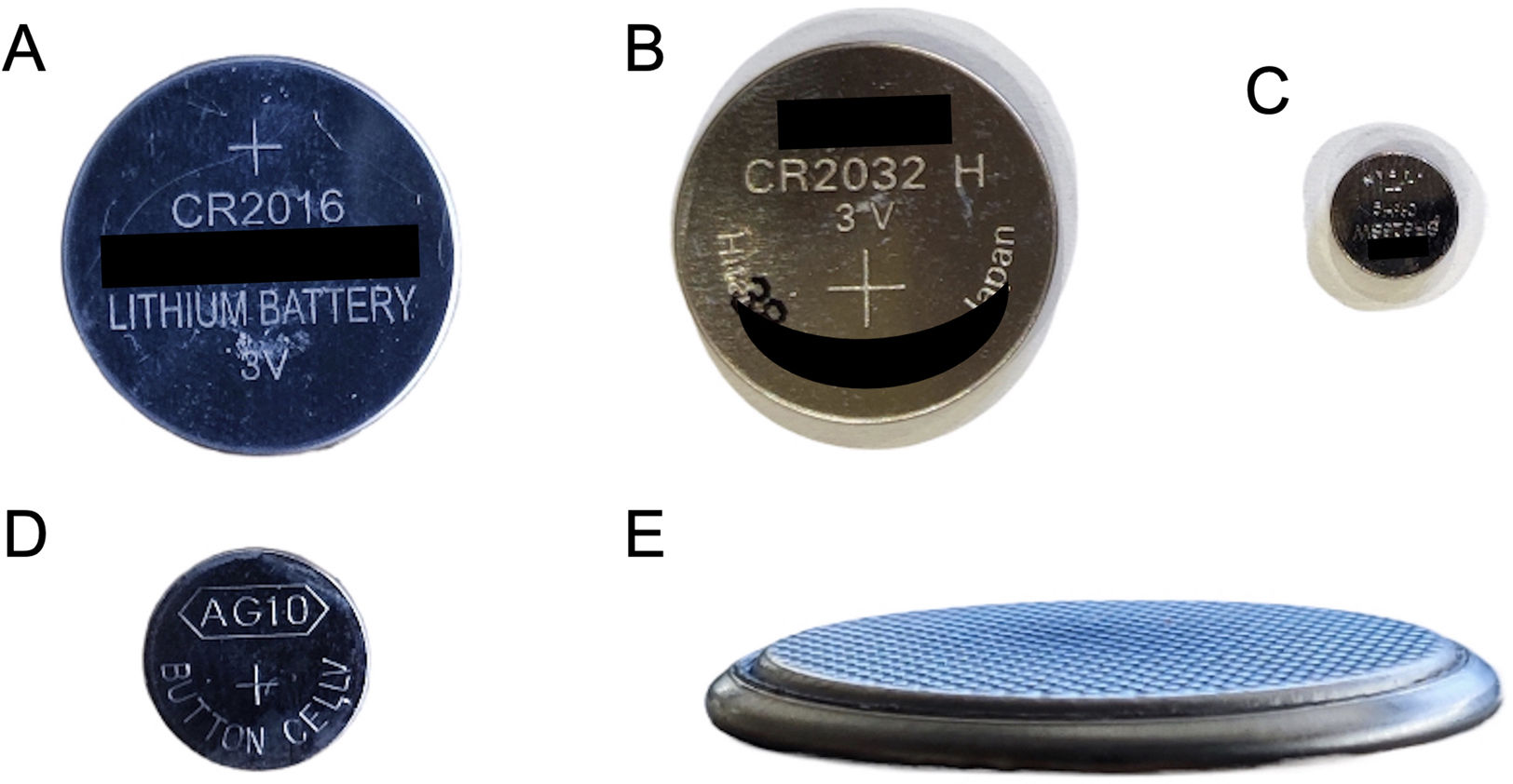
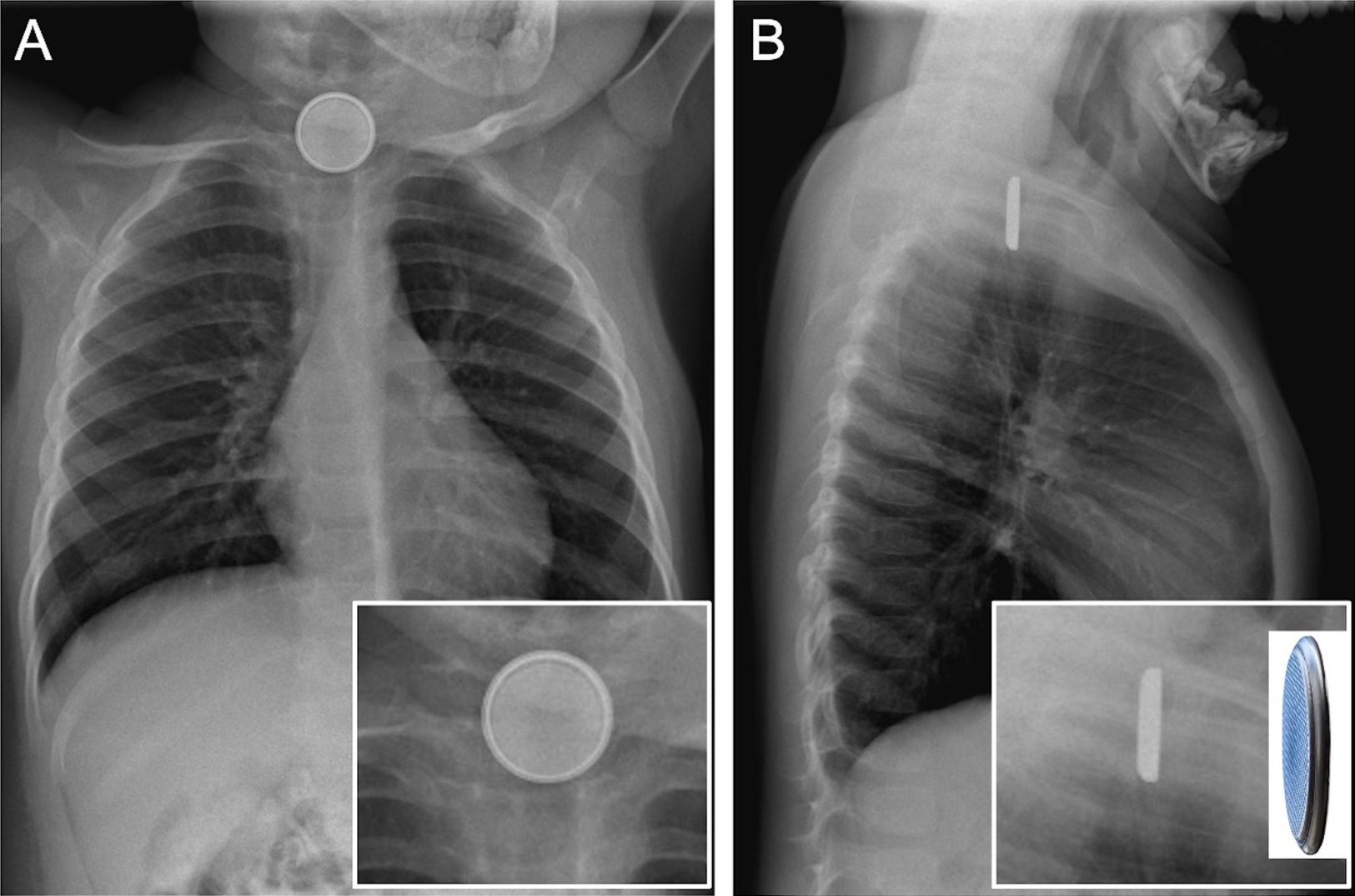
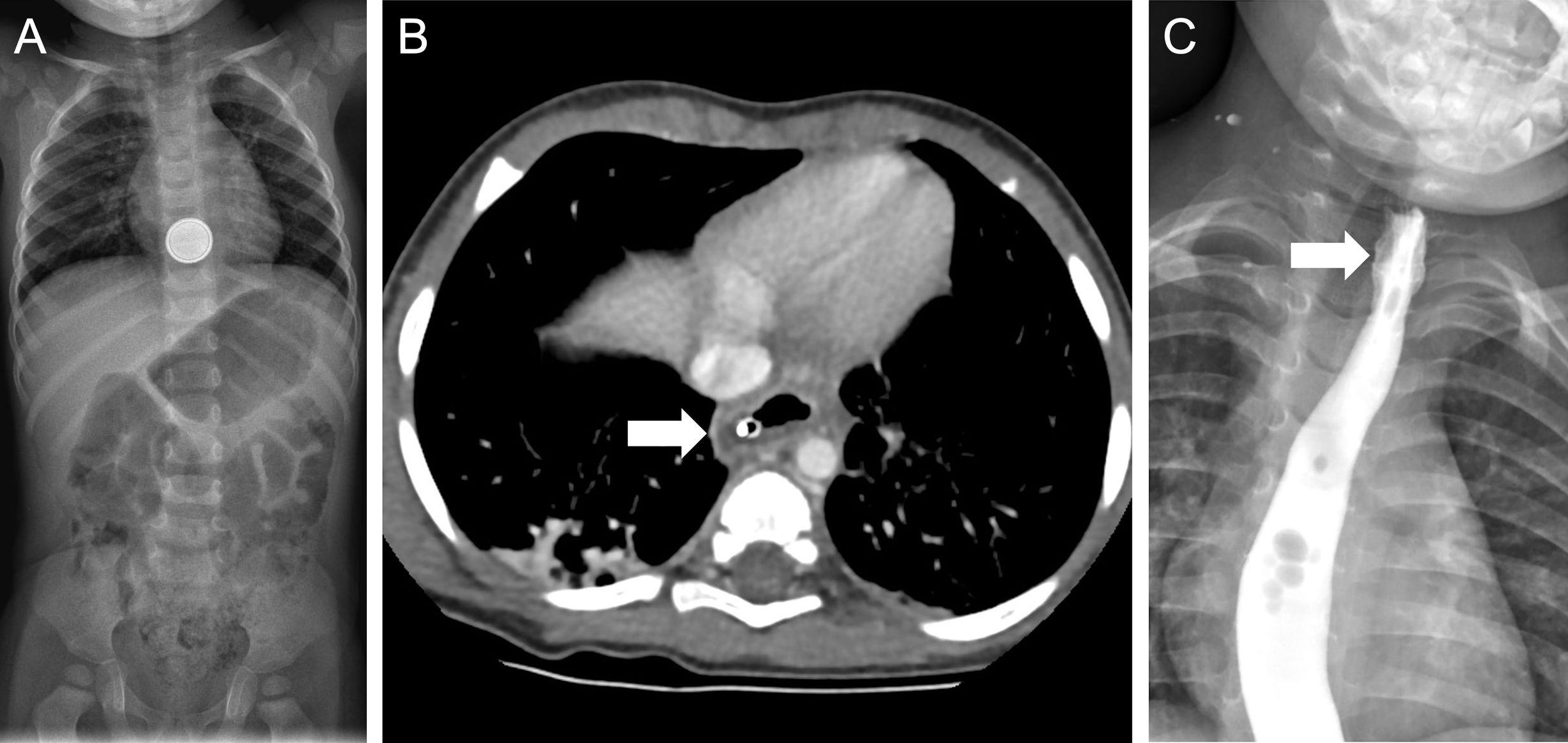
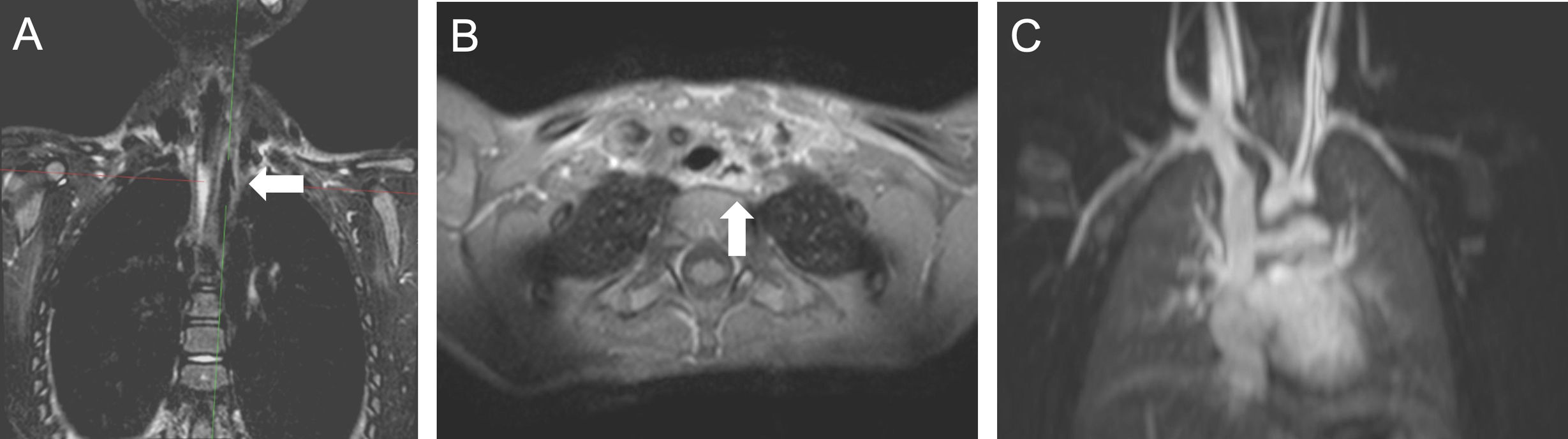
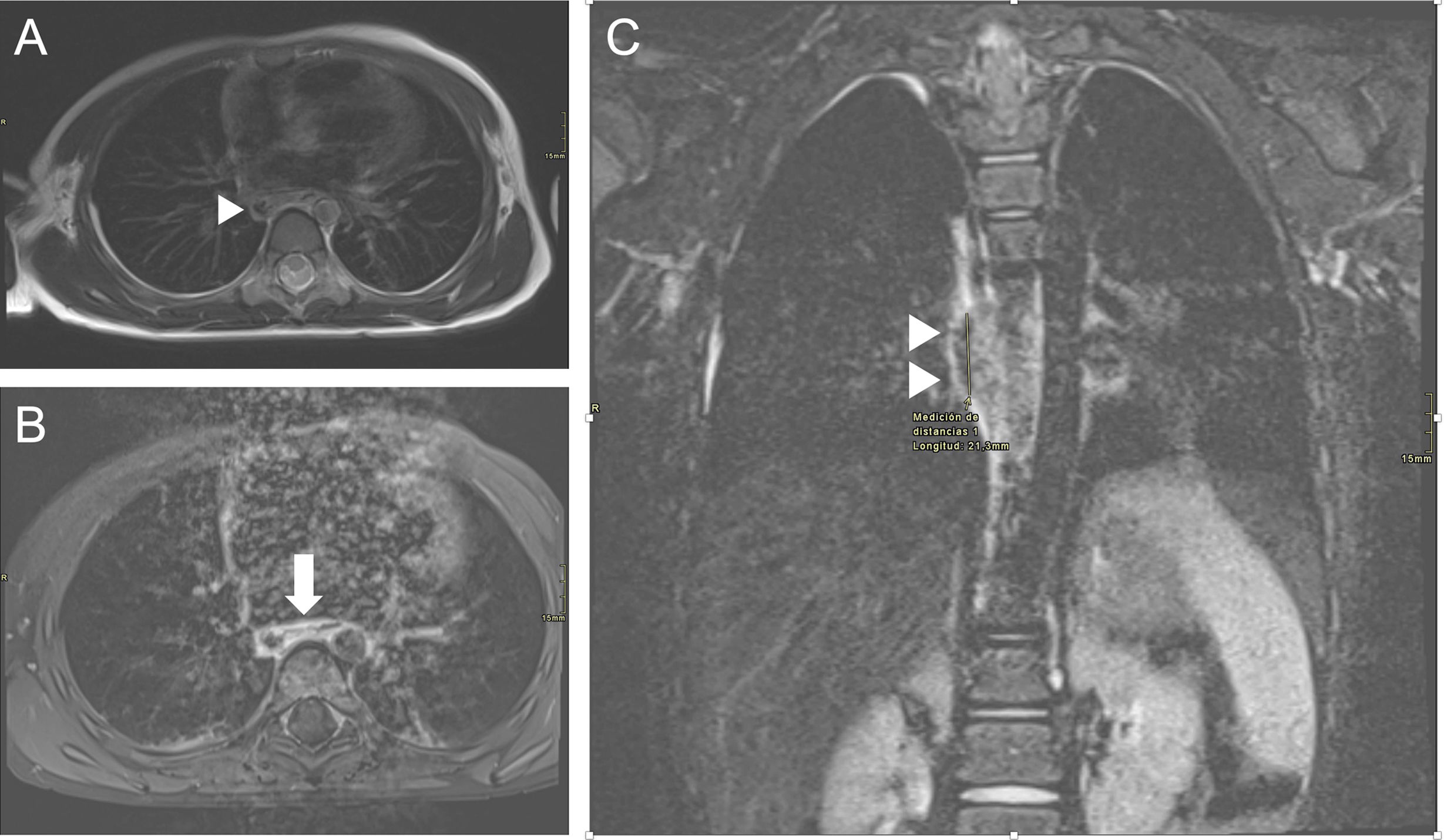
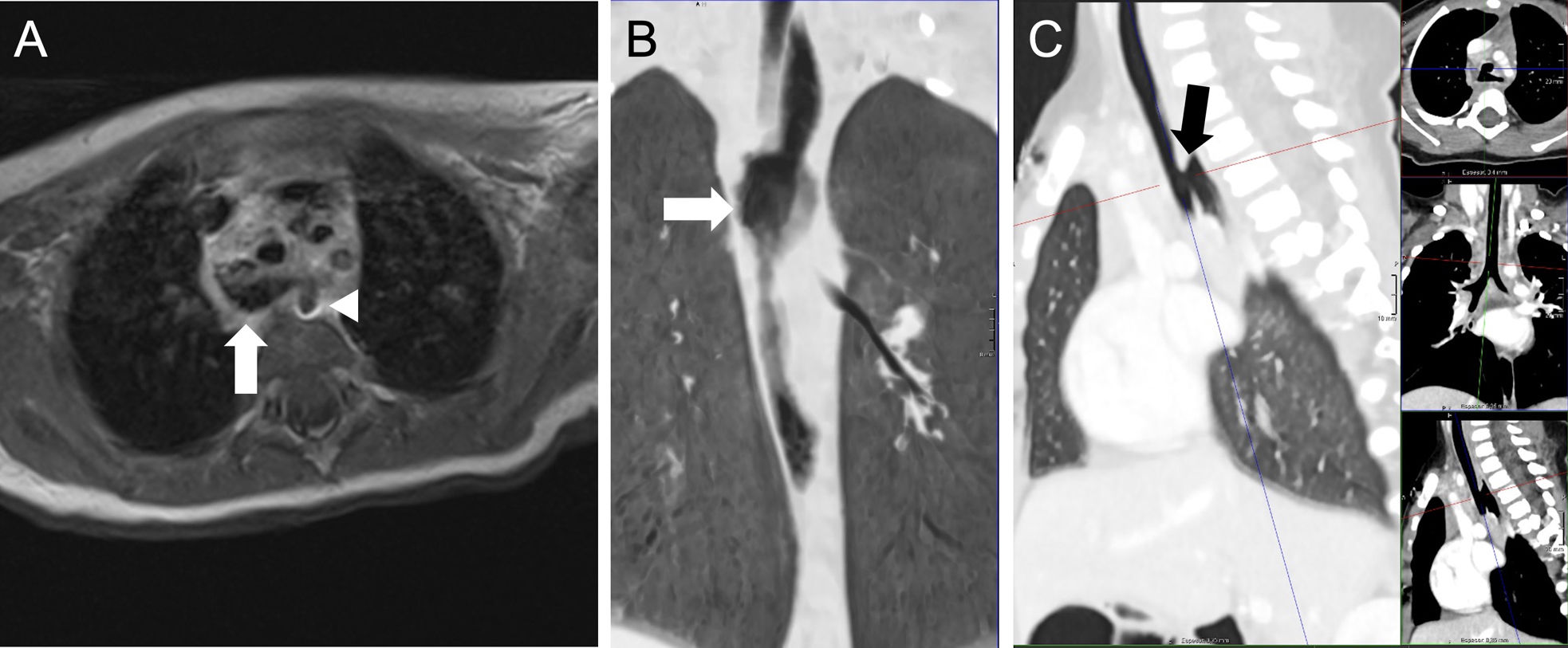
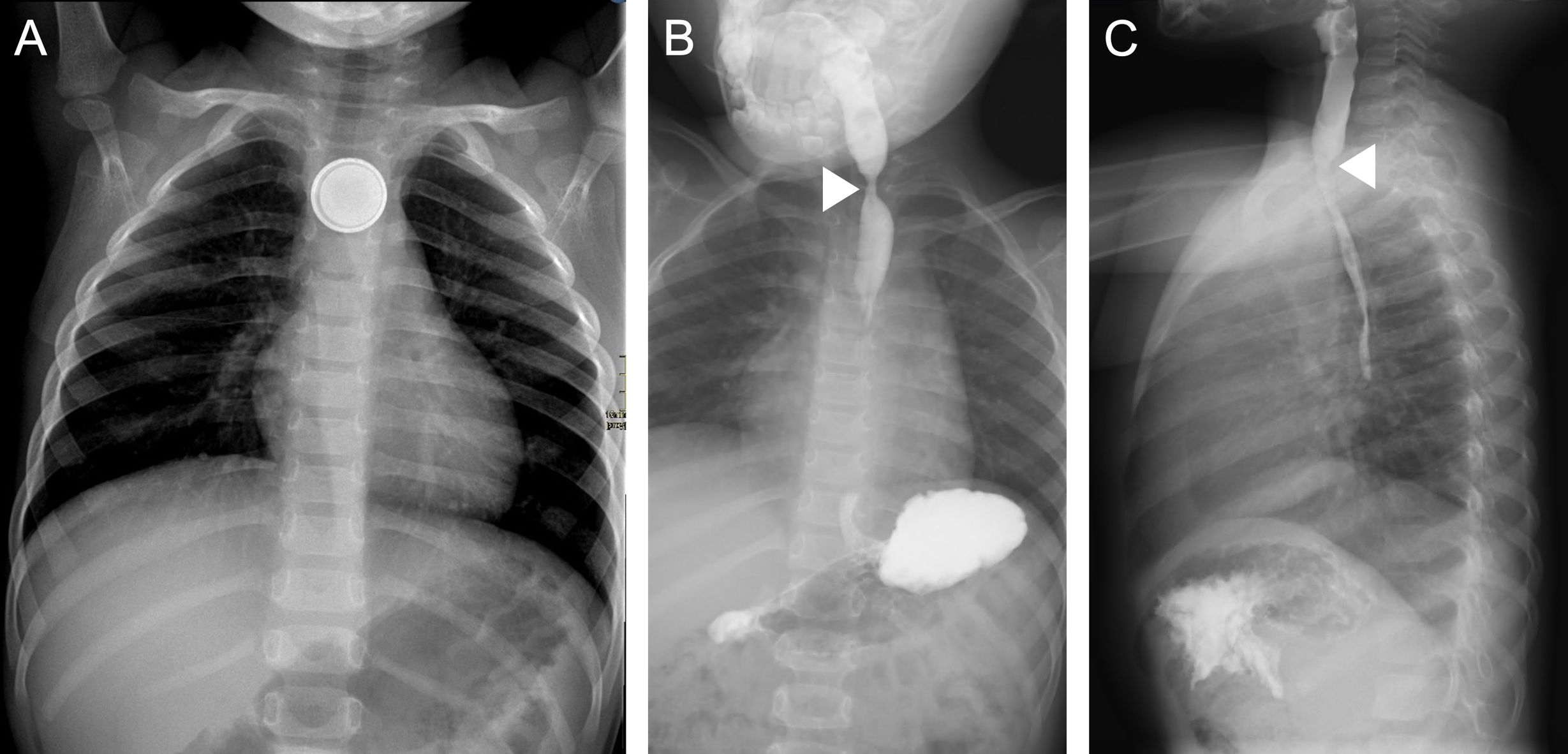
