En los últimos años se han desarrollado sistemas que utilizan inteligencia artificial (IA) para estudiar distintos aspectos de la imagen médica, como la interpretación de la radiografía de tórax para descartar enfermedad. Esto ha producido un aumento de las revisiones sistemáticas (RS) publicadas sobre este tema. Este artículo tiene como objetivo evaluar la calidad metodológica de las RS que utilizan IA para el diagnóstico de enfermedad torácica mediante radiografía de tórax.
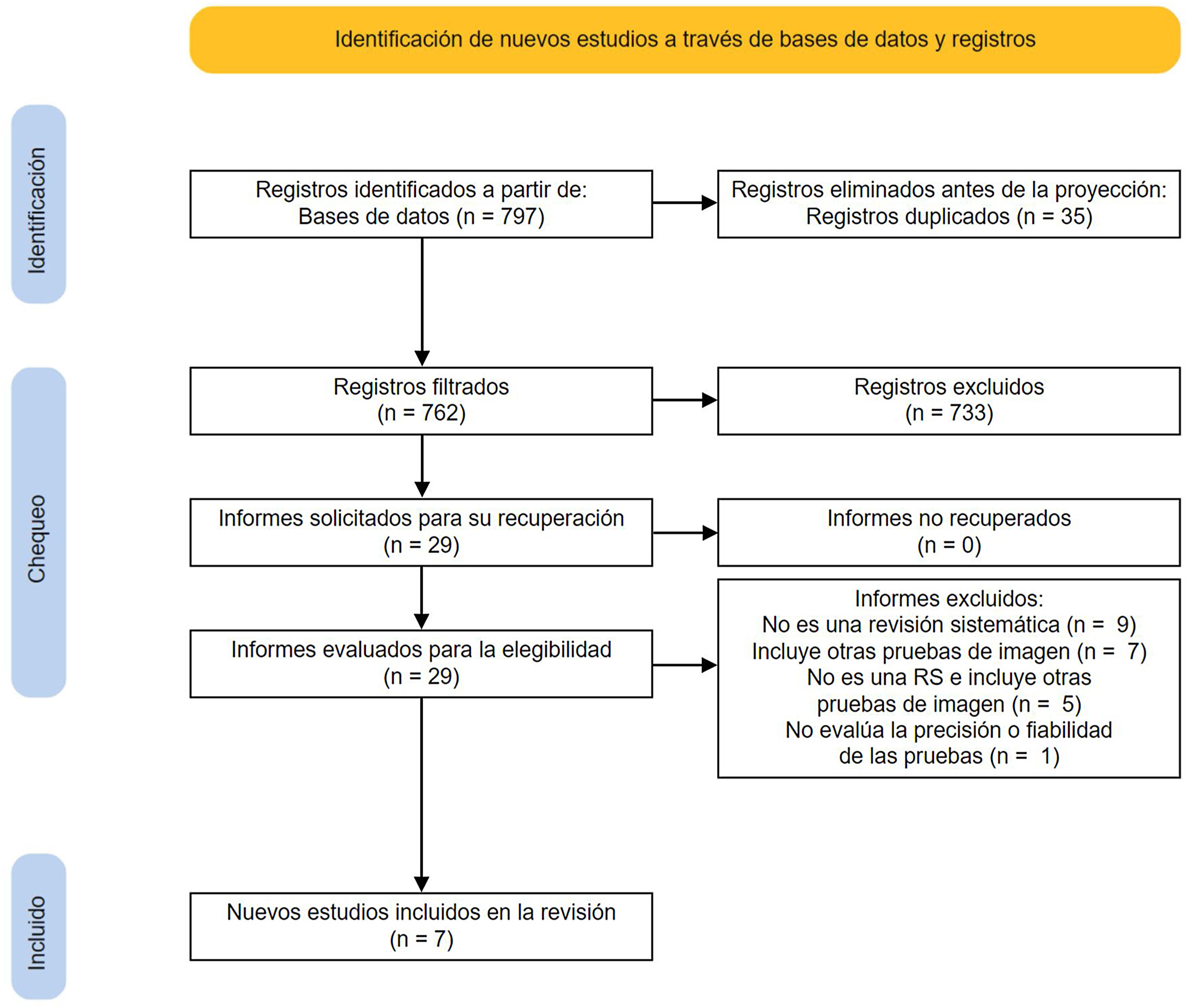
Material y métodosSe seleccionaron RS que evaluaran el uso de sistemas de IA para la lectura automática de radiografía de tórax. Se realizaron búsquedas (desde el inicio hasta mayo de 2022) en: PubMed, EMBASE y Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Dos investigadores seleccionaron los estudios. De cada RS se extrajeron elementos generales, metodológicos y de transparencia de la presentación. Se utilizaron las guías PRISMA para pruebas diagnósticas (PRISMA-DTA) y AMSTAR-2. Se realizó una síntesis narrativa de la evidencia. Registro del protocolo: Open Science Framework: https://osf.io/4b6u2/.
