La leucoencefalopatía multifocal progresiva (LMP) es una enfermedad desmielinizante del sistema nervioso central causada por la reactivación del virus JC. Esta encefalopatía oportunista se asocia mayormente a pacientes inmunodeprimidos con VIH en estadio III, y en los últimos años se ha asociado a tratamientos inmunosupresores como el natalizumab. La resonancia magnética (RM) tiene un papel importante tanto en el diagnóstico precoz como en el seguimiento de esta enfermedad. Recientemente, se han descrito en las secuencias eco de gradiente T2 (EGT2) y secuencias de susceptibilidad magnética (SWI) hipointensidades en las fibras-U y en la corteza adyacente a las lesiones de sustancia blanca características de la enfermedad.
ObjetivoNuestro objetivo es analizar la presencia y utilidad del signo de la hipointensidad cortical en secuencias EGT2 en relación con el diagnóstico de LMP, así como realizar una revisión bibliográfica sobre el tema.
Material y métodosEn este trabajo se analizan tres casos de LMP vistos en nuestro centro en 3 pacientes diferentes con inmunosupresión de distinto origen: uno con enfermedad por VIH en estadio III, otro con esclerosis múltiple en tratamiento con natalizumab y otro con artritis reumatoide en tratamiento con rituximab.
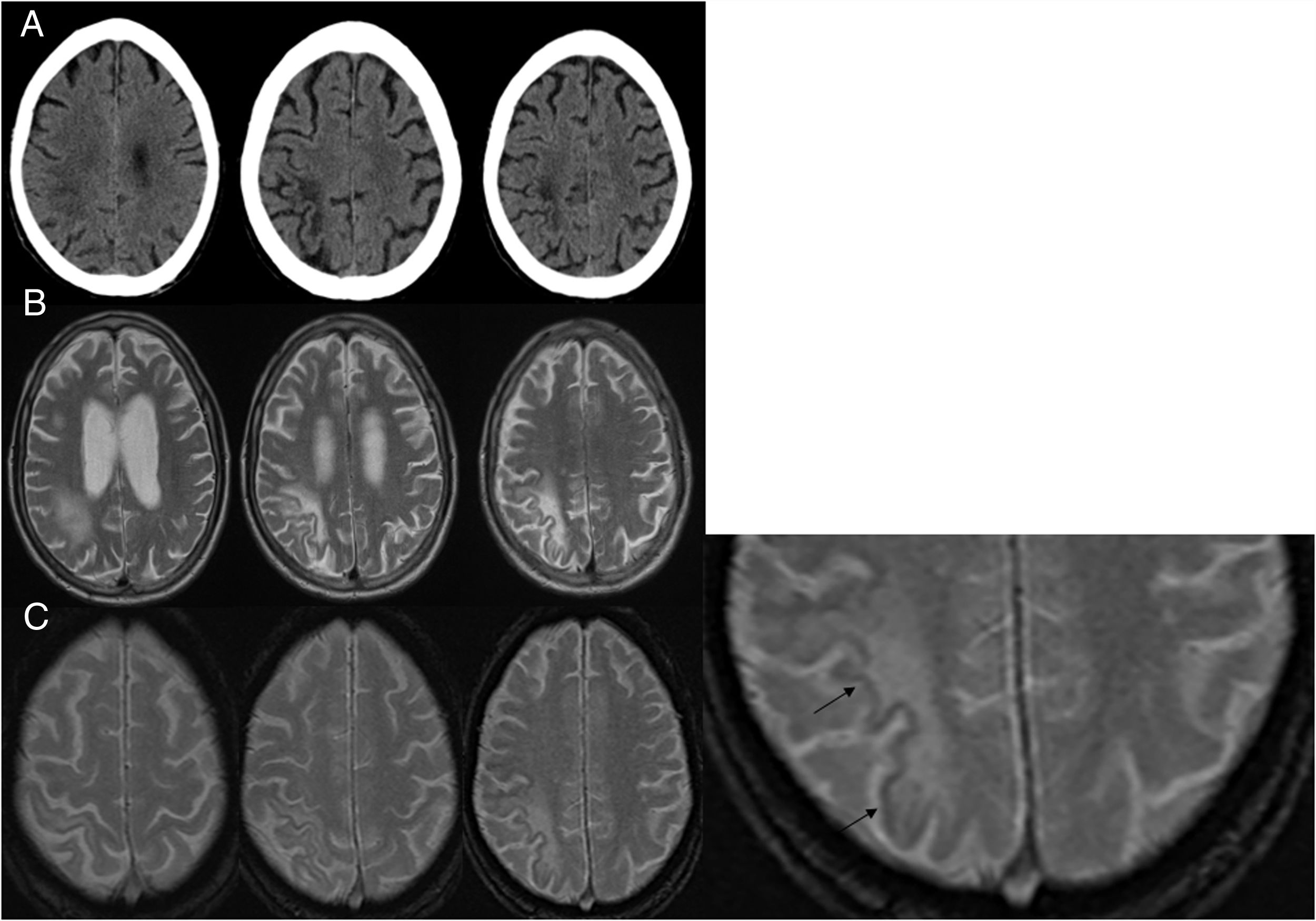
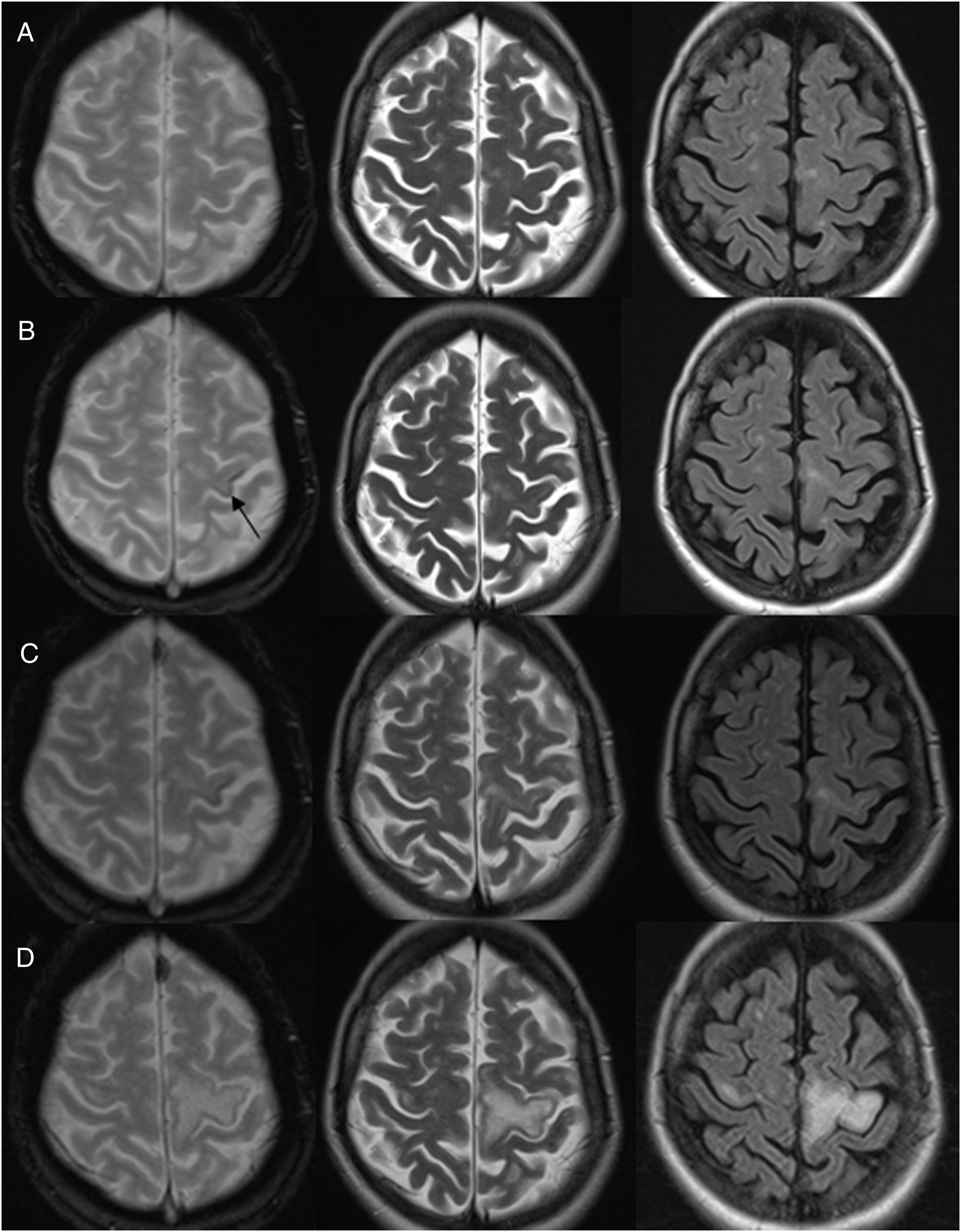
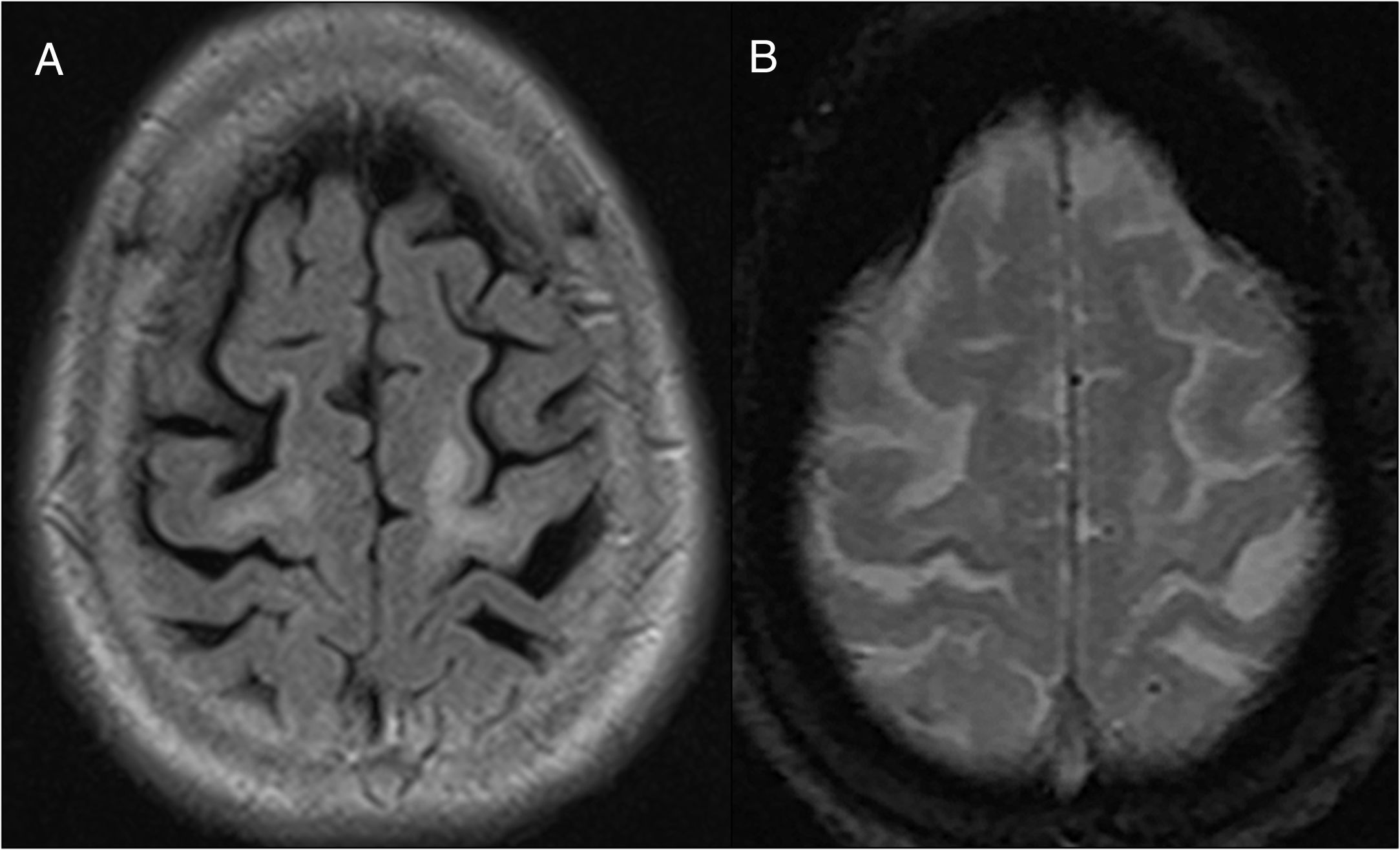
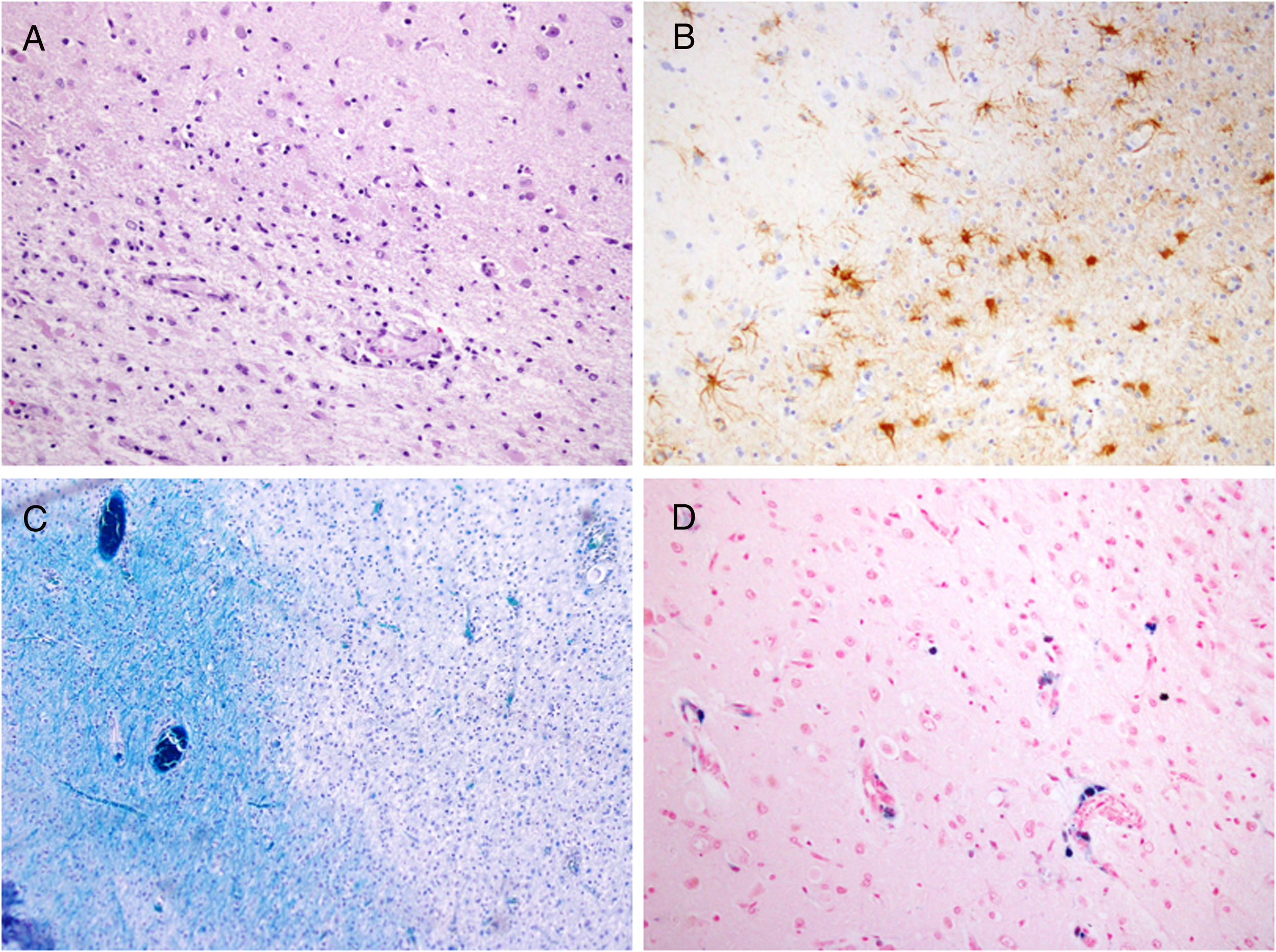
ResultadosEn los tres casos se observa en la RM el hallazgo de hipointensidad cortical adyacente a la lesión de la sustancia blanca en la secuencia EGT2. En la paciente con esclerosis múltiple, este signo fue más precoz que la alteración de señal en la sustancia blanca. El paciente en tratamiento con rituximab fue diagnosticado post mortem y se presenta una correlación radiopatológica.
ConclusiónLa hipointensidad cortical descrita en el EGT2 en los estudios de RM parece ser un hallazgo que apoyaría el diagnóstico de la LMP, independientemente del tipo de inmunosupresión, lo que nos hace plantear su inclusión de forma rutinaria entre los hallazgos a evaluar en RM en los pacientes con sospecha de LMP.