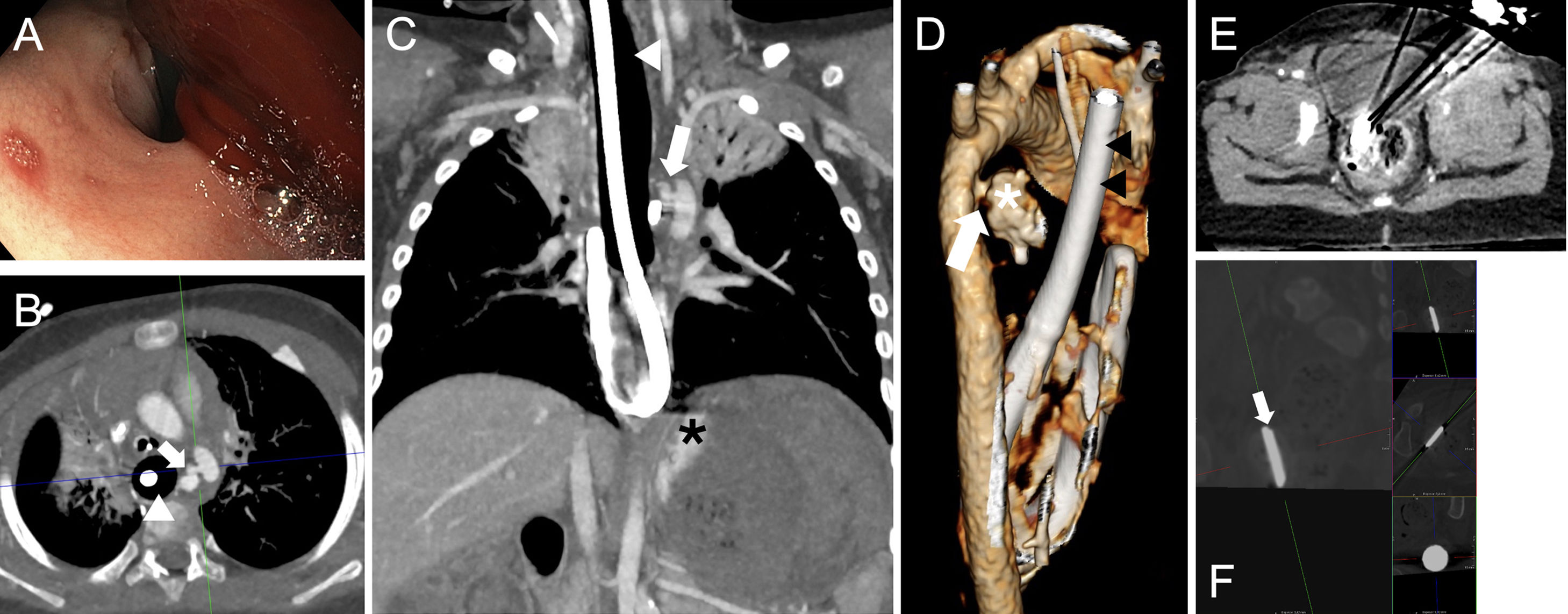
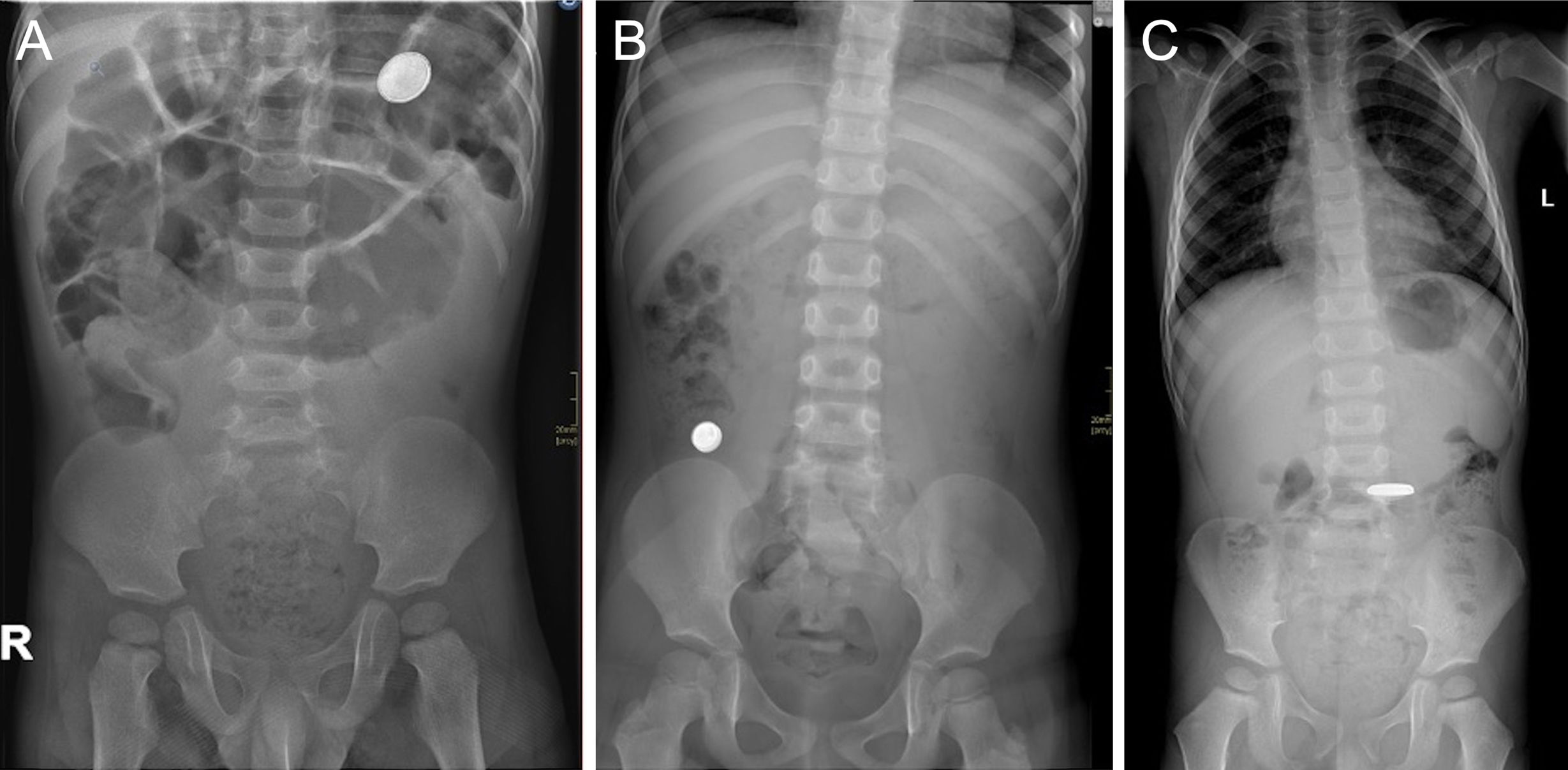
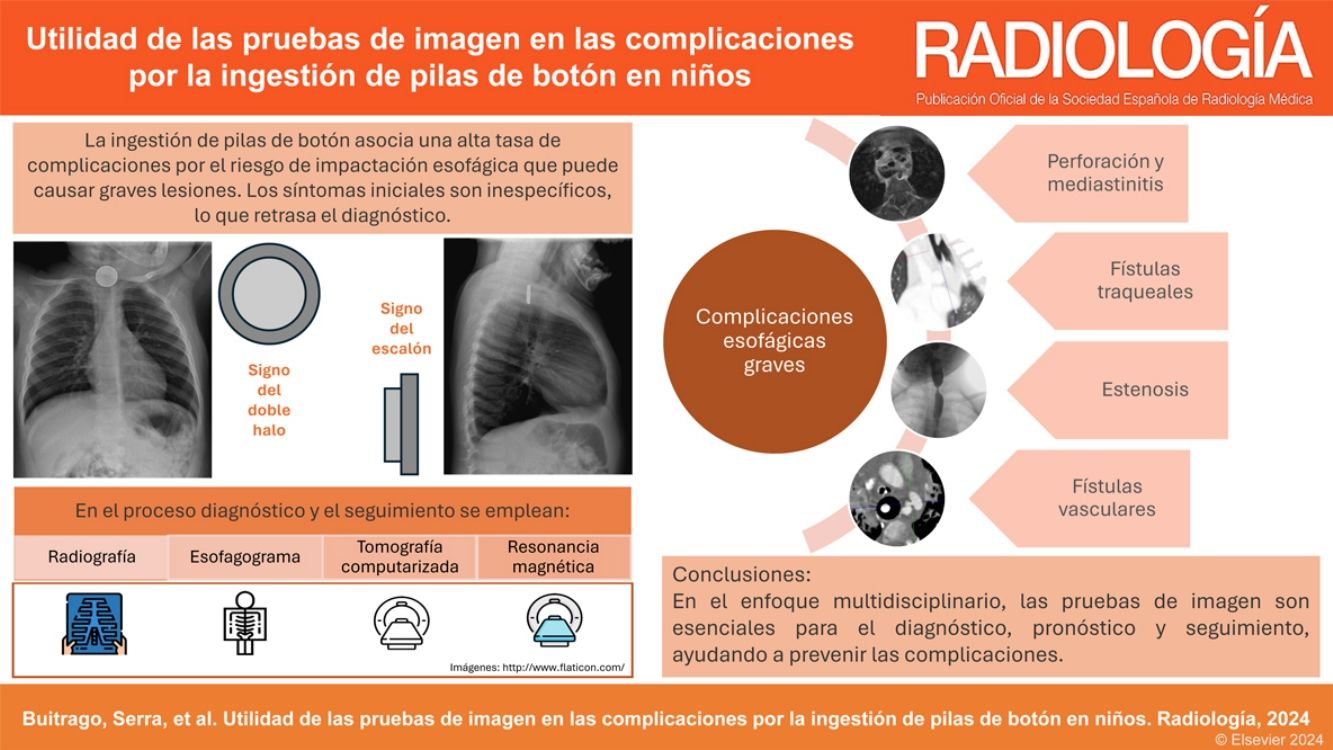
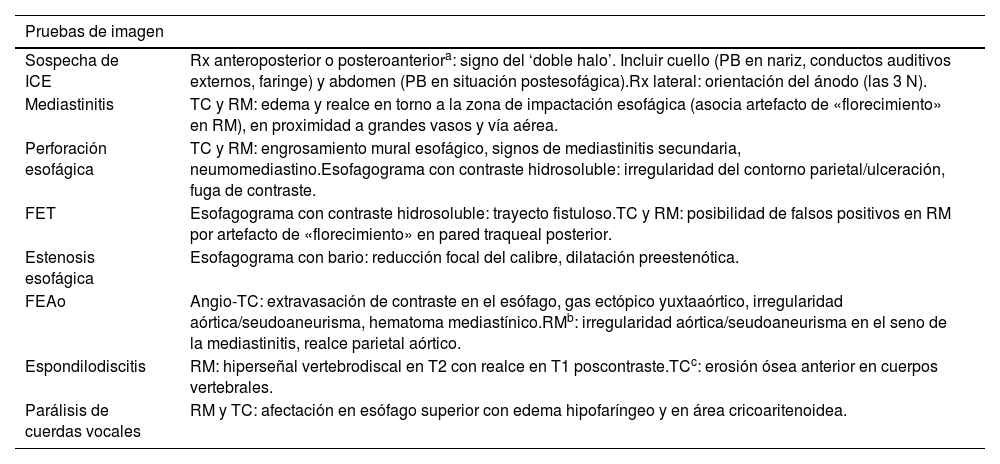
La ingestión de cuerpos extraños es un problema prevalente en niños, en particular los menores de 3 años. La mayoría pasan y se eliminan por el tracto gastrointestinal