The prevalence of gestational diabetes is increasing, and the Mediterranean diet is highly recommended for health. The objective of this study is to determine the relationship between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Materials and methodsIn this cross-sectional study the presence of GDM is the dependent variable, and socio-demographic and anthropometric characteristics and adherence to the Mediterranean diet are the independent variables in this study, which was carried out in pregnant women who were 24–28 weeks pregnant and had Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT). Adherence to the Mediterranean diet was evaluated with the Mediterranean Diet Adherence Scale (MEDAS). Data were collected through face-to-face interviews, weight and height measurements of the pregnant women were made, and the diagnosis of GDM was made with OGTT.
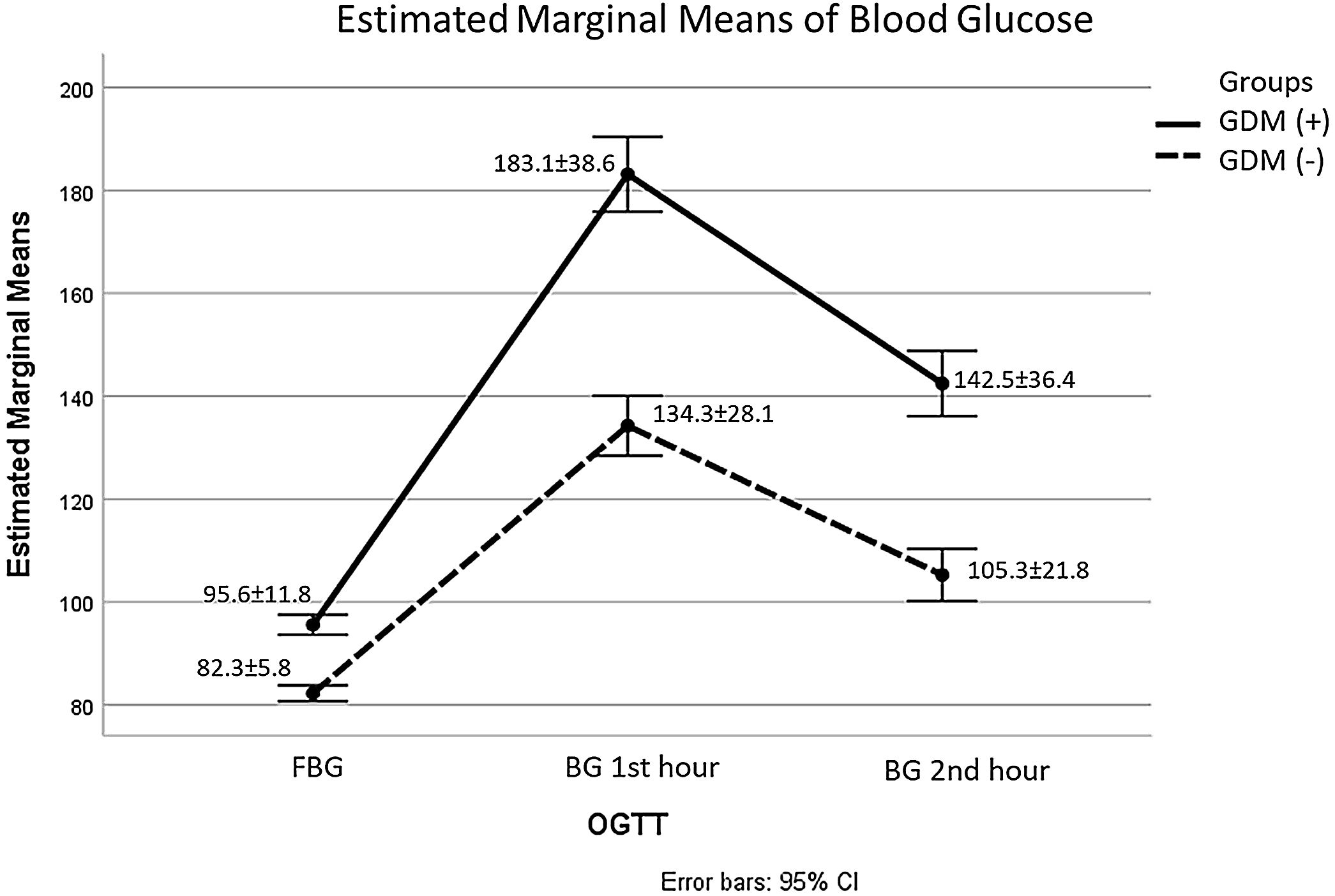
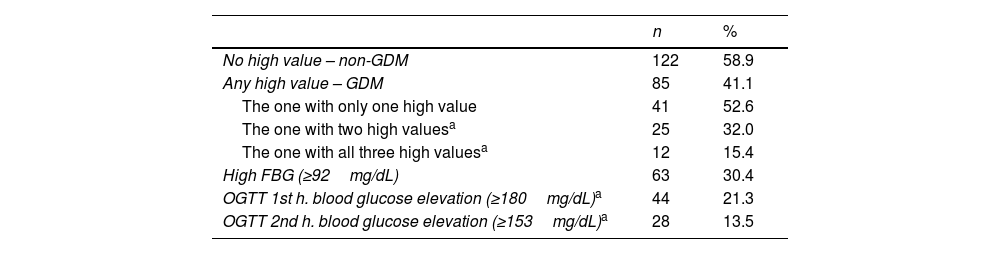
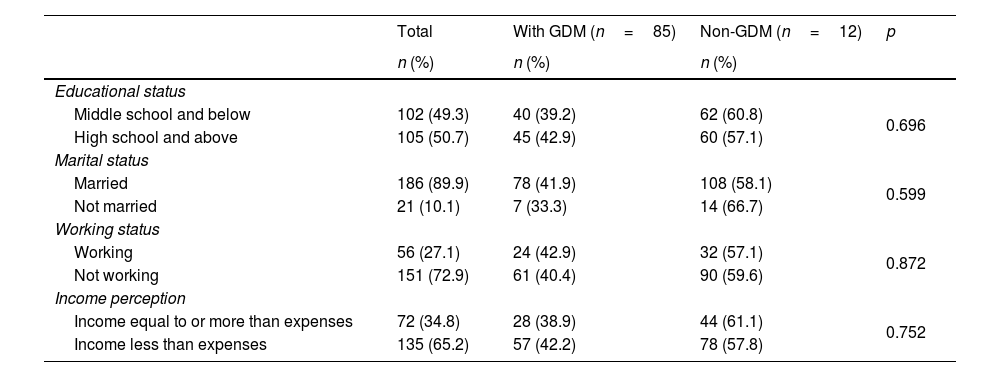
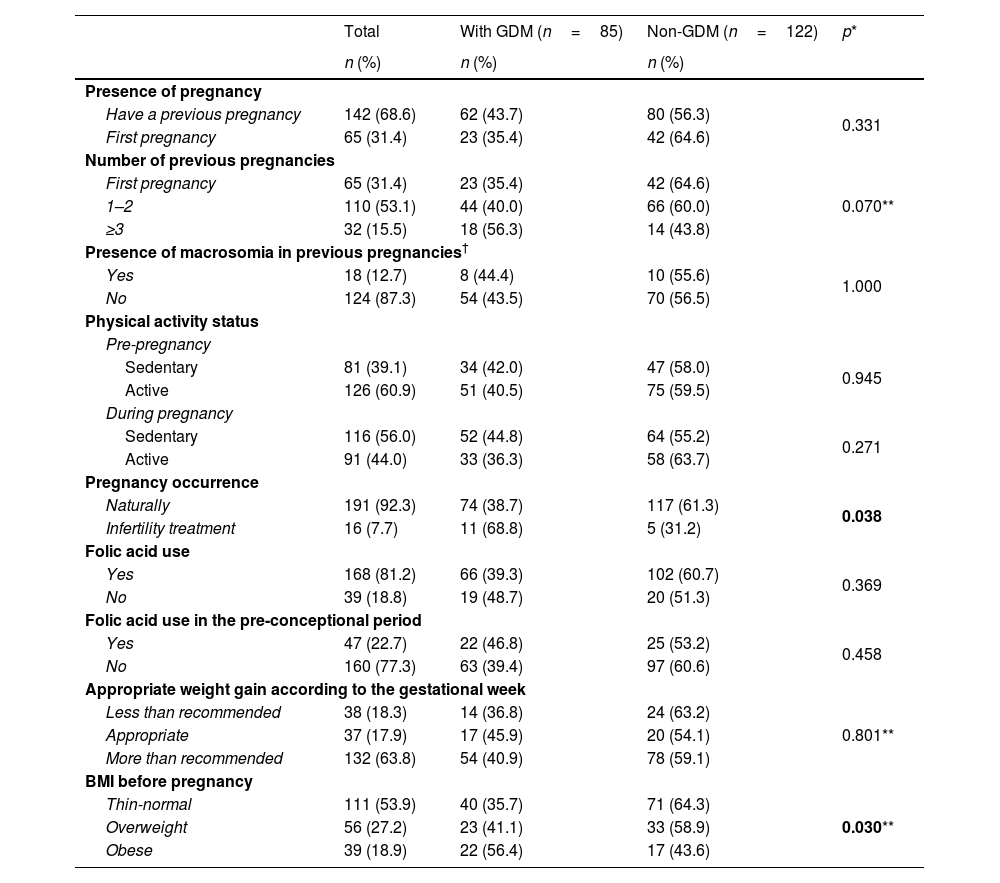
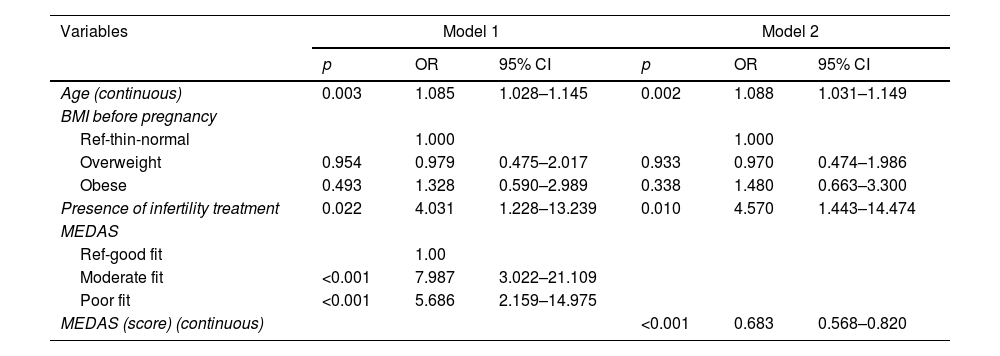
