Harlequin syndrome, described for the first time by Lance et al.1 in 1988, is an easily recognisable entity which is very rarely reported in childhood; its aetiology is still a diagnostic challenge in many cases. It is characterised by unilateral skin redness and facial sweating in response to physical exercise, heat, or emotional factors.2,3 The origin of this syndrome is a dysfunction of the sympathetic chain, which is benign in most cases. Nevertheless, it is essential to rule out malignant causes.4–6
We present the case of a 9-year-old boy who was referred to the neurology department due to a one-year history of episodes of flushing and sweating on the right side of the face and chest and the right arm triggered by exercise. The contralateral side was pale and anhydrotic. His personal history included diagnosis of left posterior superior mediastinal neuroblastoma at the age of 2. The tumour was surgically resected and the patient was administered intraoperative radiotherapy and 6 cycles of chemotherapy; total remission was achieved after one year of treatment. The patient was subsequently examined due to a difference in temperature between the hands, with the left hand permanently cold months after the procedure. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan and a local computed tomography ruled out associated vascular or other lesions. The patient did not present new symptoms until 7 years after the surgery for the neuroblastoma, when he presented the dysautonomia symptoms described.
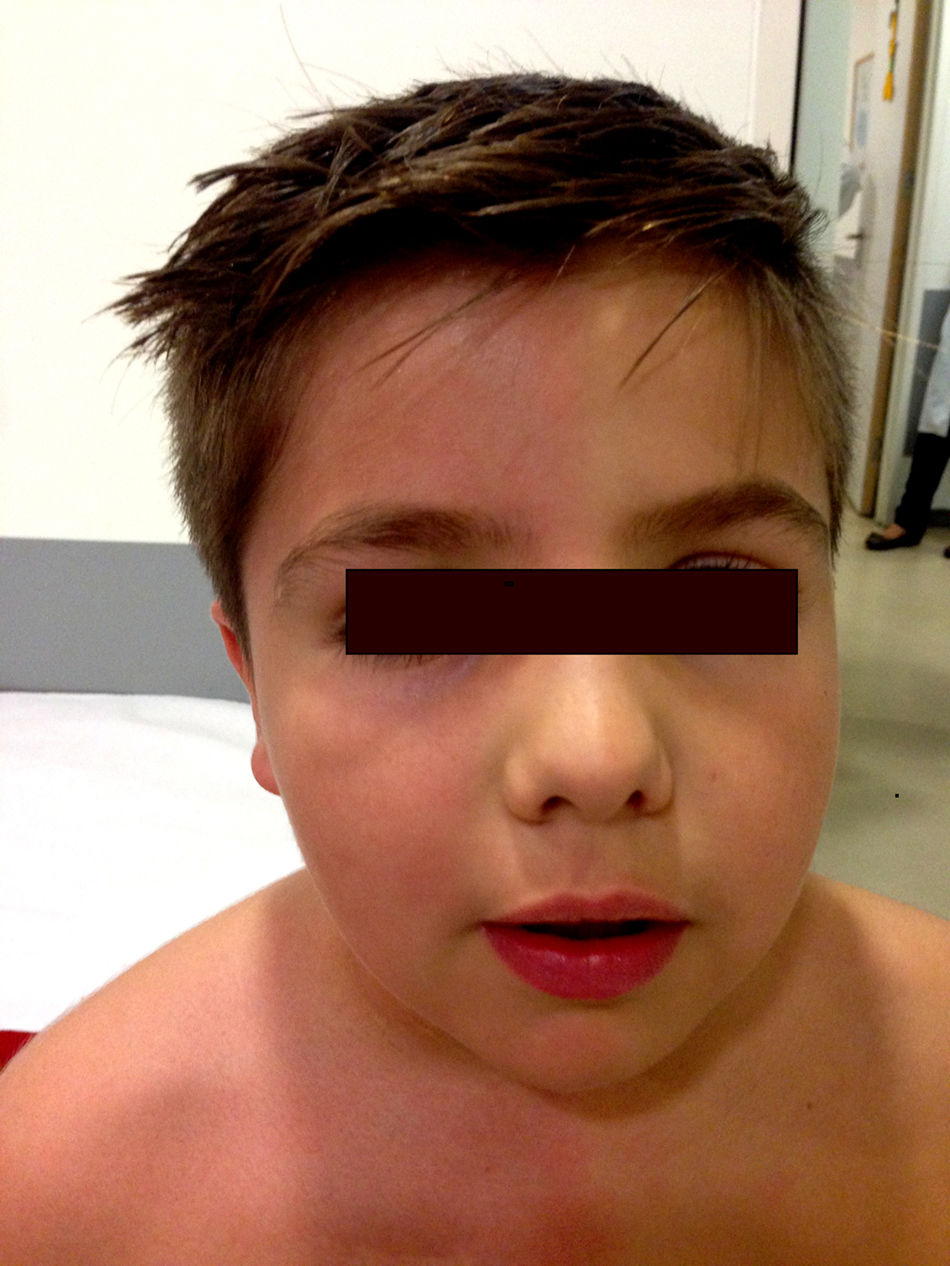
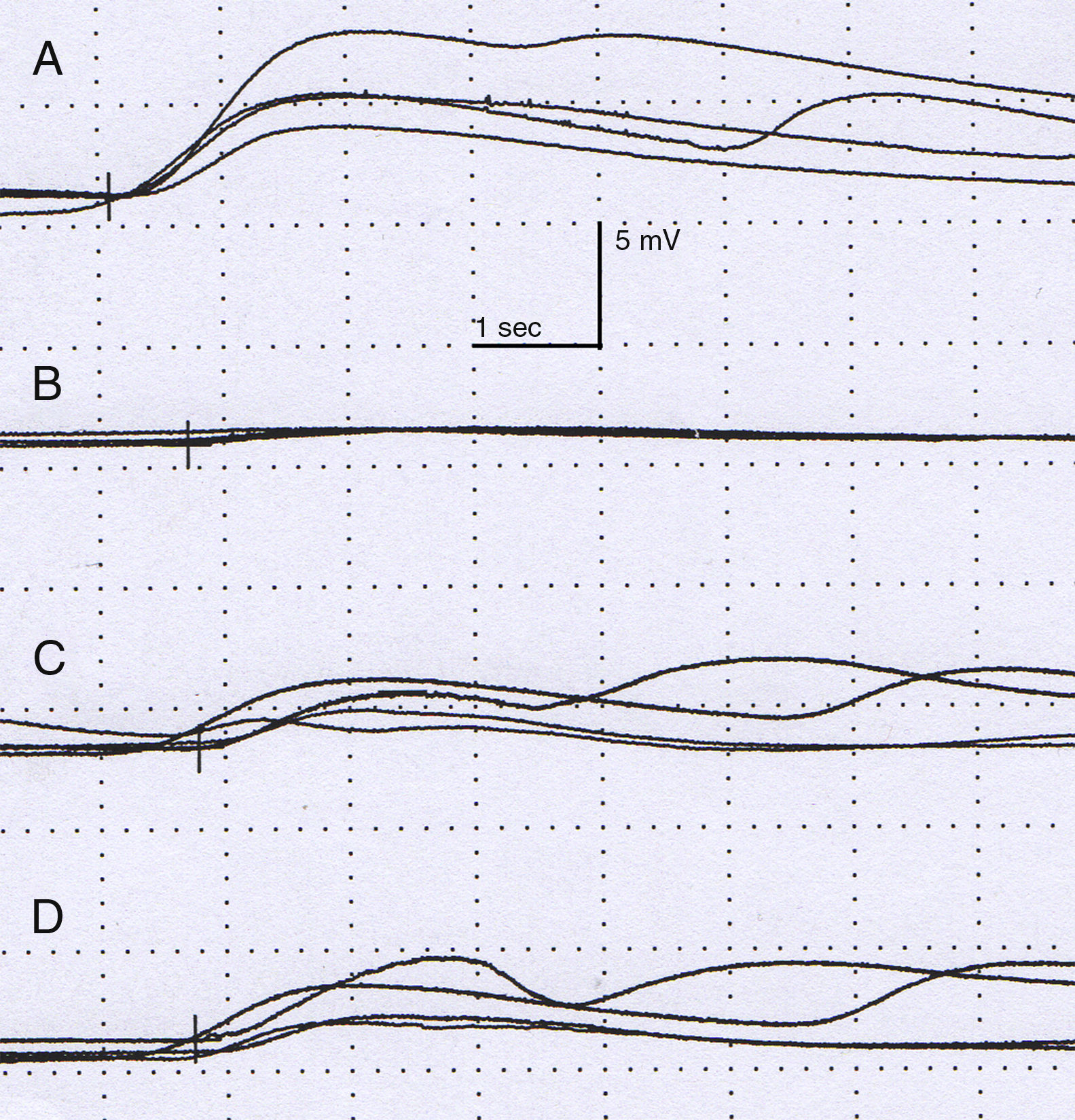
The physical examination did not show neurological alterations until the patient was asked to perform physical exercise, which triggered the described skin symptoms (Fig. 1). No ophthalmological abnormalities or symptoms of Horner syndrome were observed. The examination was completed with a chest MRI scan, which ruled out tumour recurrence. A neurophysiological study (Fig. 2) analysing the sympathetic response of the skin after stimulus in the lower and upper limbs showed that the response in the left hand was delayed and of very low amplitude in comparison with the right side; response in the feet was normal. No response was obtained on the left side of the face after stimulus was applied to the right arm. These findings are compatible with a lesion to the sympathetic chain, proximal to the stellate ganglion.
