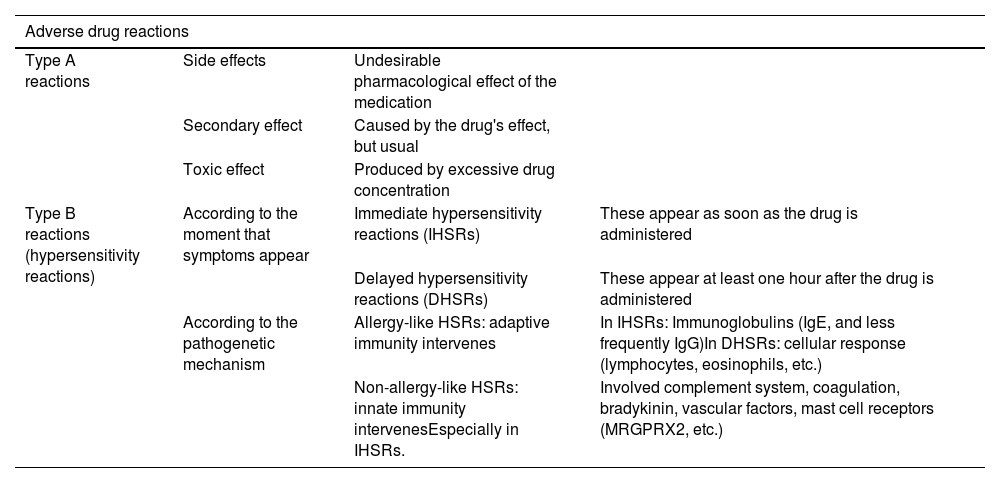
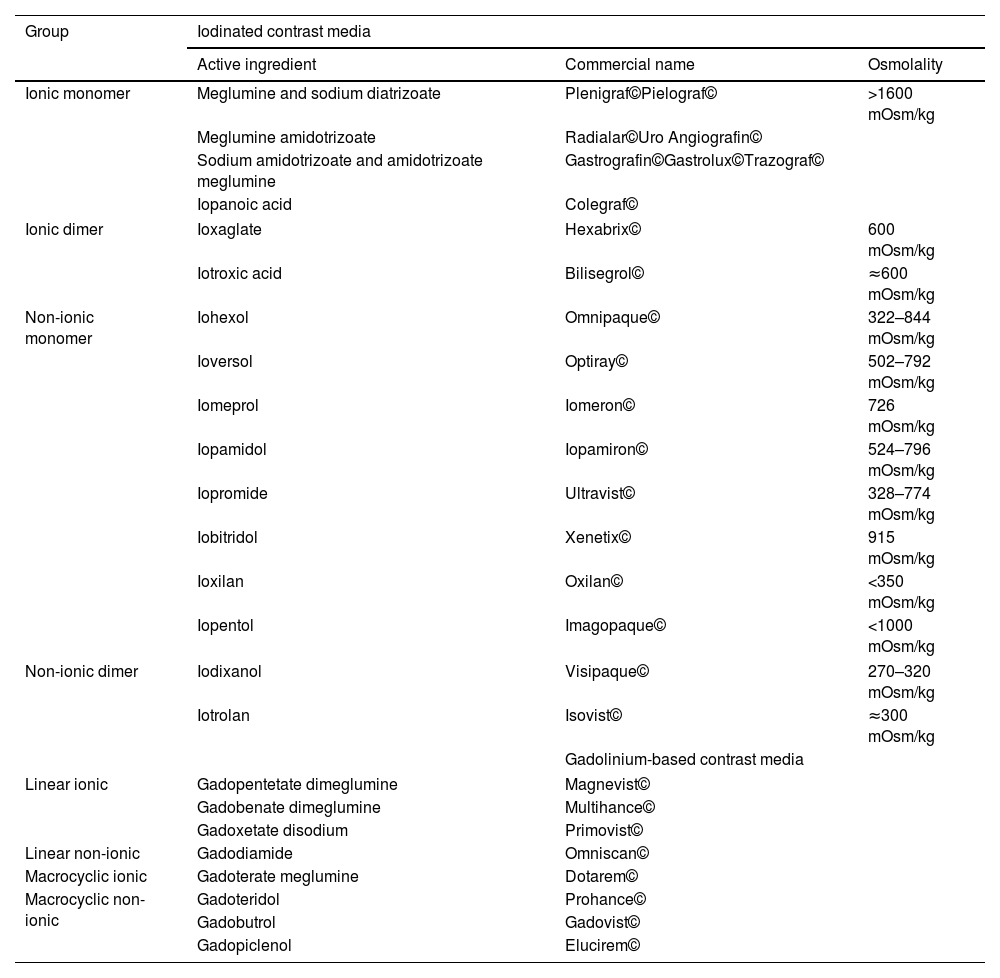
Radiological contrast media, both iodinated and gadolinium-based, can lead to adverse reactions. Type A reactions are related to the pharmacological characteristics of the contrast, including side, secondary and toxic effects. Post-contrast acute kidney injury is the most frequent adverse reaction to iodinated contrast media. Less frequently, thyroid, neurological, cardiovascular, haematological, and salivary gland effects are also detected. With gadolinium-based contrast agents, nausea is the most frequent reaction, but there is also a risk of producing nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and cerebral deposits of uncertain significance.
