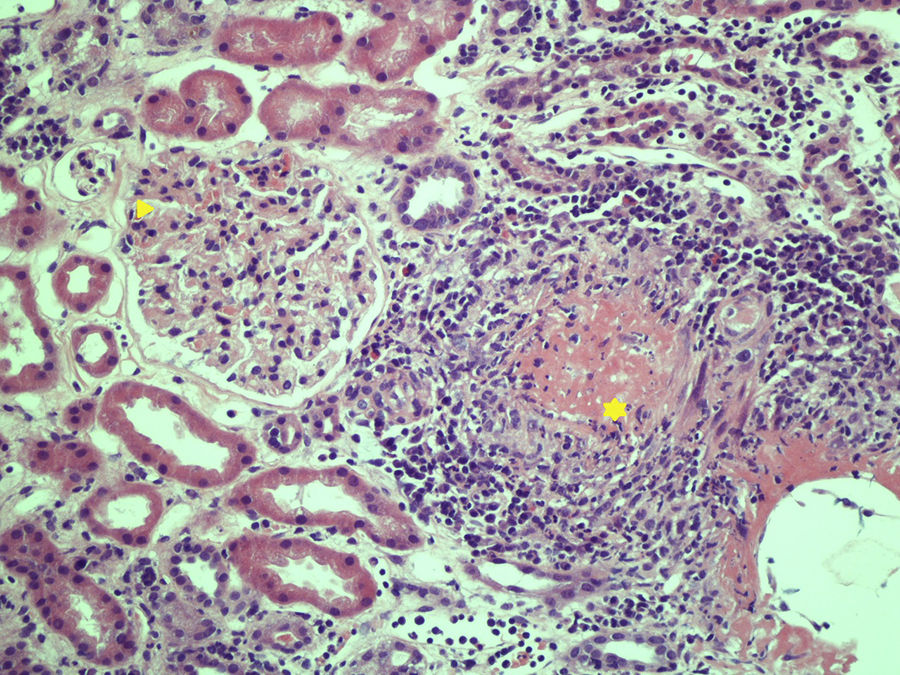
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2387020618305916" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2018.12.012" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-02-15" "aid" => "4554" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U.. All rights reserved" "copyrightAnyo" => "2018" "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2019;152:164-5" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S0025775318303658" "issn" => "00257753" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2018.05.027" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-02-15" "aid" => "4554" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2019;152:164-5" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 19 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 11 "PDF" => 8 ] ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Carta al Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Poliangitis microscópica y enfermedad pulmonar intersticial" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "164" "paginaFinal" => "165" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Microscopic polyangiitis and interstitial lung disease" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Figura 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 675 "Ancho" => 900 "Tamanyo" => 243709 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Glomérulo con ligera afectación (punta de flecha) y glomérulo con desestructuración capilar por infiltrado de neutrófilos que causan necrosis fibrinoide (asterisco). La inmunofluorescencia mostraba depósitos de inmunocomplejos de C3, C1q e IgM en paredes de pequeño vaso.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Ignacio Gayá García-Manso, Raquel García Sevila, Paloma Vela Casasempere" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Ignacio" "apellidos" => "Gayá García-Manso" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Raquel" "apellidos" => "García Sevila" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Paloma" "apellidos" => "Vela Casasempere" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2387020618305916" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2018.12.012" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020618305916?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775318303658?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/00257753/0000015200000004/v1_201901310615/S0025775318303658/v1_201901310615/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020618305862" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2018.05.054" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-02-15" "aid" => "4557" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2019;152:e19-20" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Meningeal cryptococcosis in a patient with angioimmunoblastic lymphoma treated with alemtuzumab" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "e19" "paginaFinal" => "e20" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Criptococosis meníngea en una paciente con diagnóstico de linfoma T angioinmunoblástico en tratamiento con alemtuzumab" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "David Cruz, Paula Costa, Miguel Sagüés" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "David" "apellidos" => "Cruz" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Paula" "apellidos" => "Costa" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Miguel" "apellidos" => "Sagüés" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775318303683" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2018.05.030" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775318303683?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020618305862?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000015200000004/v1_201902100719/S2387020618305862/v1_201902100719/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2387020618305849" "issn" => "23870206" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcle.2018.05.052" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-02-15" "aid" => "4553" "copyright" => "Elsevier España, S.L.U." "documento" => "simple-article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "cor" "cita" => "Med Clin. 2019;152:163-4" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:10 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Myasthenia gravis and large granular lymphocytic leukemia" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "163" "paginaFinal" => "164" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Miastenia gravis y leucemia de linfocitos T grandes granulares" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Cándido Muñoz Muñoz, Christian Homedes Pedret, Josefa López Vivancos" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Cándido" "apellidos" => "Muñoz Muñoz" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Christian" "apellidos" => "Homedes Pedret" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Josefa" "apellidos" => "López Vivancos" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0025775318303646" "doi" => "10.1016/j.medcli.2018.05.026" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0025775318303646?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020618305849?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23870206/0000015200000004/v1_201902100719/S2387020618305849/v1_201902100719/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:15 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Letter to the Editor</span>" "titulo" => "Microscopic polyangiitis and interstitial lung disease" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "saludo" => "Dear Editor," "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "164" "paginaFinal" => "165" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Ignacio Gayá García-Manso, Raquel García Sevila, Paloma Vela Casasempere" "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Ignacio" "apellidos" => "Gayá García-Manso" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "nachogaya@gmail.