ResultsTwo hundred and seven pregnant women participated in the study and 85 of them (41.1%) were diagnosed as GDM. According to Logistic Regression models, age (OR: 1.088, 95% CI: 1.031–1.149) and infertility treatment (OR: 4.570, 95% CI: 1.443–14.474) significantly increased the occurrence of GDM, while adherence to the Mediterranean diet (OR: 0.683, 95% CI: 0.568–0.820) significantly reduced the risk.
ConclusionsNearly two-fifths of pregnant women were diagnosed with GDM while only one-fourth complied with a Mediterranean diet. The increase in the frequency of GDM should be carefully monitored. It may be useful to detect risky pregnant women at the time of the first diagnosis, to measure their glucose levels, and to give suggestions about the Mediterranean diet in the early period.
La prevalencia de diabetes gestacional está aumentando y la dieta mediterránea es muy recomendable para la salud. El objetivo de este estudio es determinar la relación entre la adherencia a la dieta mediterránea y la diabetes mellitus gestacional (DMG).
Materiales y métodosEn este estudio transversal la presencia de DMG es la variable dependiente, y las características sociodemográficas y antropométricas y la adherencia a la dieta mediterránea son las variables independientes de este estudio, que se llevó a cabo en mujeres embarazadas de 24-28semanas de