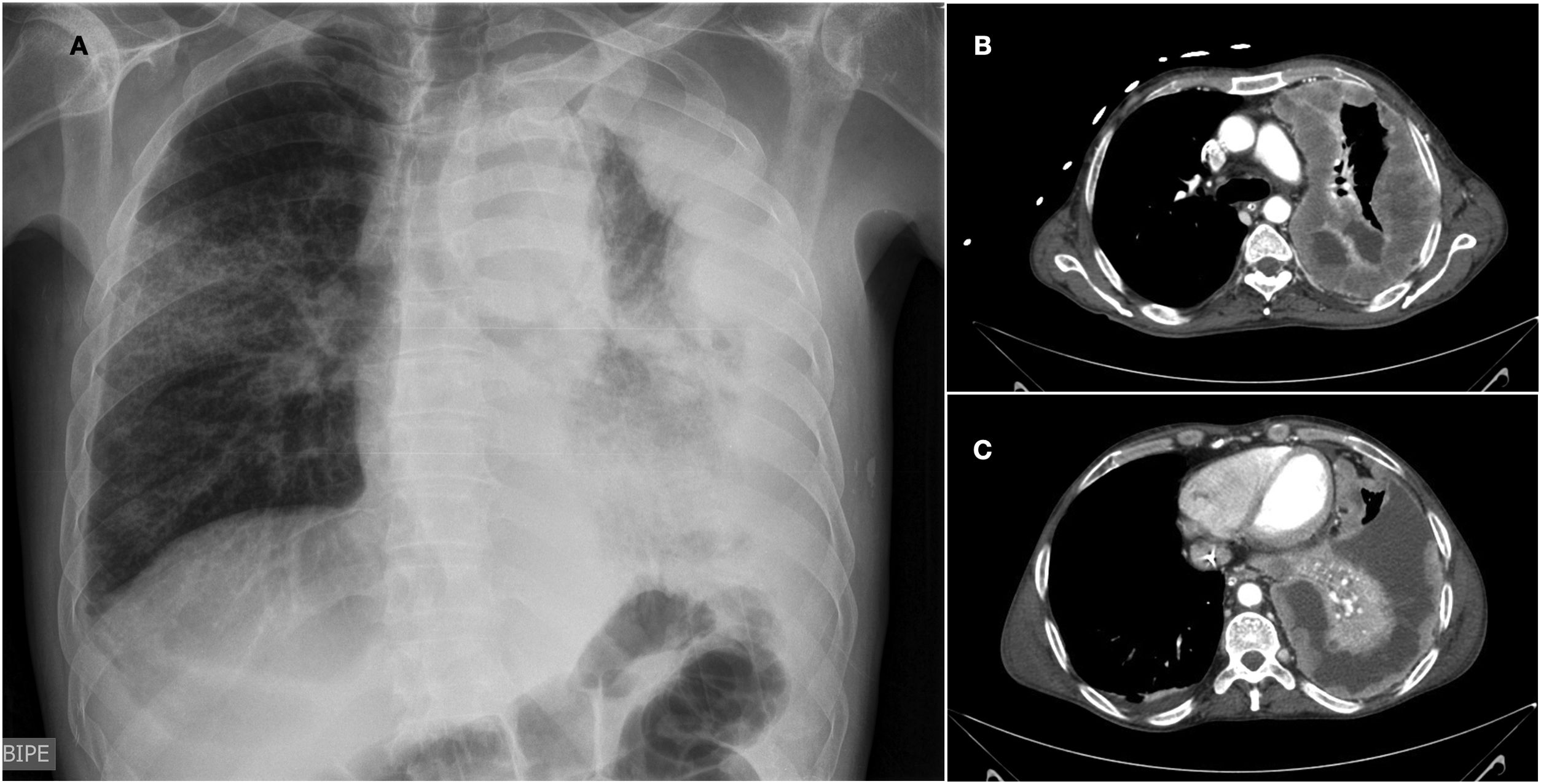
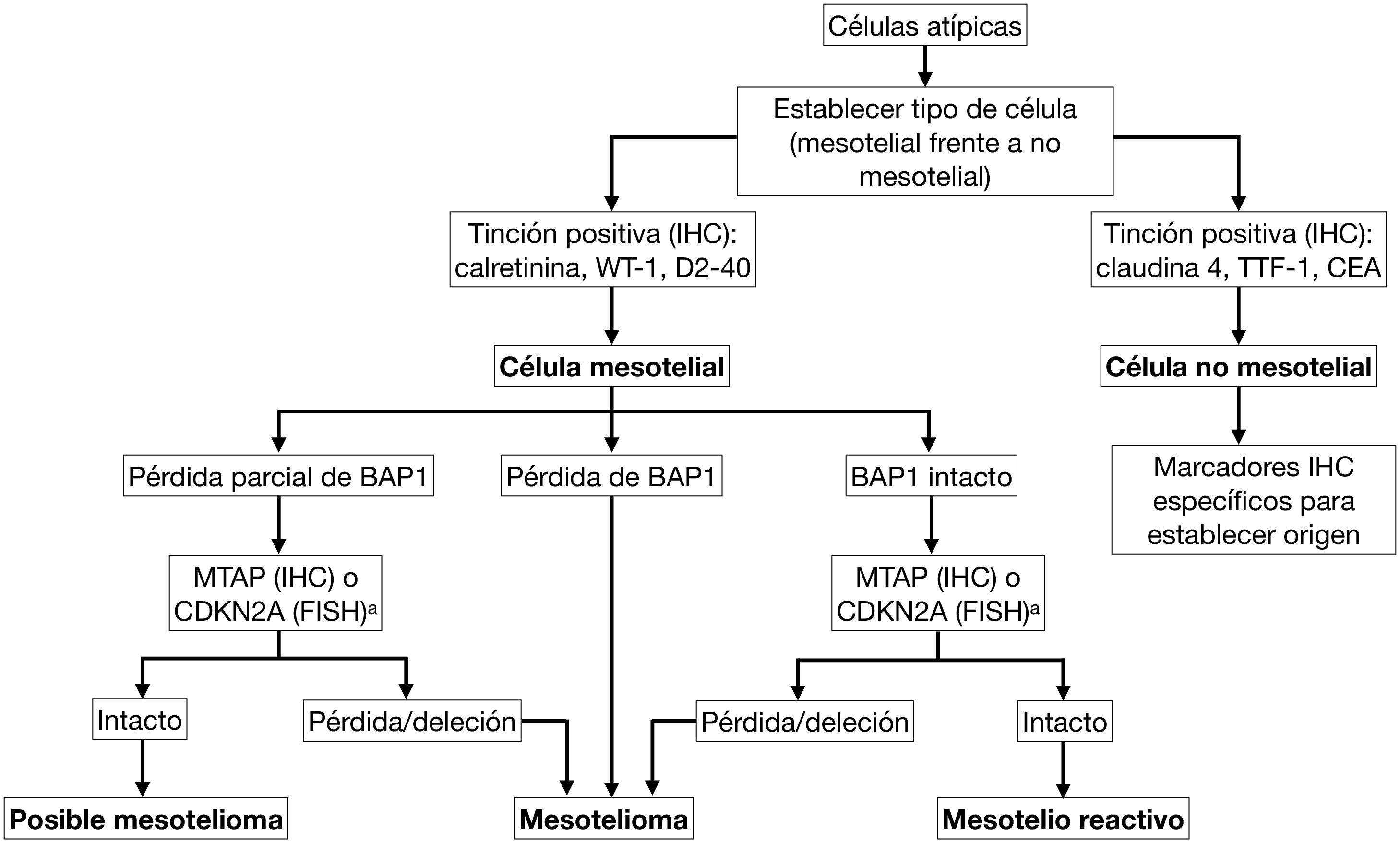
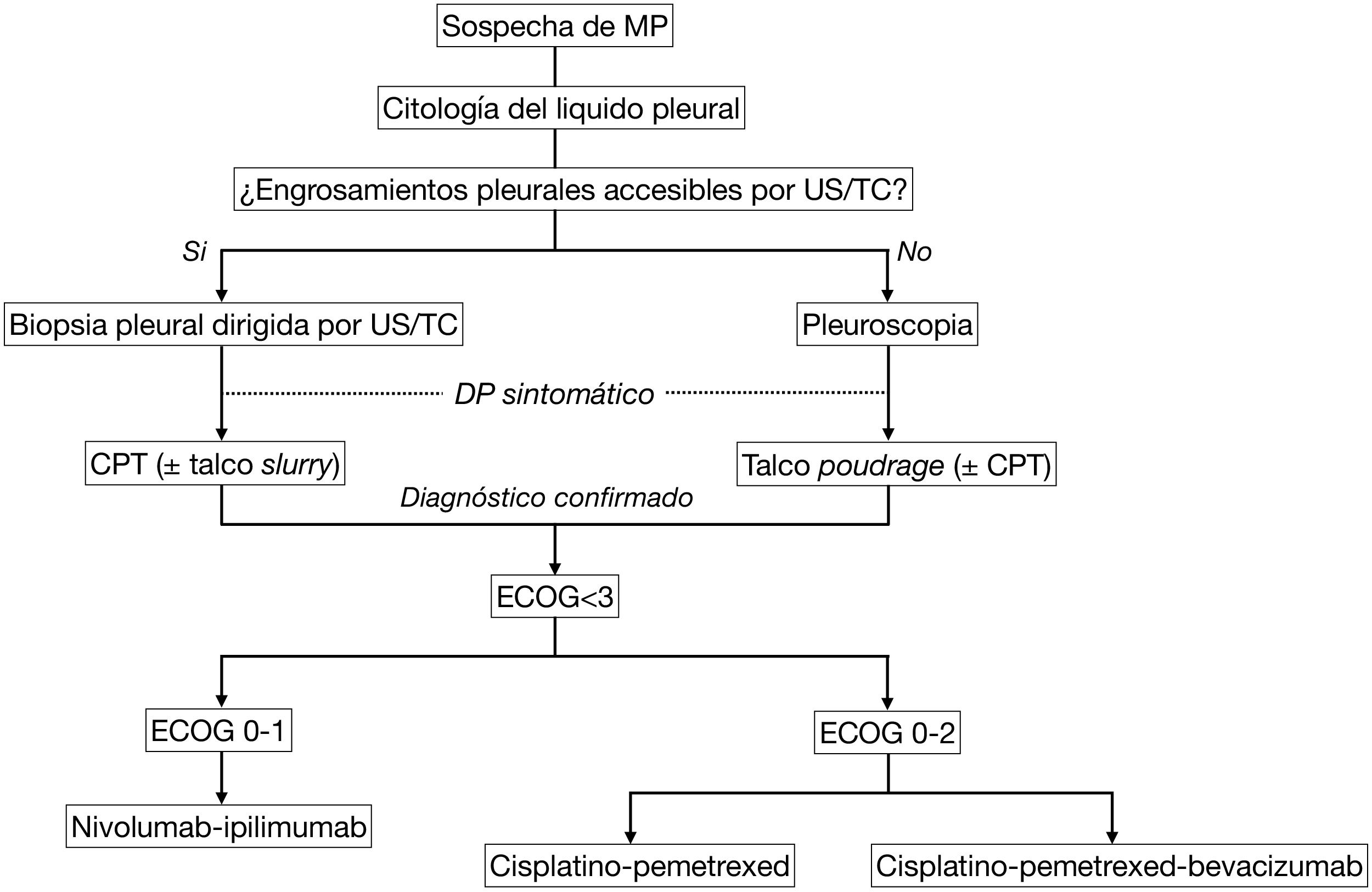
The diagnosis of diffuse pleural mesothelioma requires in most cases a pleural biopsy, performed either under imaging guidance (ultrasound or CT) or thoracoscopy. Loss of BAP1 or MTAP expression (immunohistochemistry) and homozygous deletion of CDKN2A (fluorescence in situ hybridization) are the basic molecular markers for the diagnosis of mesothelioma. The histologic type and patient’s performance status are the most important prognostic factors. Pleural effusion can be managed by the insertion of tunneled pleural catheters, either as a stand-alone measure (e.g., patients