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Raquel" "apellidos" => "García Sevila" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Paloma" "apellidos" => "Vela Casasempere" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:2 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio de Neumología, Hospital General Universitario de Alicante, Alicante, Spain" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Sección de Reumatología, Hospital General Universitario de Alicante, Alicante, Spain" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Poliangitis microscópica y enfermedad pulmonar intersticial" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 675 "Ancho" => 900 "Tamanyo" => 243761 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Slightly involved glomerulus (arrowhead) and glomerulus with damaged small blood vessels due to neutrophil infiltration that cause fibrinoid necrosis (asterisk). Immunofluorescence showed C3, C1q and IgM immune complex deposits, in small vessel walls.</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Vasculitis is a group of rare disorders which sometimes represent a diagnostic challenge. Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) is one of the vasculitis described in the 2012 Chapel Hill Classification,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0030"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> characterized by the association with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) with perinuclear pattern (p-ANCA), more specifically antimyeloperoxidase (MPO) antibodies. The relationship between ANCA-associated vasculitis and interstitial lung disease (ILD) has been widely described since the first case reports published in 1990. ILD occurs more frequently in MPA patients than in cases of granulomatosis with polyangiitis or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. This is due to its association with MPO-ANCA (p-ANCA) antibodies, which are more frequent in MPA.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0035"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a></p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">We present the case report of an 80-year-old woman with dyspnea, edema, hypoxemic respiratory failure and interstitial lung pattern, whose diagnosis was MPA with renal, pulmonary and neurological involvement.</p><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">An 80-year-old woman with high blood pressure, a 2-month history of moderate effort dyspnea, edema in lower limbs and constitutional syndrome. Examination showed acropachies in hands and feet, on auscultation we could hear velcro-like crackles in the lower two thirds of both hemithorax and the presence of foveal edema in lower limbs. The blood test results showed PCR 19.9<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/dl, ESR 64.6<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mmol/h, preserved kidney function, leukocytosis (15,380/l) with 77% neutrophils, hemoglobin 11.6<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>g/dl, thrombocytosis and hypoproteinemia (4.9<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>g/dl). The arterial blood gas test showed hypoxemic respiratory failure (<span class="elsevierStyleItalic">p</span>O<span class="elsevierStyleInf">2</span> 51<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mmHg). Lung function tests showed a moderate decrease in lung diffusion (DLCO 42%).</p><p id="par0020" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A chest high-resolution CT (HRCT) confirmed diffuse bilateral interstitial lung disease, with septal thickening and traction bronchiectasis, consistent with potential usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). It associated minimal bilateral pleural effusion and mediastinal lymphadenopathies, which pointed to a superimposed heart failure. The echocardiogram ruled out any structural heart disease.</p><p id="par0025" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">During follow-up, we could observe non-nephrotic proteinuria (protein/creatinine ratio 776<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/g). Therefore, an autoimmunity study was requested which revealed the presence of ANAs 1/320 (homogeneous pattern) and perinuclear ANCAs (p-ANCA), anti-MPO at high titers.</p><p id="par0030" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Given the suspicion of ANCA-associated vasculitis, a renal biopsy was performed (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>) it showed an acute necrotizing, focal and segmental glomerulonephritis, and a small vessel vasculitis. The patient reported generalized weakness. Therefore, she underwent an electromyography which showed a predominantly distal chronic sensorymotor polyneuropathy.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0035" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">With the definitive MPA diagnosis with renal, pulmonary and neurological involvement, 3 boluses of 500<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg-methylprednisolone and a first bolus of 600<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>mg/m<span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span> cyclophosphamide were prescribed. The patient showed good clinical response, with improvement of plasma protein levels, proteinuria and edema. The patient continued treatment with monthly cyclophosphamide boluses, with favorable prognosis at month 6.</p><p id="par0040" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The association between MPA and ILD is rare, given the low prevalence of both diseases. The ILD incidence in MPA patients varies between 7.2 and 26.2%, in the different series<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0040"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a> with UIP being the most frequent radiological pattern.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0045"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">4</span></a> In the majority of ILD patients, it occurs at the time of diagnosis, and its appearance during evolution is exceptional.