Peripheral arterial disease is a marker of vascular damage that is diagnosed by measuring the ankle-brachial index. The aim of this study was to determine the validity and agreement of the MESI ABPI-MD and Microlife WatchBP Office-ABI oscillometric devices with respect to the gold standard arterial Doppler.
Materials and methodsObservational, cross-sectional, descriptive study of inpatients who underwent ABI measurement with the three devices. Values are considered normal between 1–1.4, indeterminate between 0.91–0.99 and pathological ≤0.9 and >1.4.
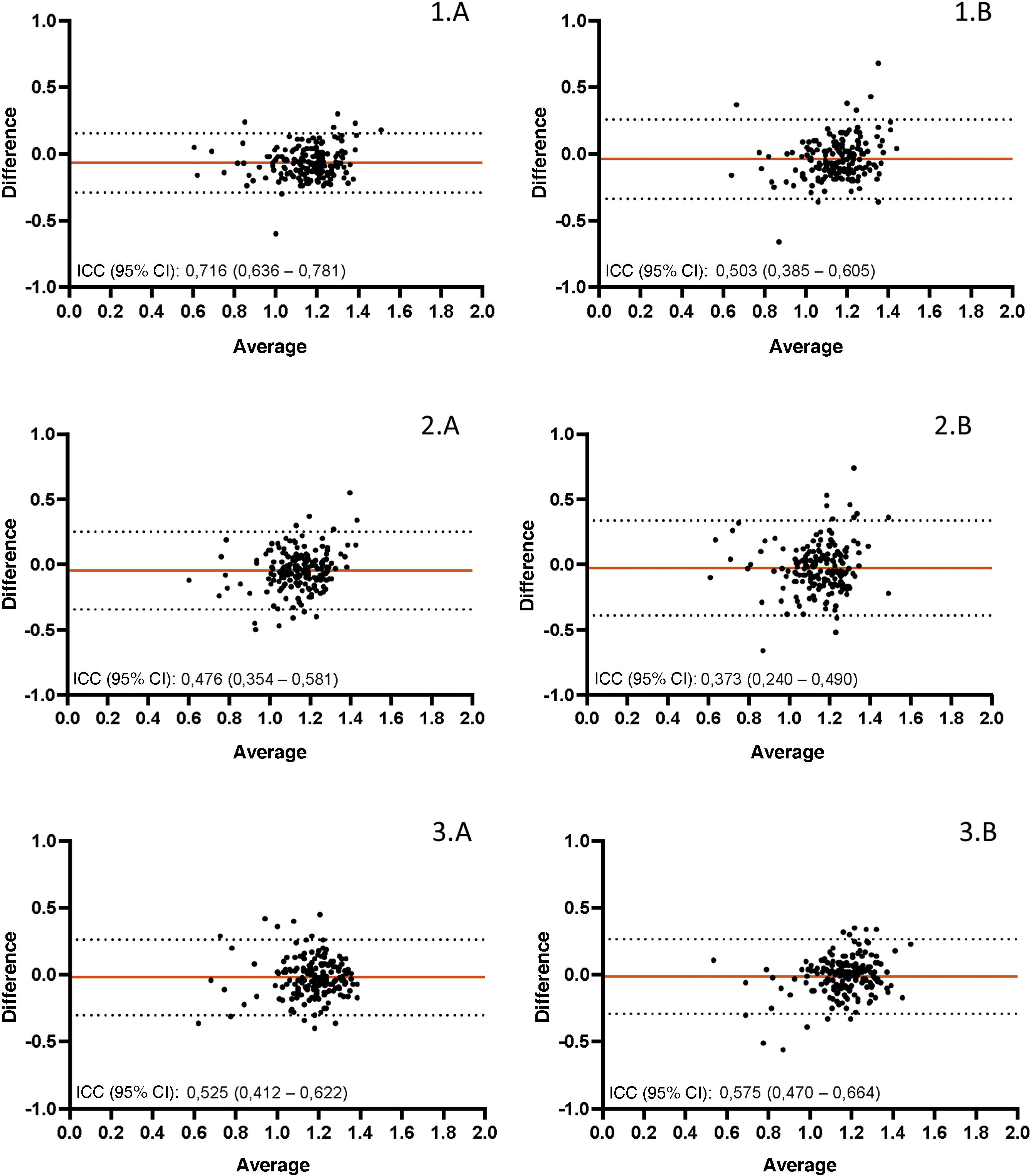
ResultsA total of 187 patients (54.4% male) with a mean age of 66 years were included. The Doppler results were inferior to those of the oscillometric devices (median [IQR] 1.1 [0.2] vs. 1.2 [0.2], p < 0.05), with no significant differences between the automated devices (p = 0.29 for the right lower limb and p = 0.342 for the left lower limb). Both devices had high specificity (96.5–99.2%) and low sensitivity (29.5–45.4%). The evaluation of the results was good-moderate for MESI and moderate for Microlife. The agreement between the two was acceptable-moderate.
ConclusionAutomated oscillometric devices could be useful in asymptomatic patients as an alternative to arterial Doppler.
La enfermedad arterial periférica constituye un marcador de daño vascular que se diagnostica mediante la medida del índice tobillo-brazo. El objetivo de este estudio es determinar la validez y concordancia de los dispositivos oscilométricos MESI ABPI-MD y Microlife WatchBP Office-ABI respecto al oppler arterial estándar dorado.
Materiales y métodosEstudio observacional, transversal y descriptivo con pacientes ingresados a quienes se les realizó la medida de ITB con los tres dispositivos. Se consideran valores normales entre 1-1,4; indeterminados entre 0,91-0,99 y patológicos ≤0,9 y >1,4.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 187 pacientes (54,4% varones) con edad media de 66 años. Los resultados del oppler fueron inferiores a los de los oscilométricos (mediana [RIC] 1,1 [0,2] vs. 1,2 [0,2], p < 0,05), sin diferencias significativas entre los automáticos (p = 0,29 para el miembro inferior derecho yp = 0,342 para el izquierdo). Ambos dispositivos presentaron elevada especificidad (96,5-99,2%) y baja sensibilidad (29,5-45,4%). La evaluación de los resultados fue buena moderada para MESI y moderada para Microlife. La concordancia entre ambos fue aceptable-moderada.
ConclusiónLos dispositivos oscilométricos automáticos podrían ser de utilidad en pacientes asintomáticos como alternativa al oppler arterial.