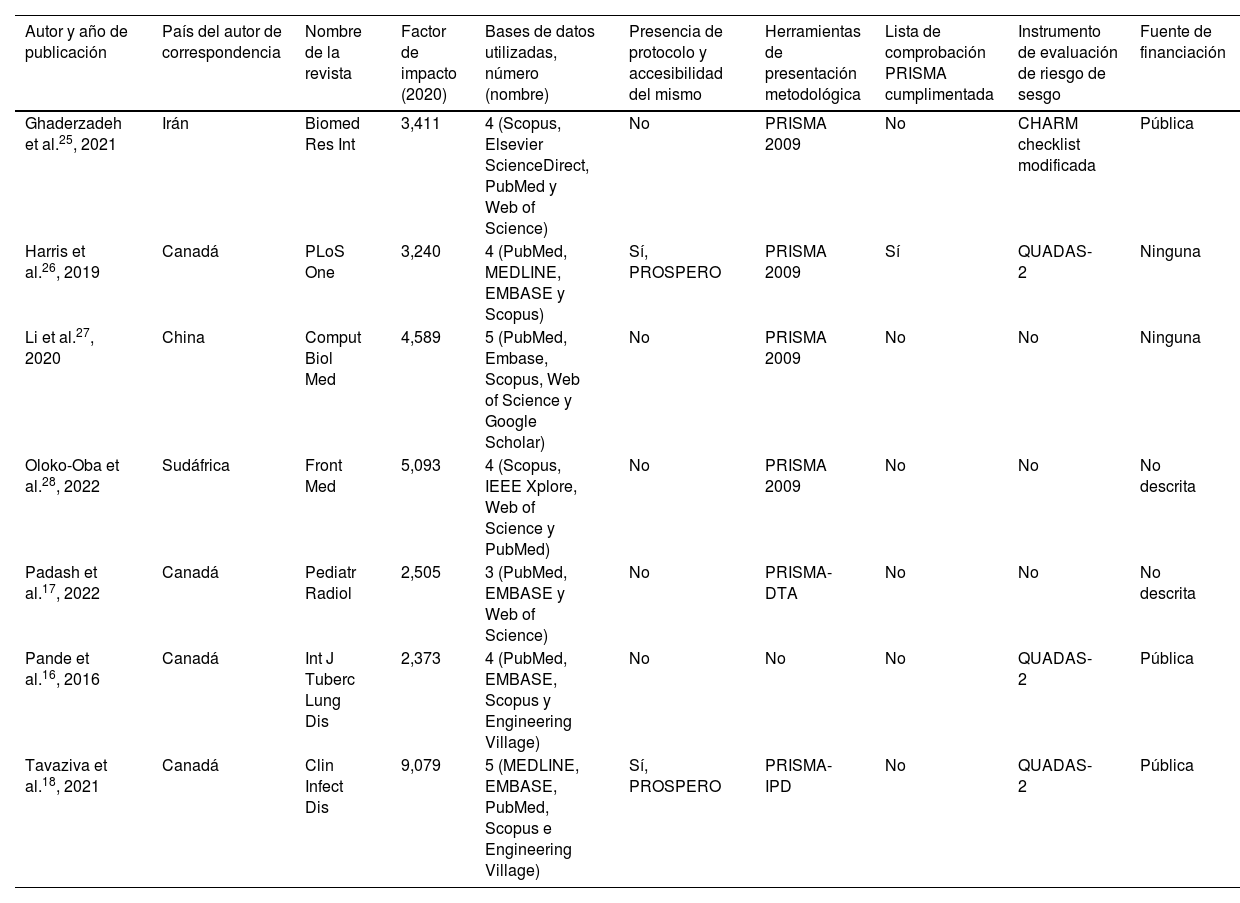
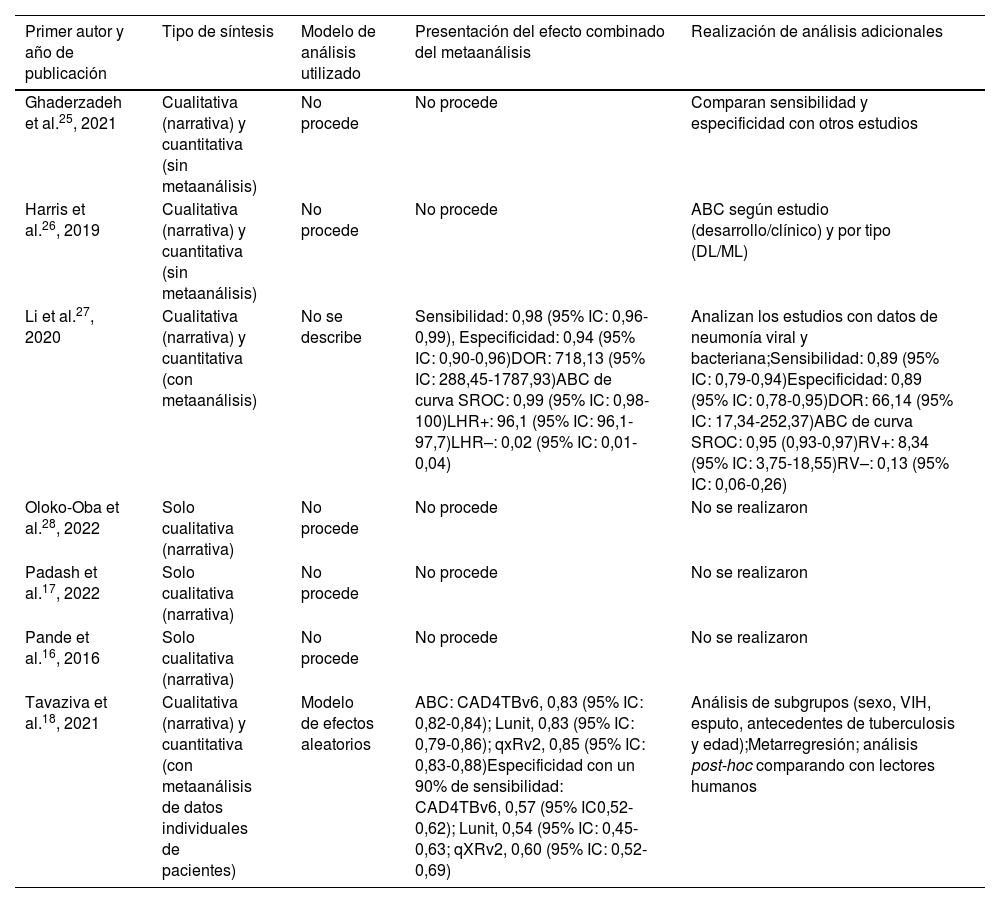
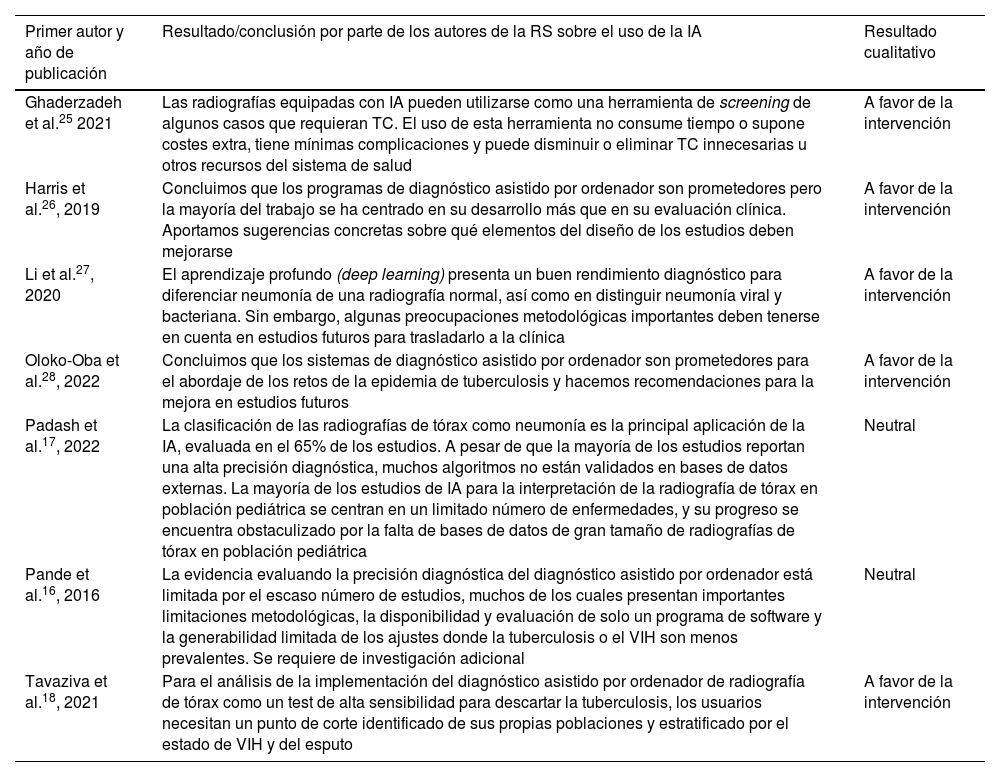
ResultadosTras aplicar los criterios de inclusión y exclusión se seleccionaron 7RS (media de 36 estudios incluidos por revisión). Todas las RS incluidas evaluaron sistemas de «aprendizaje profundo» en los que se utilizaba la radiografía de tórax para el diagnóstico de enfermedades infecciosas. Solo 2 (29%) RS indicaron la existencia de un protocolo. Ninguna RS especificó el diseño de los estudios incluidos ni facilitó una lista de estudios excluidos con su justificación. Seis (86%) RS mencionaron la utilización de PRISMA o alguna de sus extensiones. La evaluación del riesgo de sesgos se realizó en 4 (57%) RS. Una (14%) RS incluyó estudios con alguna validación de las técnicas de IA. Cinco (71%) RS presentaron resultados a favor de la capacidad diagnóstica de la intervención. Todas las RS obtuvieron la calificación «críticamente baja» siguiendo criterios AMSTAR-2.
