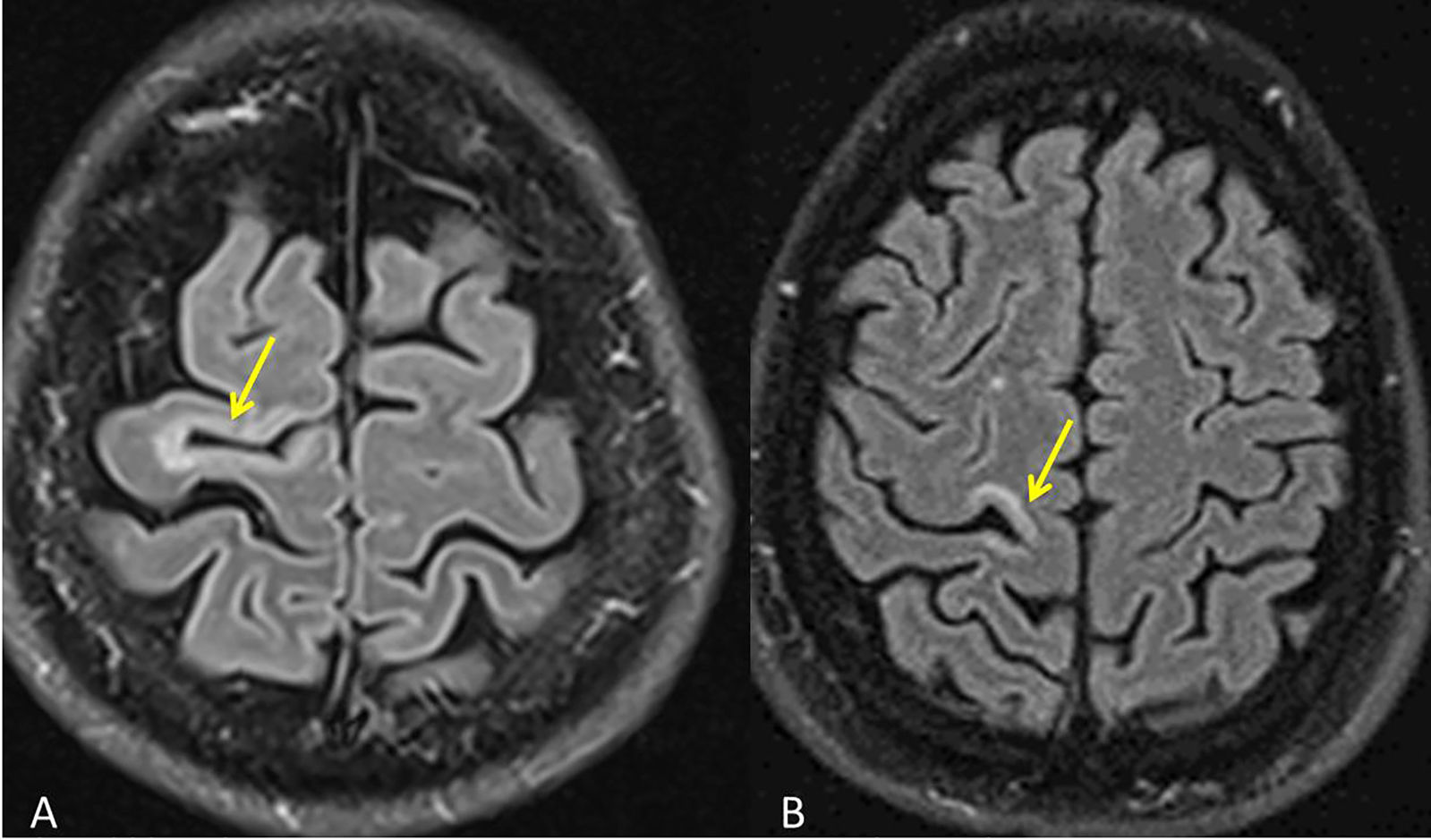
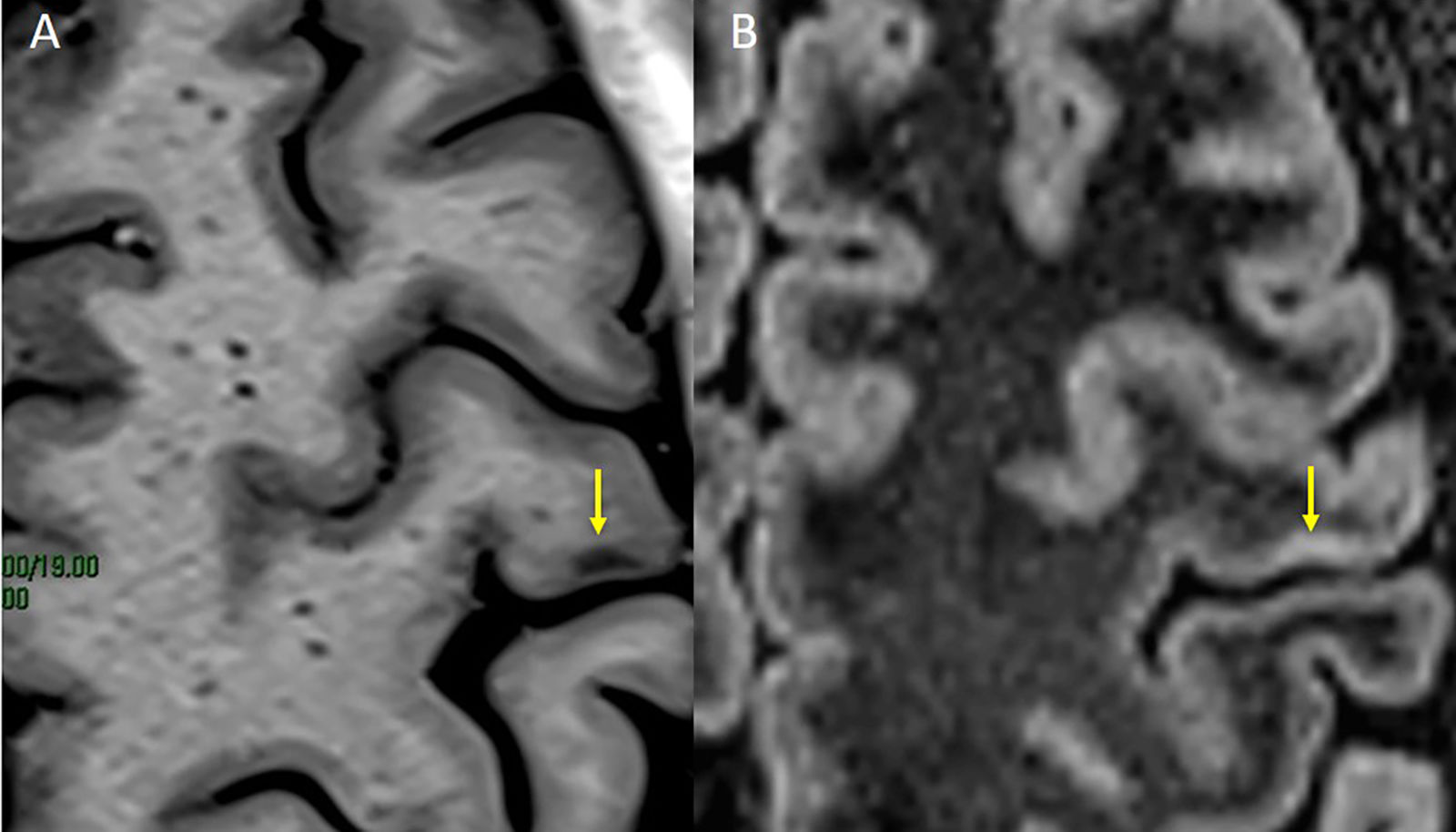
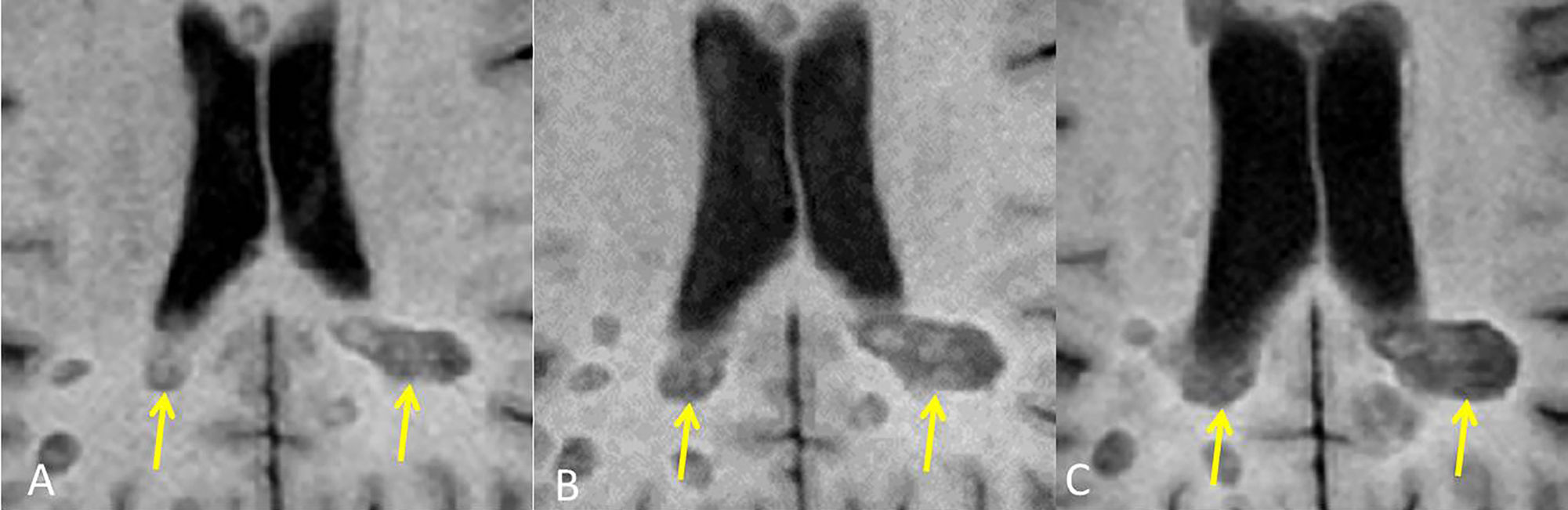
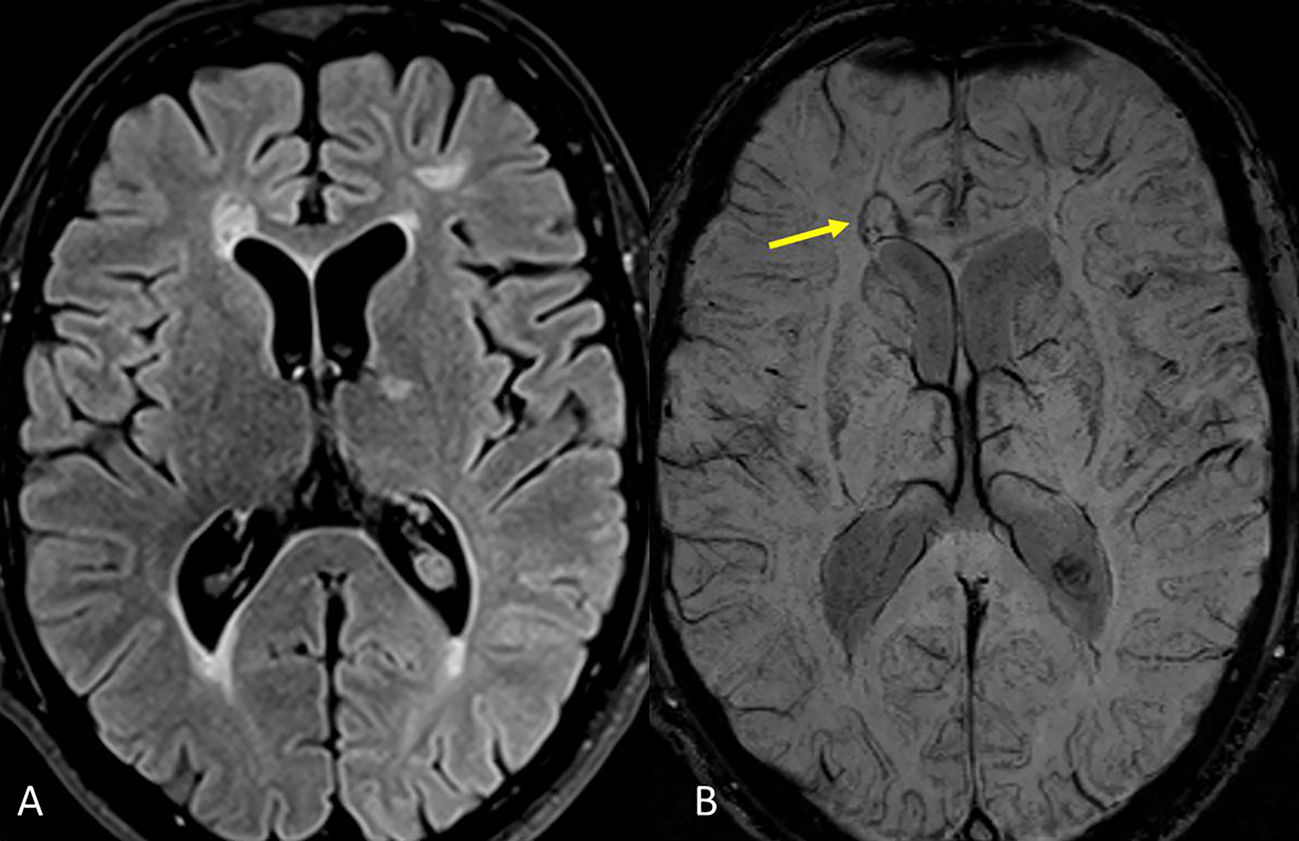
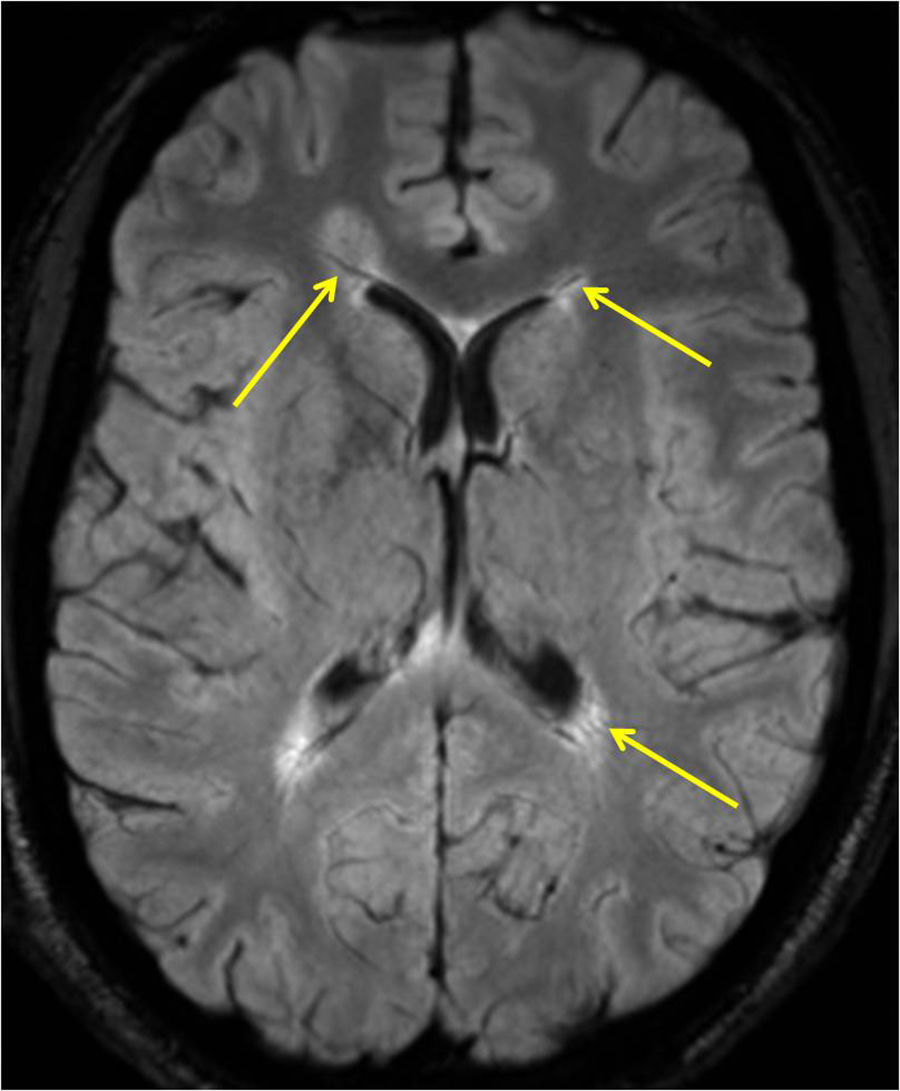
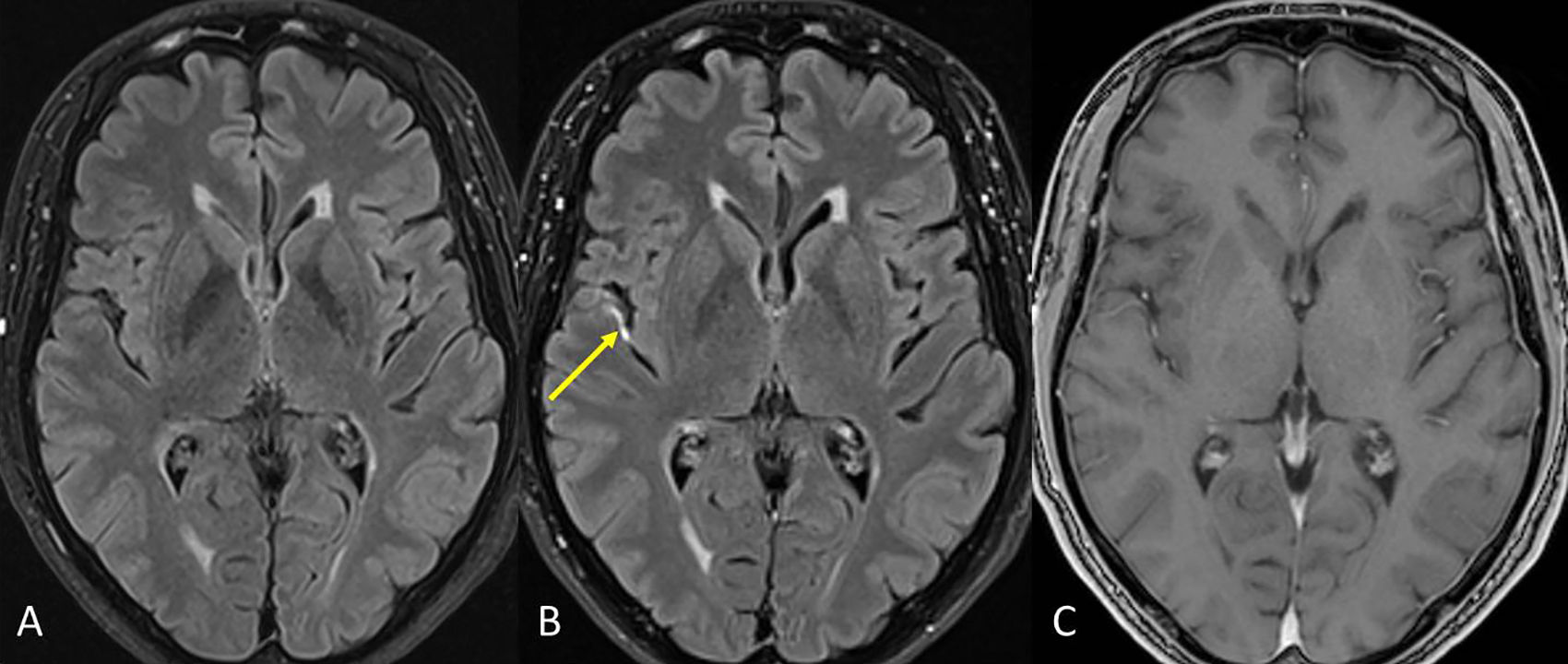
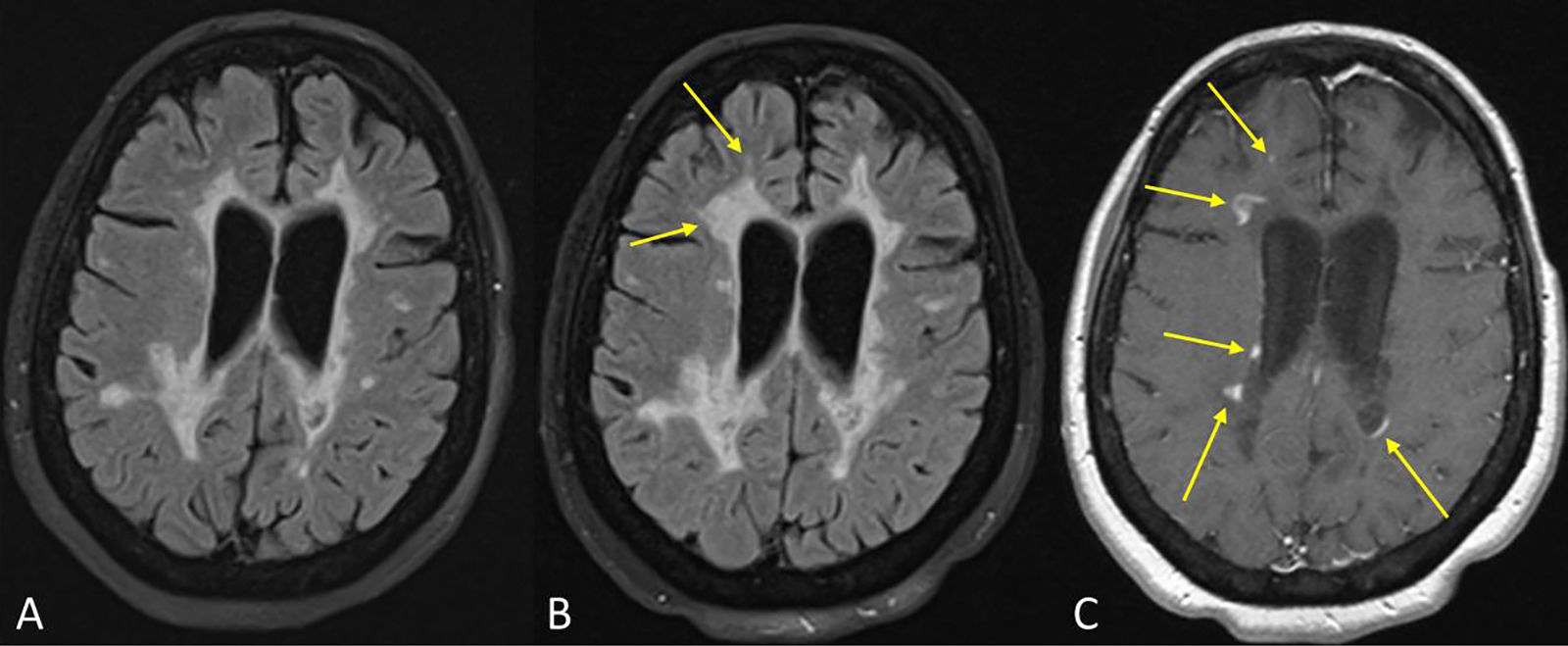
Está ampliamente aceptado que la resonancia magnética (RM) es la técnica paraclínica más relevante, no solo para establecer un diagnóstico preciso y precoz de la esclerosis múltiple (EM), sino también para predecir su pronóstico y para controlar y predecir la eficacia de los diferentes tratamientos modificadores de la enfermedad. En los últimos años se han descrito nuevos hallazgos radiológicos en la EM, y han aparecido nuevas evidencias sobre el papel de la RM en el seguimiento de la enfermedad. Asimismo, la normativa establecida por la Comisión Europea en relación con el uso de medios de contraste que contienen gadolinio ha obligado a revisar y restringir la indicación de su uso en la práctica clínica. Los radiólogos debemos estar familiarizados con estas novedades y recomendaciones para de esta manera utilizar de forma adecuada la RM en los procesos de diagnóstico y seguimiento de la EM.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely considered to be the most important paraclinical technique for establishing an accurate early diagnosis of multiple sclerosis as well as for predicting its prognosis and monitoring and predicting the efficacy of different treatments for this disease. In recent years, new imaging findings for multiple sclerosis have been described, and new evidence about the role of MRI in the follow-up of this disease has accumulated. Moreover, the European Commission's regulations of the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents have required that the indications for their use in clinical practice be revised and restricted. Radiologists need to be familiar with these developments and recommendations to use MRI appropriately in the diagnosis and follow-up of multiple sclerosis.