sin complicaciones. Sin embargo, las pilas de botón asocian mayor tasa de complicaciones, especialmente en niños más pequeños y cuando son de mayor calibre por el riesgo de impactación esofágica que puede derivar en graves lesiones. El cuadro clínico inicial es inespecífico, lo que dificulta y retrasa el diagnóstico, y en ocasiones son los síntomas graves los que advierten de las complicaciones. En el proceso diagnóstico se emplean la radiografía, el esofagograma, la tomografía computarizada y la resonancia magnética. Las complicaciones graves incluyen perforación y estenosis esofágica, mediastinitis y fístulas traqueales o vasculares, con episodios de hemorragia digestiva de alta mortalidad. Revisamos la utilidad de las pruebas de imagen en el diagnóstico inicial, la detección de las complicaciones y el seguimiento.
The ingestion of foreign bodies is a common issue among children, especially those under the age of three. Most pass through the gastrointestinal tract without any complications. However, button batteries are associated with a higher risk of complications, particularly in infants or when batteries are larger, due to the risk of oesophageal impaction, which can cause severe injuries. The initial clinical presentation is ambiguous, delaying and complicating diagnosis. There are times when complications are only suspected after symptoms become severe. Radiography, oesophagography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance are used in the diagnostic process. Oesophageal perforation or stenosis, mediastinitis, and tracheal or vascular fistulas are among the most serious complications. Episodes of gastrointestinal bleeding are associated with high death rates. This article examines the usefulness of imaging tests in the initial diagnosis, complication detection and follow-up.