not amenable to multimodality therapy who have been diagnosed by pleural fluid cytology or image-guided biopsy) or combined with the administration of aerosolized talc during a diagnostic thoracoscopy. Immunotherapy is one of the front-line approaches in inoperable patients, particularly in biphasic or sarcomatous histologic varieties.
El diagnóstico de mesotelioma pleural difuso requiere en la mayoría de los casos una biopsia pleural, realizada bajo control de imagen (ecografía o tomografía computarizada) o mediante toracoscopia. La pérdida de expresión de BAP1 o de MTAP (inmunohistoquímica) y la deleción homocigota de CDKN2A (hibridación fluorescente in situ) constituyen los marcadores moleculares básicos para el diagnóstico de mesotelioma. El tipo histológico y el estado funcional del paciente son los factores pronósticos más importantes. El control del derrame pleural se puede realizar a través de la inserción de catéteres pleurales tunelizados, bien como medida aislada (p. ej. pacientes no susceptibles de terapia multimodal que se han diagnosticado por citología del líquido pleural o biopsia guiada por imagen) o combinada con la administración de talco aerosolizado durante una toracoscopia diagnóstica. La inmunoterapia constituye una de las primeras líneas de tratamiento en pacientes inoperables, particularmente en las variedades histológicas bifásicas o sarcomatosas.