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy is a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system caused by the reactivation of the JC virus. This opportunistic encephalopathy mainly affects immunodepressed patients with stage III HIV infection, although in recent years it has also been found in association with treatment with immunosuppressors such as natalizumab. MRI plays an important role in both the early diagnosis and follow-up of this disease. Recently, it has been reported that hypointensities in U-fibers and cortex adjacent to white-matter lesions characteristic of the disease can be identified on T2-weighted gradient-echo and susceptibility-weighted sequences in patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
ObjectiveWe aimed to analyze the presence and usefulness of cortical hypointensity on T2-weighted gradient-echo sequences in relation to the diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and to review the literature on the topic.
Material and methodsWe analyze three cases of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy seen at our center in three patients with immunosuppression of different origins: one with stage III HIV infection, one with multiple sclerosis being treated with natalizumab, and one with rheumatoid arthritis being treated with rituximab.
ResultsIn all three cases MRI showed the cortical hypointensity adjacent to the white-matter lesion in the T2-weighted gradient-echo sequence. In the patient with multiple sclerosis, this sign appeared earlier than the abnormal signal in the white matter. The patient being treated with rituximab was diagnosed postmortem and the pathology findings correlated with the MRI findings.
ConclusionThe finding of cortical hypointensity on T2-weighted gradient-echo MRI sequences seems to support the diagnosis of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, regardless of the type of immunosuppression, so this finding should routinely assessed in patients suspected of having this disease.