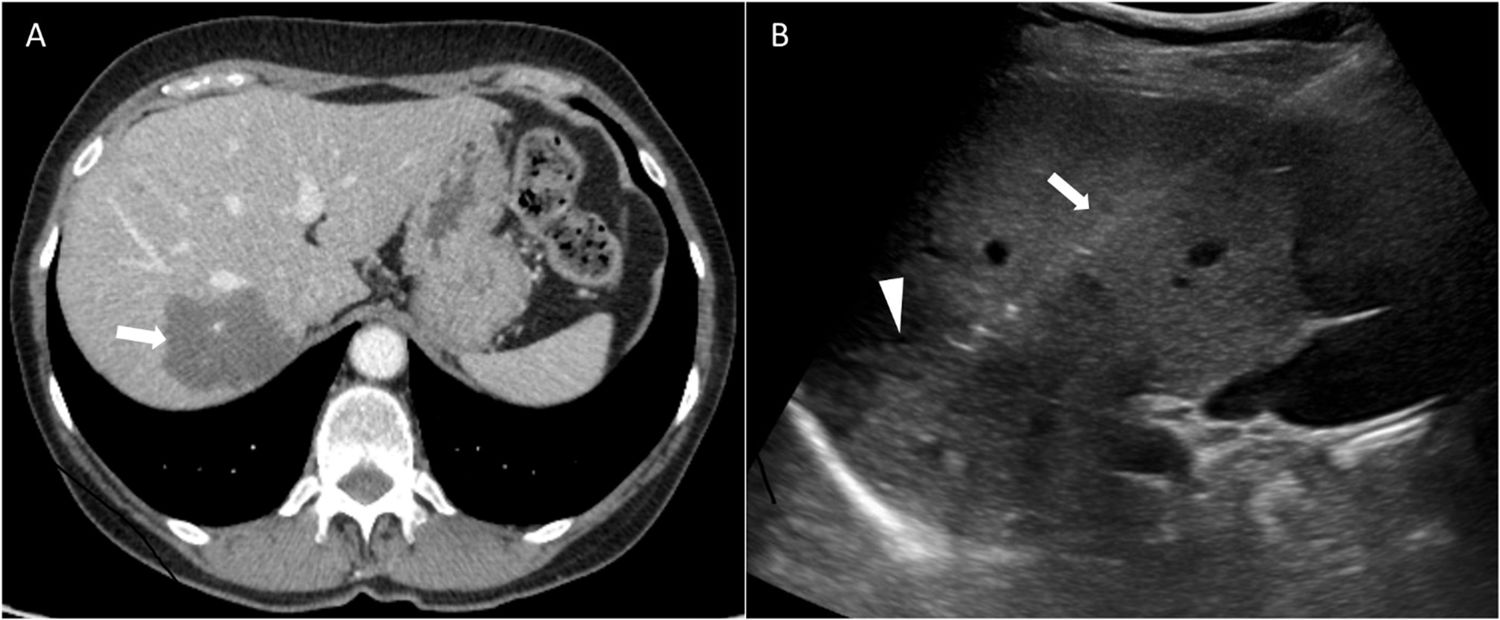
La biopsia hepática percutánea ecoguiada se considera la técnica de elección para el diagnóstico histológico de las lesiones ocupantes de espacio (LOE), dada su elevada seguridad y rentabilidad diagnóstica. Sin embargo, al tratarse de una técnica de diagnóstico invasiva, no se encuentra exenta de complicaciones. Diversos parámetros clínico-radiológicos han sido analizados como factores relacionados con la eficacia o complicaciones, con resultados contradictorios. Por todo ello, el objetivo de nuestro estudio es evaluar el impacto de diversos factores de riesgo en la eficacia y complicaciones de la biopsia hepática percutánea ecoguiada en el diagnóstico de LOE, en el ámbito de la práctica clínica habitual.