ConclusionesLa calidad metodológica de las RS que utilizan sistemas de IA en radiografía de tórax es mejorable. La falta de cumplimiento en algunos ítems de las herramientas utilizadas hace que las RS publicadas en este campo deban interpretarse con cautela.
In recent years, systems that use artificial intelligence (AI) in medical imaging have been developed, such as the interpretation of chest X-ray to rule out pathology. This has produced an increase in systematic reviews (SR) published on this topic. This article aims to evaluate the methodological quality of SRs that use AI for the diagnosis of thoracic pathology by simple chest X-ray.
Material and methodsSRs evaluating the use of AI systems for the automatic reading of chest X-ray were selected. Searches were conducted (from inception to May 2022): PubMed, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Two investigators selected the reviews. From each SR, general, methodological and transparency characteristics were extracted. The PRISMA statement for diagnostic tests (PRISMA-DTA) and AMSTAR-2 were used. A narrative synthesis of the evidence was performed. Protocol registry: Open Science Framework: https://osf.io/4b6u2/.
ResultsAfter applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 7 SRs were selected (mean of 36 included studies per review). All the included SRs evaluated “deep learning” systems in which chest X-ray was used for the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Only 2 (29%) SRs indicated the existence of a review protocol. None of the SRs specified the design of the included studies or provided a list of excluded studies with their justification. Six (86%) SRs mentioned the use of PRISMA or one of its extensions. The risk of bias assessment was performed in 4 (57%) SRs. One (14%) SR included studies with some validation of AI techniques. Five (71%) SRs presented results in favour of the diagnostic capacity of the intervention. All SRs were rated “critically low” following AMSTAR-2 criteria.
ConclusionsThe methodological quality of SRs that use AI systems in chest radiography can be improved. The lack of compliance in some items of the tools used means that the SRs published in this field must be interpreted with caution.