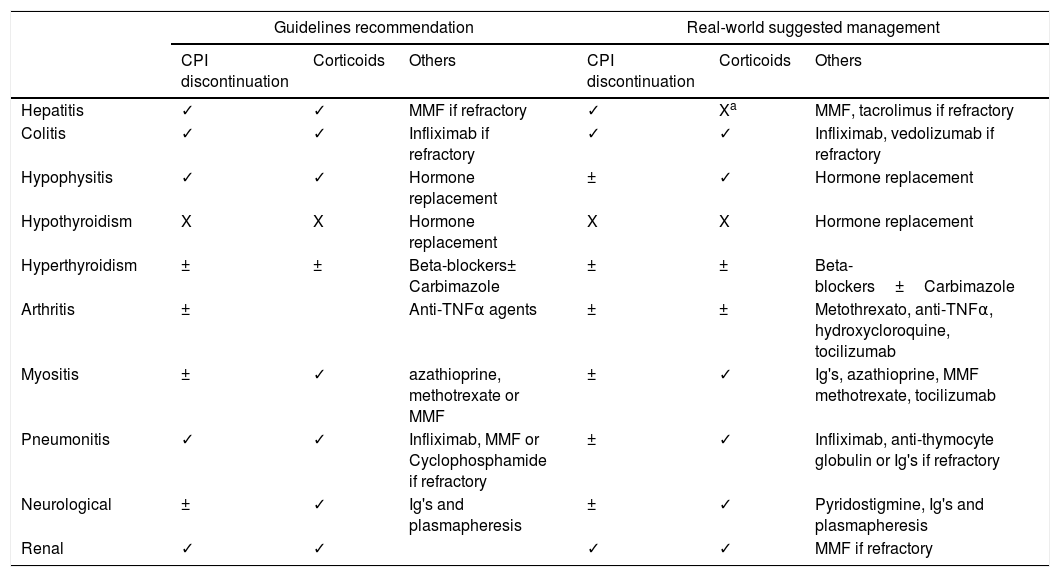
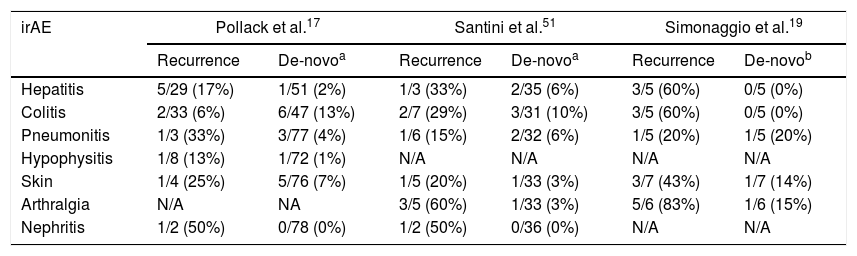
In recent years, immunotherapy has become an important pillar of cancer treatment, with high response rates regardless of tumour histology or baseline mutations. However, immune activation associated with check-point inhibitors is not selective and a large variety of immune-related adverse events have been associated with anti-PD1, anti-PD-1/L-1 and anti-CTLA-4 agents. Though diagnosis and treatment of these toxicities have been established according to the recommendations from clinical trials and in line with the autoimmune disorders that they mimic, increasing real-world data is coming up showing that these adverse events may have differential characteristics and management, especially in terms of the use of corticoids, second-line treatments, salvage therapy for life-threatening cases and reintroduction of immunotherapy. Herein we present a comprehensive review of current recommendations and real-world data on the main immune-related adverse events of immunotherapy.
En los últimos años la inmunoterapia se ha convertido en un pilar fundamental para el tratamiento del cáncer, con altas tasas de respuesta, independientemente de la histología tumoral o de las mutaciones basales. Sin embargo, la activación inmune asociada a los inhibidores de control no es selectiva, habiéndose asociado una gran variedad de efectos adversos relacionados con la inmunidad a los agentes anti-PD1, anti-PD-1/L-1 y anti-CTLA-4. Aunque se han establecido el diagnóstico y el tratamiento de estas toxicidades en virtud de las recomendaciones de los ensayos clínicos, en consonancia con los trastornos autoinmunes que imitan, el incremento de los datos del mundo real refleja que dichos efectos adversos pueden tener características y manejos diferenciales, especialmente en términos de uso de corticoides, tratamientos de segunda línea, terapia de rescate para casos potencialmente letales, y reintroducción de la inmunoterapia. Presentamos aquí una revisión amplia de las recomendaciones actuales y los datos del mundo real sobre los principales efectos adversos de la inmunoterapia.