Material y métodosLlevamos a cabo un estudio observacional, retrospectivo, unicéntrico de pacientes sometidos a biopsia hepática percutánea ecoguiada en tiempo real con técnica de manos libres para el diagnóstico de LOE, realizadas en el Servicio de Radiodiagnóstico del Hospital Clínico Universitario de Santiago de Compostela entre diciembre 2012 y febrero 2018. Seleccionamos como factores de riesgo: la localización de la LOE en los segmentos hepáticos superiores (II, IVa, VII y VIII), la proximidad a la cápsula hepática, la distancia entre piel y LOE mayor de 100mm, la interposición de estructuras óseas o vasculares, la incapacidad para atravesar parénquima sano o la falta de colaboración del paciente durante el procedimiento. La eficacia fue analizada en términos de número de cilindros extraídos y porcentaje de biopsias satisfactorias; y la seguridad, en términos de porcentaje de complicaciones presentadas, clasificándolas, a su vez, en complicaciones mayores y menores.
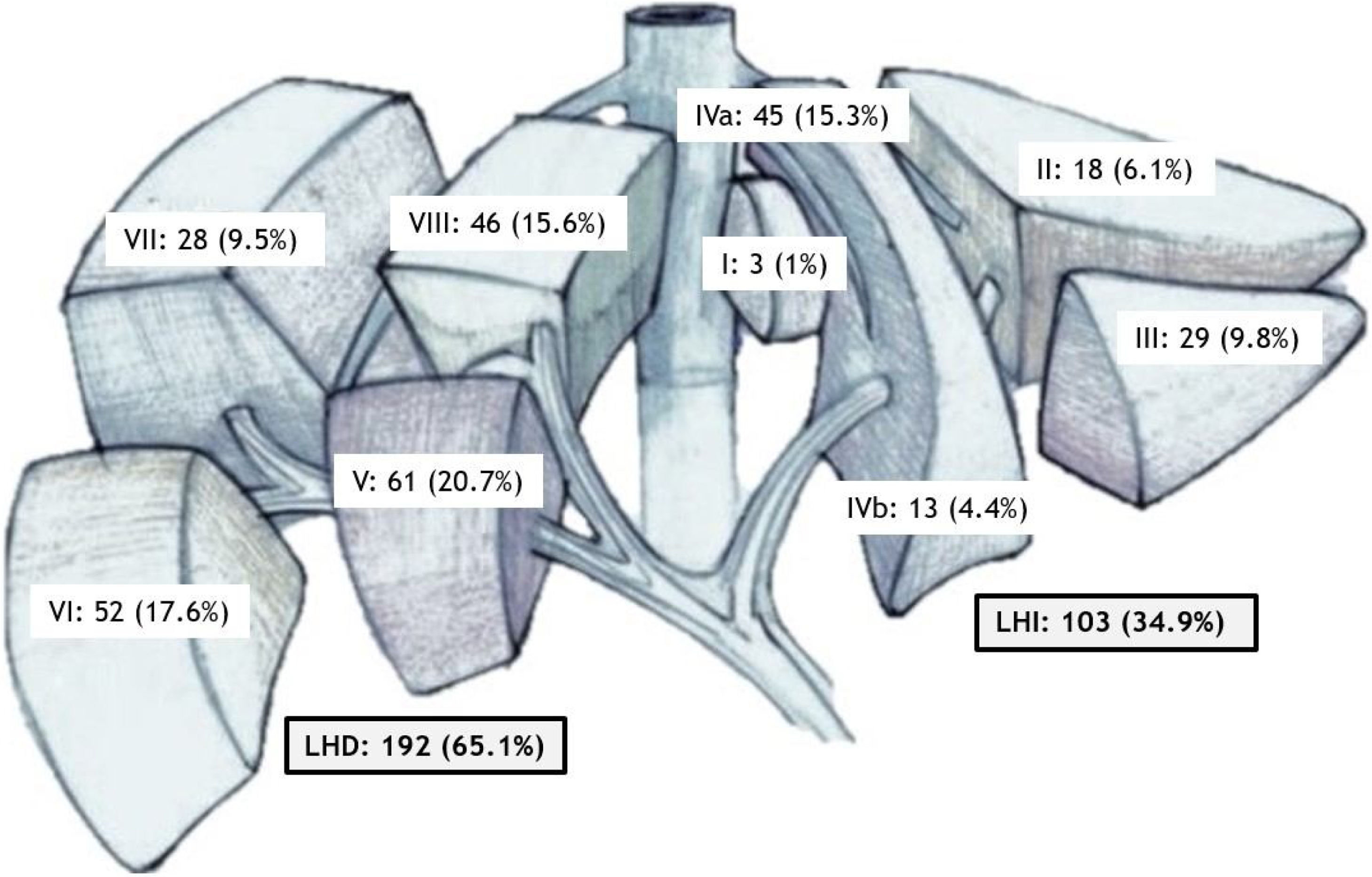
ResultadosSe incluyeron 295 biopsias de 278 pacientes. La mediana de edad fue de 69 años, el 64,1% eran varones y el 44,7% tenía una neoplasia previa. El 61,4% de las biopsias se indicaron para el diagnóstico inicial, el 82,4% se realizaron con el paciente ingresado y el 65% de las lesiones se localizaban en el lóbulo hepático derecho.
La mediana de cilindros extraídos fue de 3 (rango 1-6). El 91,2% de las biopsias fueron satisfactorias, sin diferencias en función de la presencia de factores de riesgo, y el 92,2% fueron clasificadas como útiles desde el punto de vista clínico. Diez (3,4%) pacientes presentaron complicaciones, en 3 (0,9%) fueron complicaciones mayores, en 2 (0,6%) complicaciones hemorrágicas y en 1 (0,3%) complicaciones infecciosas; y en los 7 restantes (2,4%), complicaciones menores. Se observó un porcentaje significativamente superior de complicaciones en pacientes no colaboradores durante el procedimiento (p=0.04).
ConclusionesLa biopsia hepática percutánea ecoguiada es una técnica eficaz y segura para el diagnóstico histológico de LOE. Se confirma el impacto en el desarrollo de complicaciones en el paciente no colaborador durante el procedimiento de biopsia.
Ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy is considered the technique of choice for the histological diagnosis of space-occupying lesions, given its high level of safety and diagnostic performance. However, since it is an invasive diagnostic procedure, complications can occur. Various clinical and radiological parameters have been analyzed as factors related with the efficacy of the technique or with its complications; however, the results have been contradictory. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the impact of various risk factors on the efficacy and complications of ultrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy in the diagnosis of space-occupying lesions in ordinary clinical practice.
Material and methodsThis retrospective observational study included all patients who underwent real-time ultrasound-guided percutaneous biopsies of space-occupying liver lesions with the free-hand technique between December 2012 and February 2018 in the diagnostic imaging department at the Hospital Clínico Universitario de Santiago de Compostela. We analyzed the following risk factors: location of the lesion in upper liver segments (II, IVa, VII, or VIII); proximity to the liver capsule, distance from the skin > 100mm, interposition of osseus or vascular structures, inability to go through healthy parenchyma, and lack of patient cooperation during the procedure. Efficacy was analyzed in terms of the number of cylinders obtained and the percentage of adequate biopsies; safety was analyzed in terms of the percentage of complications, which were classified as major or minor.
ResultsWe included 295 biopsies in 278 patients (median age, 69 years; 64.1% male; 44.7% had prior neoplasms). In 61.4%, the biopsy was indicated for the initial diagnosis; 82.4% of biopsies were done in hospitalized patients, and 65% of the lesions were located in the right liver lobe.
The median number of cylinders obtained was 3 (range 1-6); 91.2% of the biopsies were adequate and 92.2% were considered clinically useful. These percentages did not differ significantly according to the presence of risk factors. Complications occurred in 10 (3.4%) patients. Complications were considered major in 3 (0.9%) patients (2 (0.6%) bleeding complications and 1 (0.3%) infectious complication) and minor in 7 (2.4%). The percentage of complications was significantly higher in patients who did not cooperate during the procedure (p=0.04).
ConclusionsUltrasound-guided percutaneous liver biopsy is an efficacious and safe technique for the histological diagnosis of space-occupying liver lesions. Our results confirm the increased rate of complications when patients fail to cooperate during the procedure.