Suplemento:Actualización y buenas prácticas en los usos de los medios de contraste
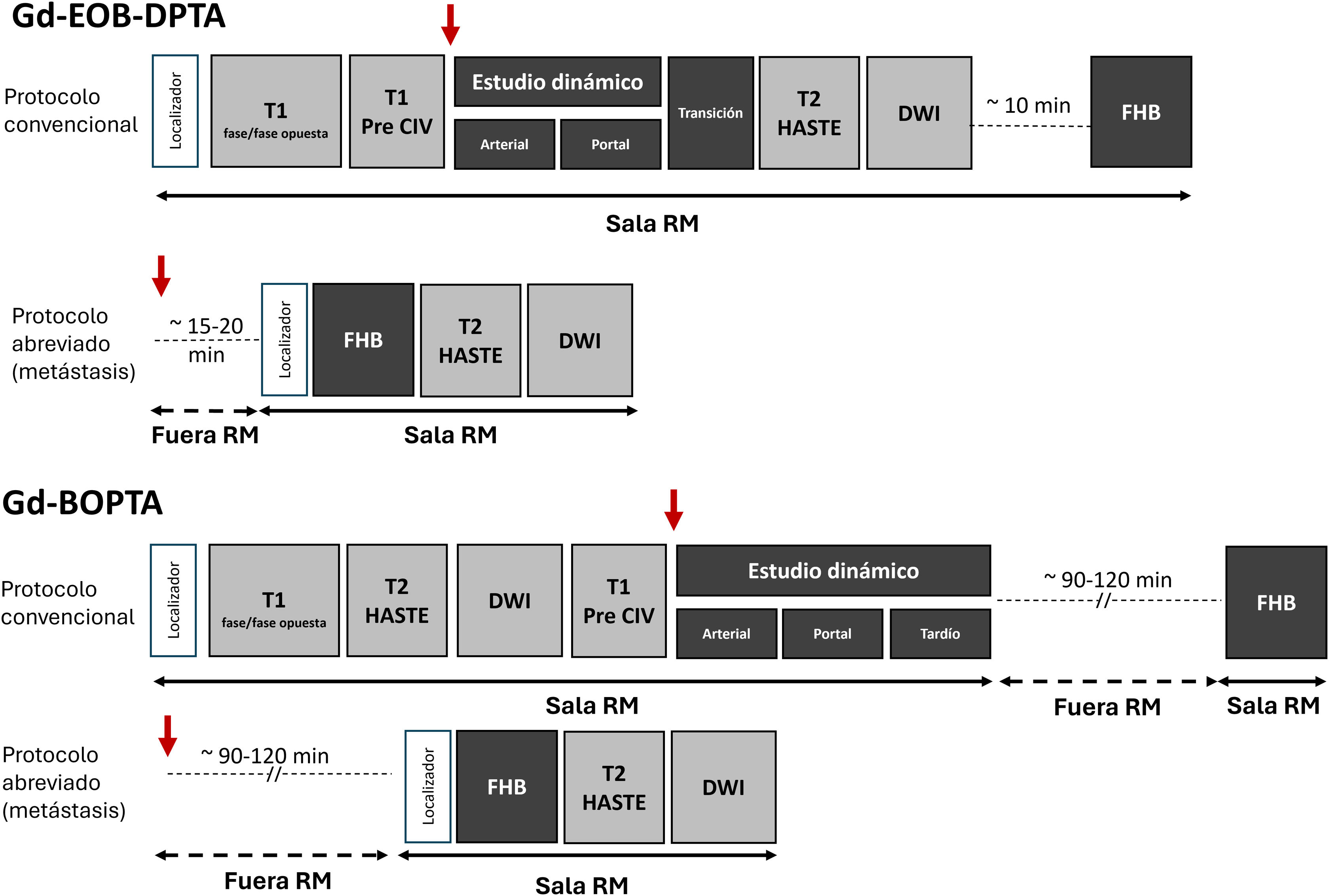
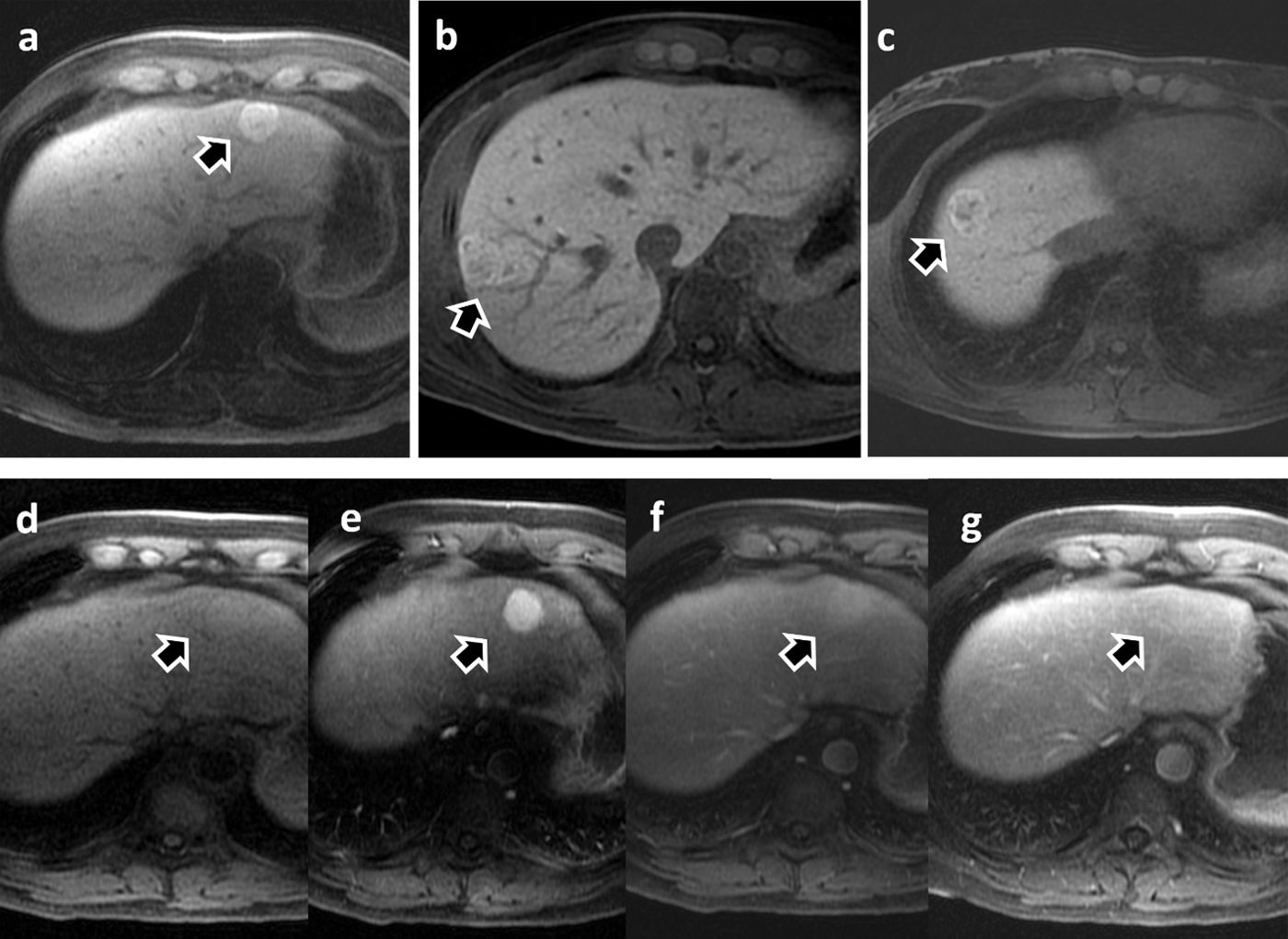
More infoLa resonancia magnética hepática con medios de contraste hepatoespecíficos es una herramienta diagnóstica crucial para evaluar las enfermedades hepáticas. Permite la detección y la caracterización de lesiones focales y alteraciones vasculares hepáticas, así como la evaluación y la gradación de la hepatopatía crónica. Los contrastes hepatoespecíficos paramagnéticos están basados en el gadolinio, se incorporan parcialmente a los hepatocitos, y se excretan tanto por la vía renal como por la biliar. Actualmente se dispone comercialmente de 2 moléculas lineales iónicas: el ácido gadobénico (Gd-BOPTA) y el ácido gadoxético (Gd-EOB-DTPA). Sus principales indicaciones clínicas incluyen diferenciar y caracterizar lesiones focales hepáticas sobre el hígado sano, diagnosticar y estadificar el carcinoma hepatocelular en los pacientes con hepatopatía crónica, e incrementar la fiabilidad en la detección de metástasis hepáticas en pacientes oncológicos, especialmente antes de la cirugía. También son útiles en la evaluación anatómica de la vía biliar y las complicaciones de la cirugía hepática como la fuga biliar.
The use of hepatobiliary-specific contrast agents in liver MRI is a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating liver disease, enabling the detection and characterisation of focal lesions and vascular alterations, as well as the assessment and grading of chronic hepatopathy. Paramagnetic hepatobiliary-specific contrast agents are gadolinium-based, partially taken up by hepatocytes, and excreted via both renal and biliary pathways. There are two linear ionic molecules that are currently commercially available: gadobenic acid (Gd-BOPTA) and gadoxetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA). Their main clinical indications include distinguishing and characterising focal liver lesions on healthy liver tissue, diagnosing and staging hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatopathy, and increasing reliability in the detection of hepatic metastases in oncology patients, especially prior to surgery. They are also useful in the evaluation of the biliary tract and in assessing complications of hepatic surgery such as bile leaks.