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0050"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5</span></a></p><p id="par0045" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Vasculitis with interstitial lung involvement have a worse prognosis,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0050"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5</span></a> with 50% survival at year 5.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0040"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a> Currently there are no specific treatments for these patients and they are treated regularly as in other small vessel vasculitis, with the use of corticosteroids and/or immunosuppressants.</p><p id="par0050" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">In conclusion, this case report highlights the importance of maintaining a high level of suspicion to diagnose an ILD-associated vasculitis having such unspecific data as the occurrence of hypoproteinemia or proteinuria (even in non-nephrotic range and with preserved renal function, as in this case), especially in elderly patients or with comorbidities, where these data might go unnoticed. In addition, given the poor prognosis of the ANCA- and ILD-associated vasculitis, providing a proper diagnosis is key to prescribe a more intensive first treatment that might modify the course of the disease. It is necessary to include the systematic evaluation of ANCAs in any case of interstitial lung disease, as recommended in the medical literature, regardless of the data that point to a systemic involvement.</p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: Gayá García-Manso I, García Sevila R, Vela Casasempere P. Poliangitis microscópica y enfermedad pulmonar intersticial. Med Clin (Barc). 2019;152;164–165.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 675 "Ancho" => 900 "Tamanyo" => 243761 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Slightly involved glomerulus (arrowhead) and glomerulus with damaged small blood vessels due to neutrophil infiltration that cause fibrinoid necrosis (asterisk). Immunofluorescence showed C3, C1q and IgM immune complex deposits, in small vessel walls.</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0015" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:5 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0030" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "J.C. Jennette" 1 => "R.J. Falk" 2 => "P.A. Bacon" 3 => "N. Basu" 4 => "M.C. Cid" 5 => "F. Ferrario" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1002/art.37715" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Arthritis Rheum" "fecha" => "2013" "volumen" => "65" "paginaInicial" => "1" "paginaFinal" => "11" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23045170" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0035" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Classification and characteristics of Japanese patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis in a nationwide, prospective, inception cohort study" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "K.E. Sada" 1 => "M. Yamamura" 2 => "M. Harigai" 3 => "T. Fujii" 4 => "H. Dobashi" 5 => "Y. Takasaki" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1186/ar4550" "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Arthritis Res Ther" "fecha" => "2014" "volumen" => "16" "paginaInicial" => "R101" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24758294" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0040" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Pulmonary involvements of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated renal vasculitis in Japan" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "K. Hirayama" 1 => "M. Kobayashi" 2 => "J. Usui" 3 => "Y. Arimura" 4 => "H. Sugiyama" 5 => "K. Nitta" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1093/ndt/gfu385" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Nephrol Dial Transplant" "fecha" => "2015" "volumen" => "30" "numero" => "Suppl. 1" "paginaInicial" => "i83" "paginaFinal" => "i93" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25613541" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0045" "etiqueta" => "4" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Pulmonary fibrosis in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)-associated vasculitis: a series of 49 patients and review of the literature" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "C. Comarmond" 1 => "B. Crestani" 2 => "A. Tazi" 3 => "B. Hervier" 4 => "S. Adam-Marchand" 5 => "H. Nunes" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Medicine (Baltimore)" "fecha" => "2014" "volumen" => "93" "paginaInicial" => "340" "paginaFinal" => "349" ] ] ] ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0050" "etiqueta" => "5" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Prevalence and outcome of pulmonary fibrosis in microscopic polyangiitis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "G.E. Tzelepis" 1 => "M. Kokosi" 2 => "A. Tzioufas" 3 => "S.P. Toya" 4 => "K.A. Boki" 5 => "A. Zormpala" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Eur Resp J" "fecha" => "2010" "volumen" => "36" "paginaInicial" => "116" "paginaFinal" => "121" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/23870206/0000015200000004/v1_201902100719/S2387020618305916/v1_201902100719/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "43309" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Letters to the Editor" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/23870206/0000015200000004/v1_201902100719/S2387020618305916/v1_201902100719/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2387020618305916?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Journal Information
Vol. 152. Issue 4.
Pages 164-165 (February 2019)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 152. Issue 4.
Pages 164-165 (February 2019)
Letter to the Editor
Microscopic polyangiitis and interstitial lung disease
Poliangitis microscópica y enfermedad pulmonar intersticial
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail