El manejo actual de la diverticulitis aguda de colon izquierdo requiere pruebas con alto valor pronóstico. Los objetivos del estudio son analizar la utilidad de la ecografía como método diagnóstico inicial y evaluar la validez de las clasificaciones actuales de gravedad de dicha enfermedad.
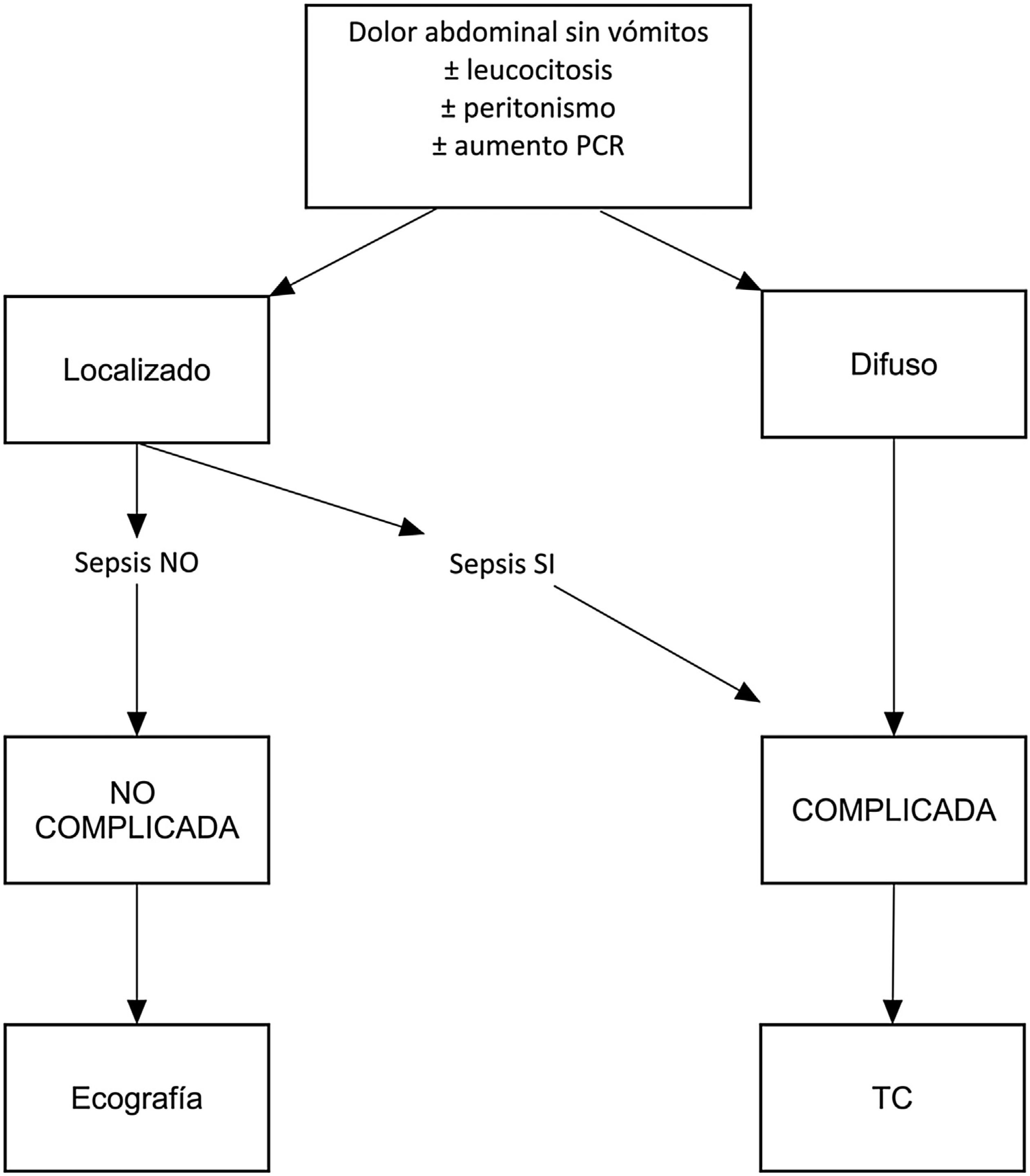
PacientesEstudio observacional retrospectivo de pacientes con diverticulitis aguda de colon izquierdo. Se solicitó ecografía o tomografía computarizada (TC) siguiendo un algoritmo clínico. Tras los hallazgos de imagen, se clasificó la enfermedad como leve, localmente complicada y complicada. Se evaluaron la eficacia de la ecografía como herramienta diagnóstica inicial y las razones por las que se realizó una TC como técnica inicial. Se compararon los hallazgos con las clasificaciones de diverticulitis publicadas.
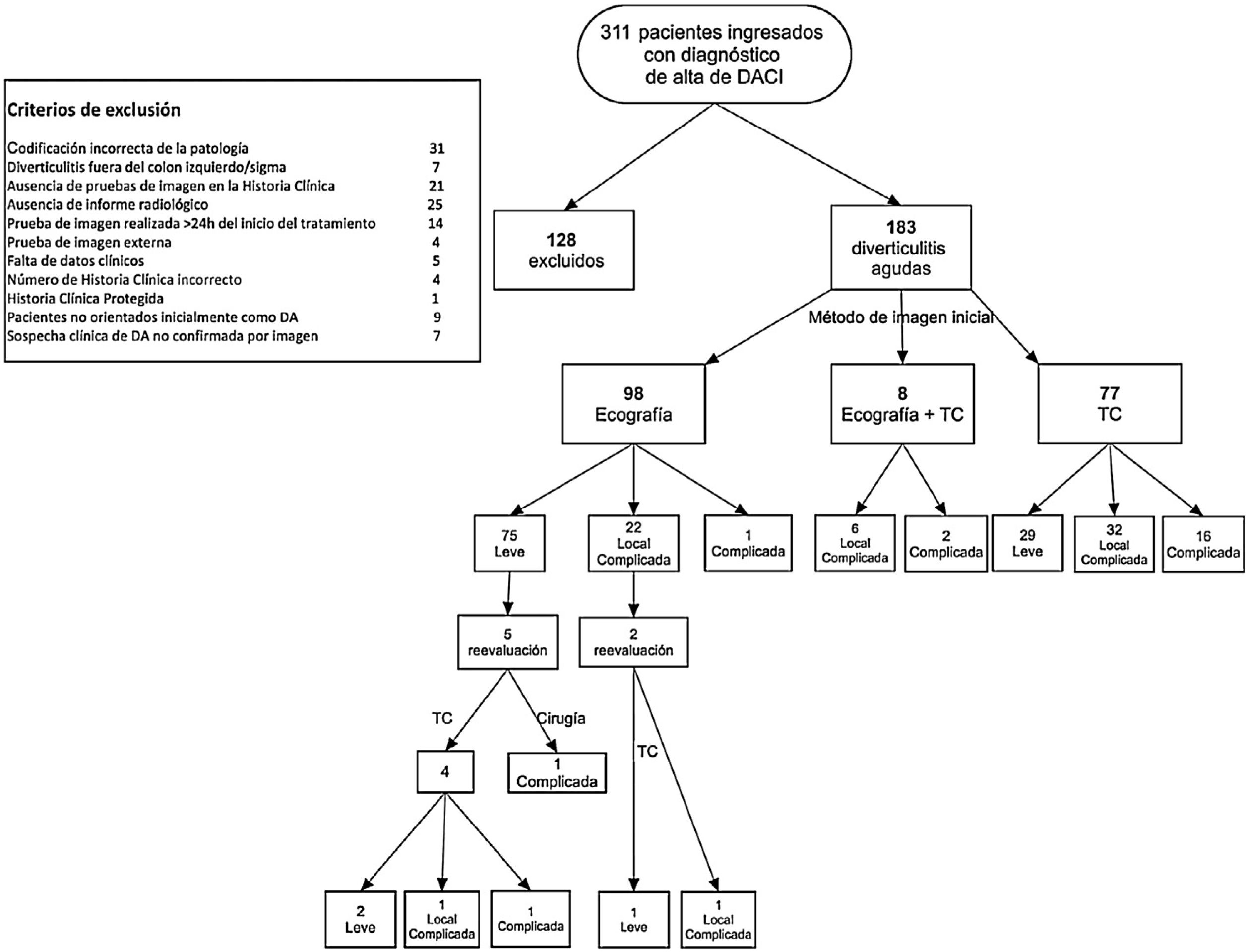
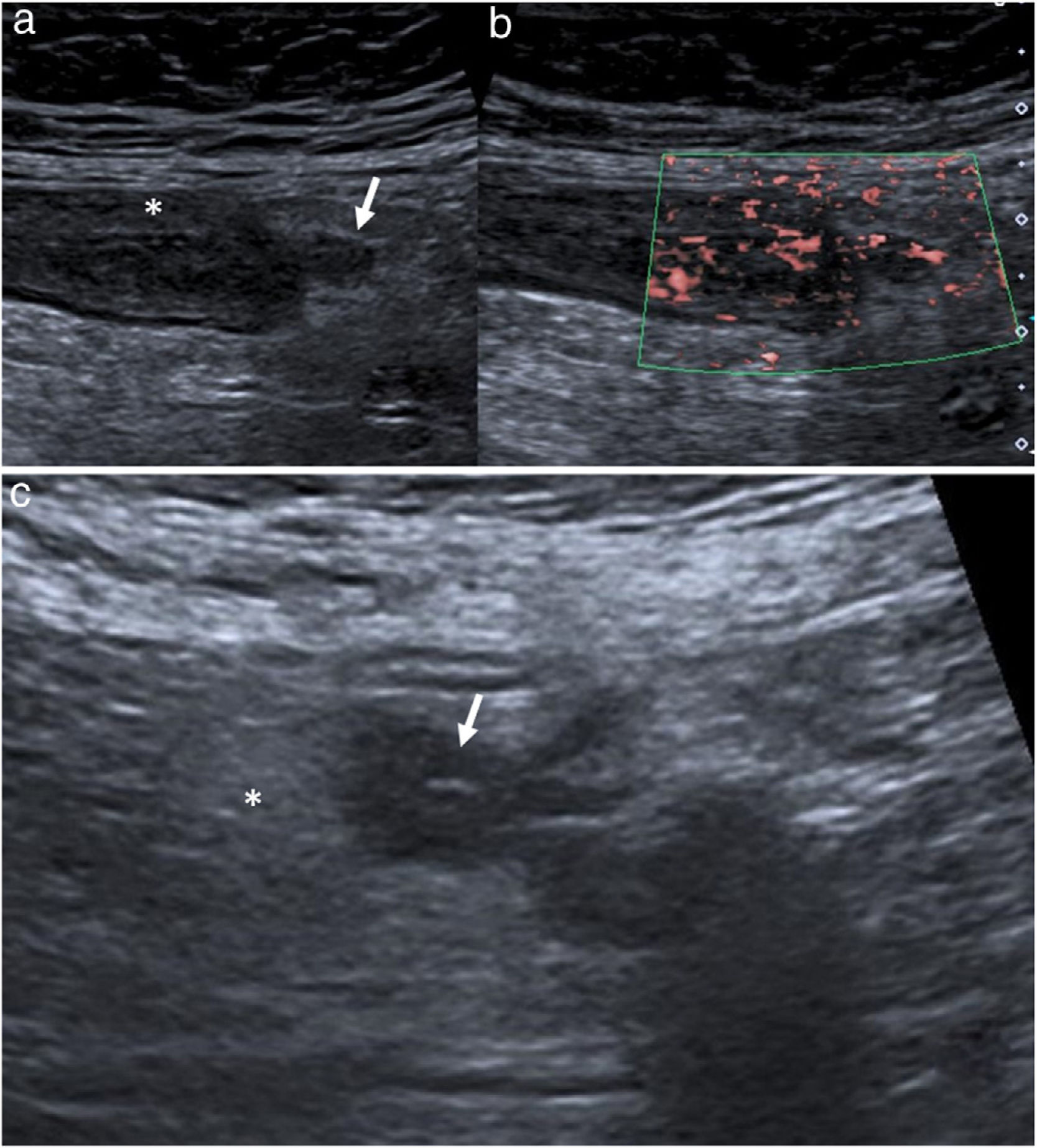
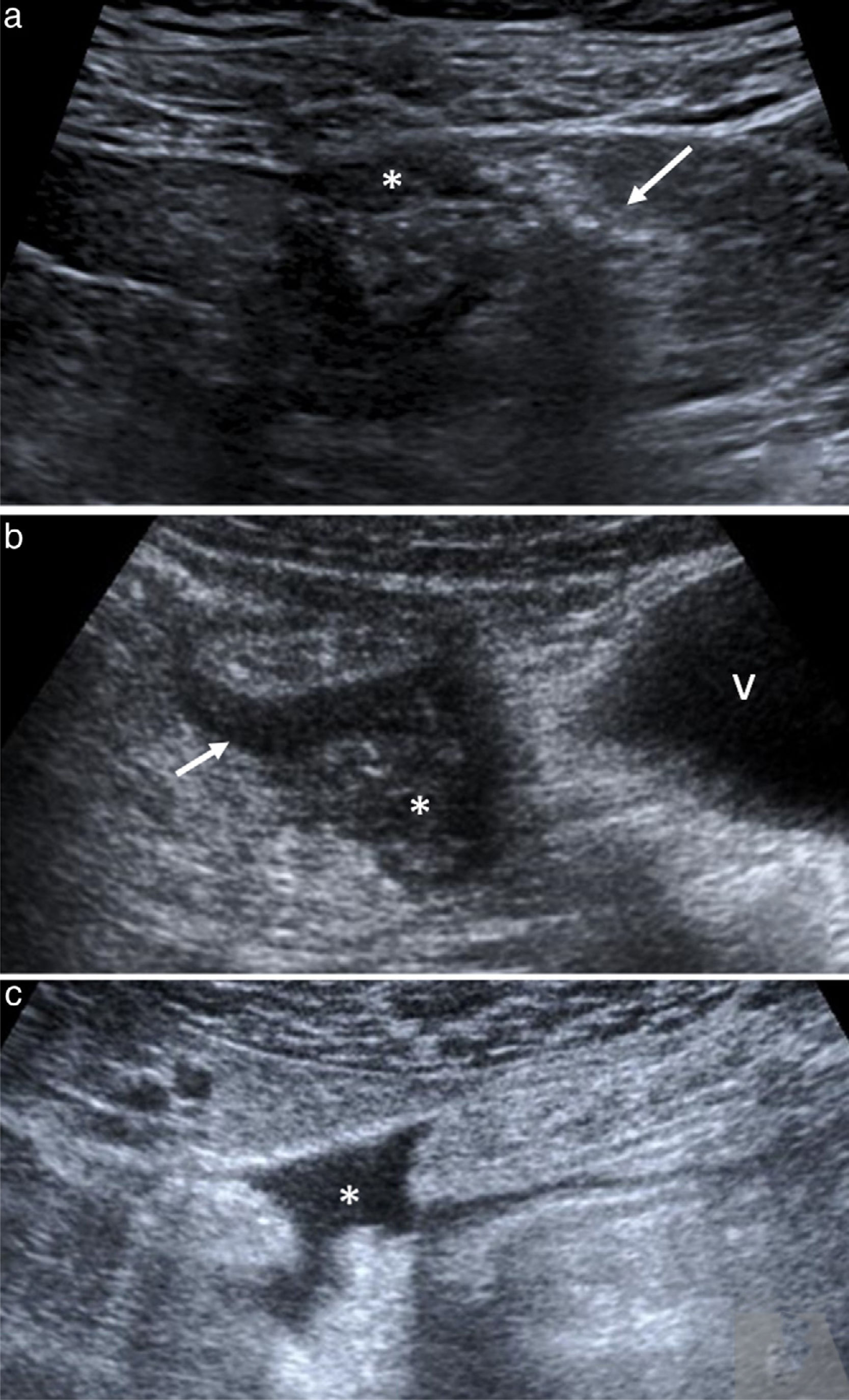
ResultadosDe 311 pacientes con diverticulitis aguda, se seleccionaron 183 con diverticulitis aguda de colon izquierdo, que fueron clasificadas por imagen como leves (104), localmente complicadas (60) y complicadas (19). En 98 pacientes, el diagnóstico se realizó por ecografía, en 77 por TC y en 8 mediante ambas. Las principales razones de utilización inicial de TC fueron falta de experiencia del radiólogo en ecografía abdominal y falta de disponibilidad de un radiólogo de guardia. A 6 pacientes diagnosticados por ecografía se les realizó una nueva evaluación por TC, pero solo en 3 cambió la clasificación. Ninguna de las clasificaciones publicadas recoge todos los hallazgos en imagen.
ConclusionesLa ecografía debería ser la primera técnica a utilizar para el diagnóstico de diverticulitis aguda de colon izquierdo. Para establecer el pronóstico de la enfermedad, son útiles diversos parámetros analíticos y hallazgos de imagen. Para una apropiada toma de decisión terapéutica se necesitarían nuevas clasificaciones de gravedad.
The current management of acute diverticulitis of the left colon (ADLC) requires tests with high prognostic value. This paper analyzes the usefulness of ultrasonography (US) in the initial diagnosis of ADLC and the validity of current classifications schemes for ADLC.
PatientsThis retrospective observational study included patients with ADLC scheduled to undergo US or computed tomography (CT) following a clinical algorithm. According to the imaging findings, ADLC was classified as mild, locally complicated, or complicated. We analyzed the efficacy of US in the initial diagnosis and the reasons why CT was used as the first-line technique. We compared the findings with published classifications schemes for ADLC.
ResultsA total of 311 patients were diagnosed with acute diverticulitis; 183 had ADLC, classified at imaging as mild in 104, locally complicated in 60, and complicated in 19. The diagnosis was reached by US alone in 98 patients, by CT alone in 77, and by combined US and CT in 8. The main reasons for using CT as the first-line technique were the radiologist's lack of experience in abdominal US and the unavailability of a radiologists on call. Six patients diagnosed by US were reexamined by CT, but the classification changed in only three. None of the published classification schemes included all the imaging findings.
ConclusionsUS should be the first-line imaging technique in patients with suspected ADLC. Various laboratory and imaging findings are useful in establishing the prognosis of ADLC. New schemes to classify the severity of ADLC are necessary to ensure optimal clinical decision making.