gestación a las que se les realizó el Test de Tolerancia Oral a la Glucosa (TTOG). La adherencia a la dieta mediterránea se evaluó con la Escala de Adherencia a la Dieta Mediterránea (Mediterranean Diet Adherence Scale [MEDAS]). Los datos se recogieron mediante entrevistas cara a cara, se midió el peso y la talla de las embarazadas y se diagnosticó la DMG con el TTOG.
ResultadosUn total de 207 embarazadas participaron en el estudio, y 85 de ellas (41,1%) fueron diagnosticadas de DMG. Según los modelos de regresión logística, la edad (OR: 1,088; IC95%: 1,031-1,149) y el tratamiento de la infertilidad (OR: 4,570; IC95%: 1,443-14,474) aumentaron significativamente la aparición de DMG, mientras que la adherencia a la dieta mediterránea (OR: 0,683; IC95%: 0,568-0,820) redujo significativamente el riesgo.
ConclusionesCasi dos quintas partes de las embarazadas fueron diagnosticadas de DMG, mientras que solo una cuarta parte cumplían con la dieta mediterránea. Debe vigilarse atentamente el aumento de la frecuencia de la DMG. Puede ser útil detectar a las embarazadas de riesgo en el momento del primer diagnóstico, medir sus niveles de glucosa y dar sugerencias sobre la dieta mediterránea en el periodo inicial.