Neurophysiological study. Amplitude (mV) and latency (s). Sympathetic response of the skin after stimulating the right median nerve is normal in the right hand (A), with the left hand showing a delayed, low-amplitude response in comparison to the contralateral side. The response on the right (C) and left (D) leg shows no alterations.
Harlequin syndrome is an interesting but infrequent entity, characterised by an autonomic alteration due to an ipsilateral dysfunction of the vasodilator and sudomotor sympathetic pathways, causing unilateral anhydrosis and lack of facial flushing with exercise, heat, or emotional response. The upper limbs and the chest may also be affected.2,3 It has been suggested that the contralateral side may in turn present a compensatory hyperreactivity of the sympathetic activity, intensifying the characteristic flushing and sweating observed in this syndrome.7
Lesions to the cervical sympathetic pathway may involve any of its 3 levels (preganglionic fibres, superior cervical ganglion, and postganglionic fibres). The first neuron originates in the hypothalamus and forms a synapse with the second neuron (preganglionic) in the spinal cord at the level of C8-T2. This preganglionic neuron subsequently travels through the stellate ganglion and ascends to the superior cervical ganglion through the paravertebral sympathetic chain. The second (preganglionic) and third (postganglionic) neurons form a synapse in this ganglion. Two branches leave the superior cervical ganglion. One runs along the internal carotid artery and includes the vasomotor and sudomotor fibres innervating the nose and medial frontal region and the sympathetic fibres which cause the iris to dilate; the second branch runs along the external carotid artery and includes the postganglionic fibres innervating the rest of the face.2,8 When the oculosympathetic innervation is affected, we observe Horner syndrome (myosis and ptosis); this association is more frequent in paediatric patients.4–6,9 The arm receives postganglionic fibres from the stellate ganglion, so a lesion to or proximal to this ganglion will cause vasomotor and sudomotor alterations in the arm, neck, and upper part of the trunk, whereas a lesion distal to the stellate ganglion will affect only the face.2,8
The aetiology of this entity is very diverse. Most cases described in children and adults are benign. Harlequin syndrome may manifest in up to 10% of newborns, especially in preterm children, due to a transient hypothalamic immaturity.10 Idiopathic aetiology is frequent in older children and adults, with other possible causes including iatrogenic lesions (sustained during surgery and other procedures in the cervicothoracic region)8,10,11 and other more alarming conditions such as masses and neoplasms (toxic goitre, superior mediastinal tumours, and apical lung tumour).2–5 Other less frequent causes are neurotropic virus infection, such autoimmune diseases as multiple sclerosis, syringomyelia,2 etc.
The diagnostic process should aim to rule out malignant causes, as well as surgeries or previous procedures. A thorough physical, neurological, and ophthalmological examination is essential. Depending on the symptoms and working diagnosis, the study will be completed with imaging techniques or neurophysiological studies, with a view to excluding possible underlying causes or confirming the lesion to the sympathetic pathway.6
Our patient was diagnosed with vasomotor impairment secondary to dysfunction of the sympathetic pathway, with the unusual detail that symptoms started 7 years after surgery for neuroblastoma. The literature reports that symptoms secondary to iatrogenic causes can occur immediately or days after the procedure.5,10,11 For this reason, the aetiology in our patient is not entirely clear: although the disorder is probably secondary to the thoracic surgery, an idiopathic or other aetiology cannot be completely ruled out. We consider that this phenomenon may be due to delayed adverse effects of the intraoperative radiotherapy that the patient received, although the literature does not to date include any reports of Harlequin syndrome related to radiotherapy.
Primary or idiopathic Harlequin syndrome does not usually require treatment. If symptoms are severe, strongly impact the patient's daily life, or have a significant psychological impact, a contralateral sympathectomy may be considered; stellate ganglion block techniques constitute a less invasive option.2,3,11 With these techniques, flushing of the normally functioning side would be inhibited; however, both procedures are fairly limited since they cause neuron destruction. For this reason, it is essential to inform the patient about the normally benign course of the disease, once all possible organic causes have been excluded.
FundingThis study received no funding of any kind.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Butragueño Laiseca L, Vázquez López M, Polo Arrondo A. Síndrome de arlequín en un paciente pediátrico, a menudo un reto diagnóstico. Neurología. 2018;33:478–480.