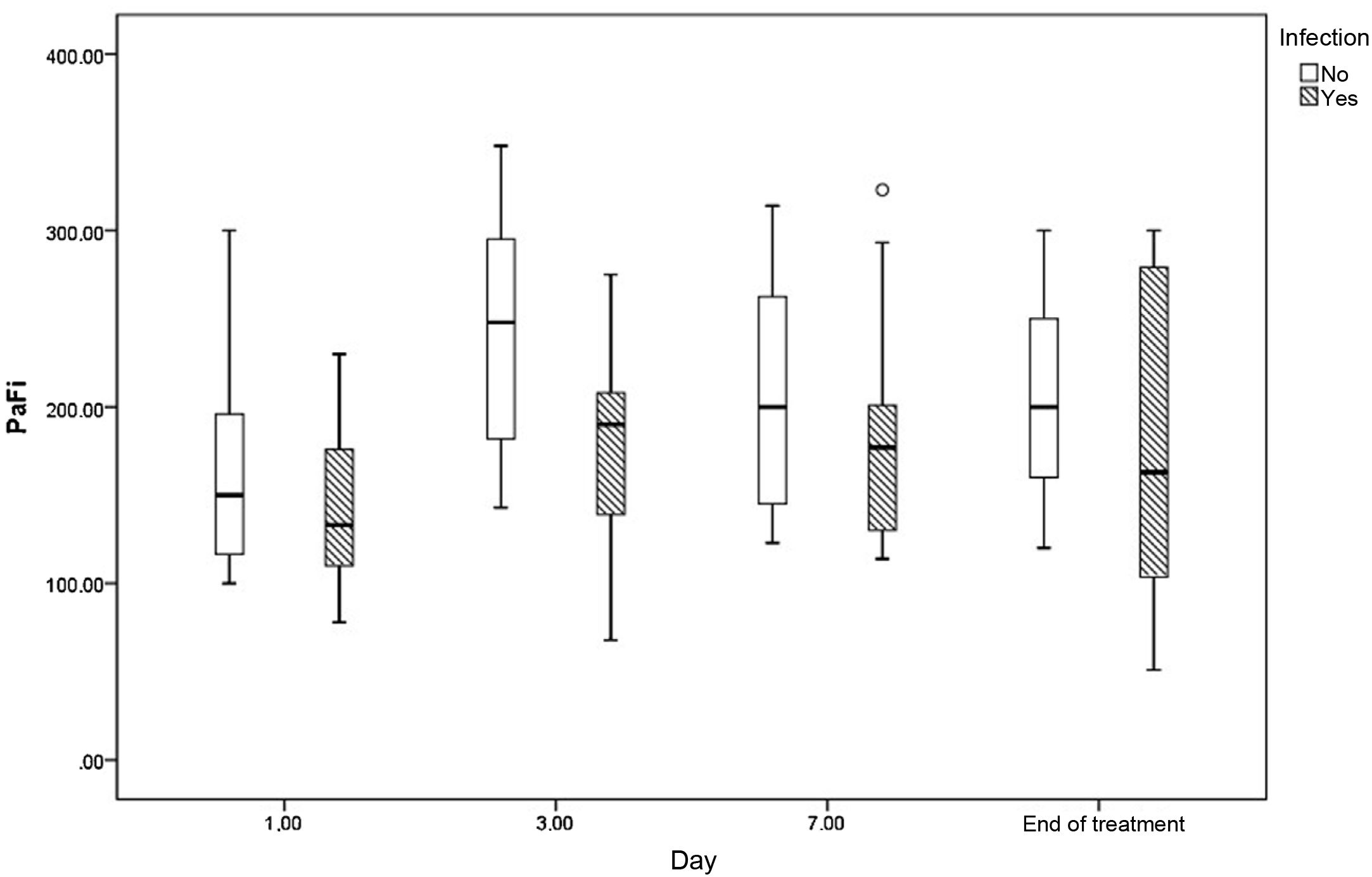
ResultsDuring the study period (November 28, 2020 to April 13, 2021) was admitted 224 patients in ICU diagnosed of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. Eighty-three patients of them had undergone BAL, with HSV-1 PCR positive result in 47 (56%), and negative result in 36 (43.4%). We performed pathological anatomy study in BAL samples on 26 of the total BAL realized. Typical cytopathic characteristics of HSV-1 were found in 13 samples (50%) and 11 of them (84.6%) have had HSV-1 PCR positive result. Thirty days mortality was significantly higher in the group of patients with HSV-1 PCR positive result (33.5% vs. 57.4%, p = 0.015). This difference was stronger in the group of patients with HSV-1 findings in the pathological anatomy study (30.8% vs. 69.2%, p = 0.047).
ConclusionOur results suggest that ARDS secondary to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia is highly associated to HSV-1 reactivation and that the finding of HSV-1 in lower airway is associated with a worst prognostic and with significantly mortality increase. It is necessary to carry out more extensive studies to determinate if treatment with acyclovir can improve the prognosis of these patients.
Las reactivaciones del virus herpes simple (VHS) están descritas en los pacientes en ventilación mecánica invasiva y recientemente en el síndrome de distrés respiratorio agudo (SDRA) por COVID-19, con tasas más altas que las descritas previamente en pacientes críticos, y aunque el diagnóstico de neumonía por VHS es difícil, su presencia se asocia con aumento de la morbimortalidad. El objetivo de este estudio es determinar si la identificación de VHS en el tracto respiratorio inferior en pacientes en ventilación mecánica con SDRA por COVID-19 influye sobre la evolución clínica y la mortalidad.
MétodoSe revisaron 224 pacientes ingresados en el servicio de medicina intensiva del Complejo Hospitalario de Toledo con el diagnóstico de neumonía por SARS-CoV-2 y se seleccionaron los pacientes en ventilación mecánica a los que se les había realizado lavado broncoalveolar (LBA). Se registraron todos los resultados de la PCR, tanto si fue positiva como si fue negativa para VHS.
ResultadosDurante el periodo de estudio (del 28 de noviembre de 2020 hasta el 13 de abril de 2021) ingresaron 224 pacientes en la UCI con el diagnóstico de neumonía por SARS-CoV-2. De ellos, en 83 se realizó lavado broncoalveolar (LBA), siendo la PCR para VHS-1 positiva en 47 y negativa en 36 (56,6%). Realizamos estudio anatomopatológico en muestras de LBA a 26 pacientes del total de la muestra. Se encontraron características citopáticas típicas de infección por herpes en 13 (50%), de los cuales 11 (84,6%) tenían PCR positiva. La mortalidad a los 30 días fue significativamente mayor en el grupo de pacientes con PCR positiva (33,5% vs 57,4%, p = 0,015). Esta diferencia fue aún más marcada en el grupo con hallazgos anatomopatológicos compatibles con neumonía por VHS (30,8% versus 69,2%, p = 0,047).
ConclusiónNuestros resultados sugieren que el SDRA secundario a neumonía por SARS-CoV-2 se asocia a una alta reactivación del VHS y que su hallazgo en el tracto respiratorio inferior se asocia con un peor pronóstico y un aumento significativo de la mortalidad. Son necesarios estudios más amplios para determinar si el tratamiento con aciclovir puede mejorar el pronóstico de estos pacientes.