The most effective way of avoiding type A reactions is to decrease the dose and frequency of contrast media administration, especially in patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency. To prevent post-contrast acute kidney injury, adequate hydration of the patient should be maintained orally or intravenously, avoiding prolonged periods of liquid fasting.
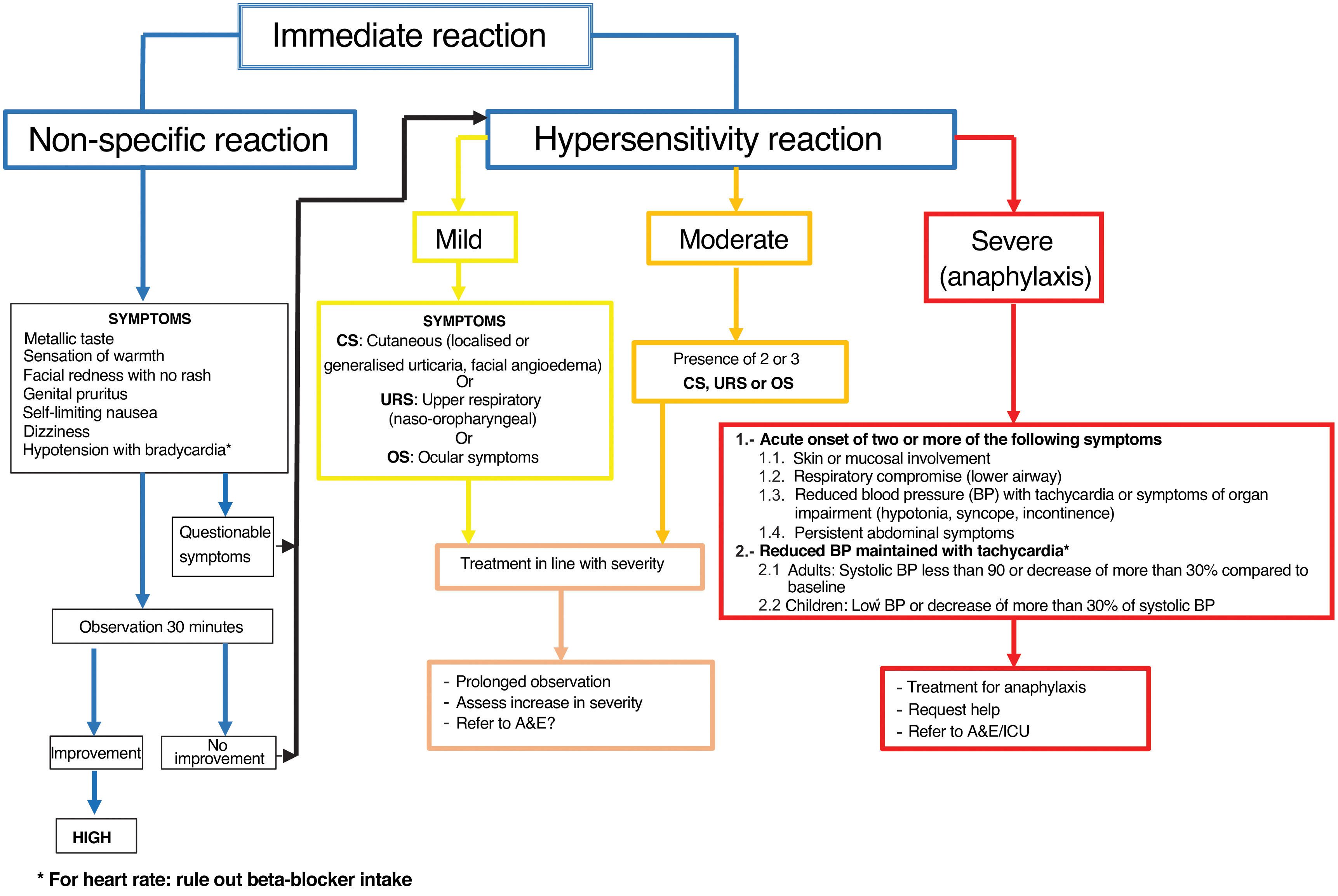
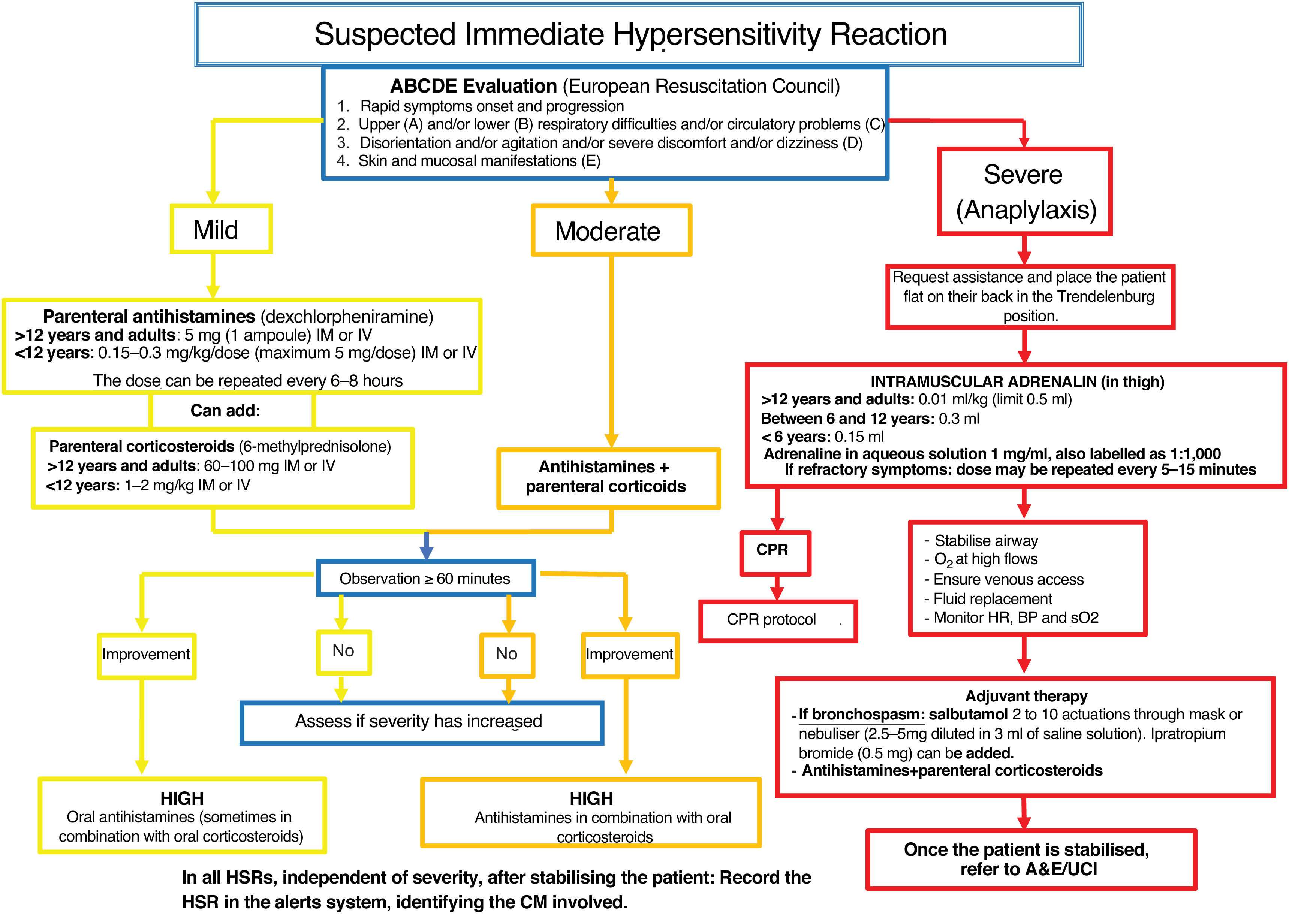
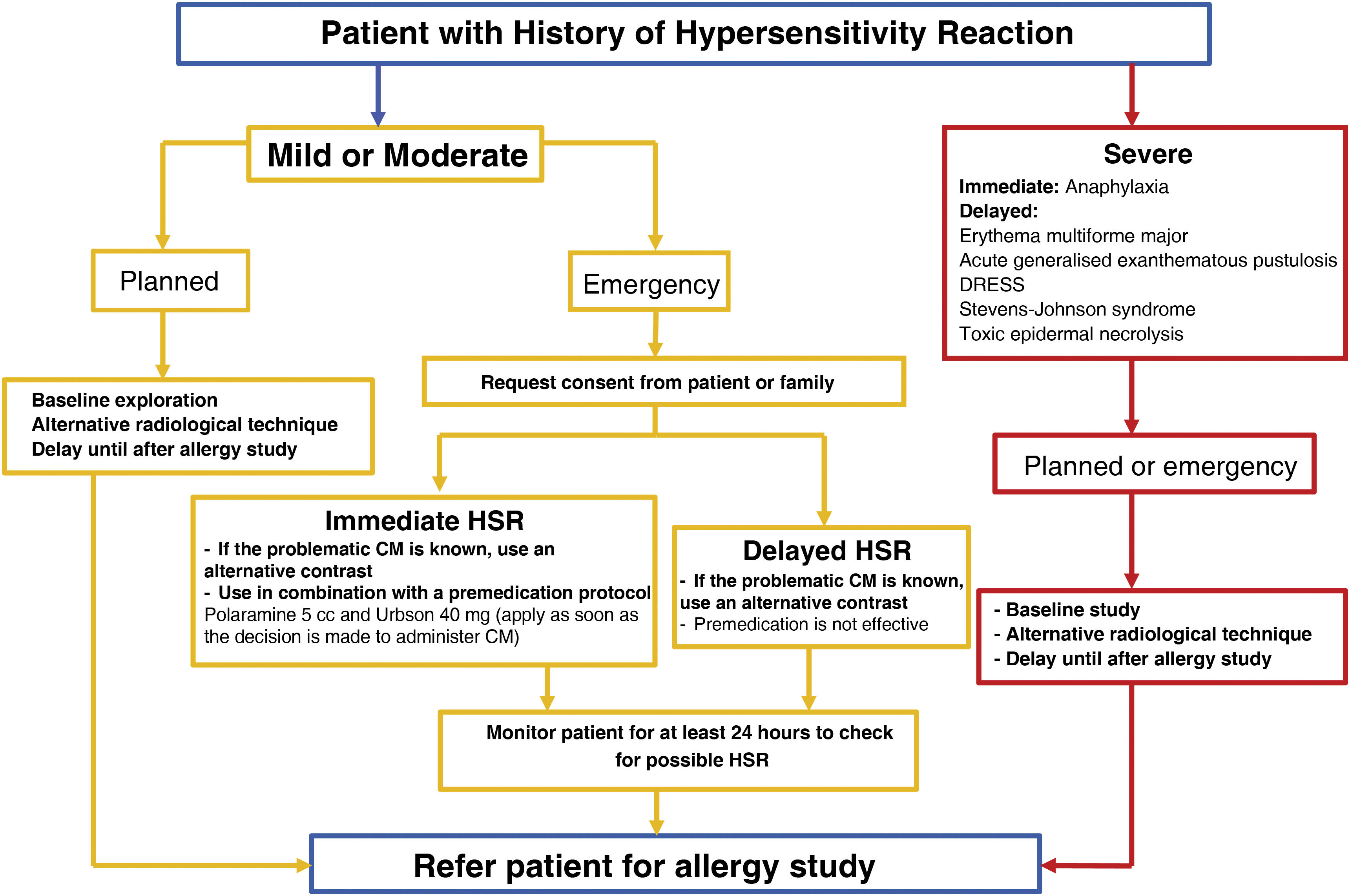
On the other hand, hypersensitivity reactions are dose-independent and clinically can range from mild cutaneous reactions to anaphylaxis. This article proposes an algorithm that differentiates between nonspecific reactions and true hypersensitivity reactions, as well as levels of severity. It also provides a treatment scheme for immediate reactions adjusted to the severity level, with a focus on the management of anaphylaxis and an early intramuscular administration of adrenaline. Finally, it sets out recommendations for the management of patients with previous hypersensitivity reactions who require elective or urgent contrast administration, favouring the use of alternative contrast media with confirmed tolerance instead of the indiscriminate use of premedication.
Los medios de contraste radiológicos, tanto los yodados como los de gadolinio pueden inducir reacciones adversas. Las reacciones tipo A están relacionadas con las características farmacológicas del contraste, incluyendo los efectos colaterales, los secundarios y los tóxicos. En el caso de los contrastes yodados, la lesión renal aguda post-contraste es la afectación más frecuente. Con menor frecuencia se pueden inducir efectos a nivel tiroideo, neurológico, cardiovascular, hematológico y de glándula salivares. Con los contrastes de gadolinio la reacción más frecuente es la aparición de náuseas, existiendo riesgo de producir fibrosis sistémica nefrogénica y depósitos cerebrales de significado incierto.
La medida más eficaz para evitar las reacciones tipo A es disminuir la dosis y la frecuencia de administración del contraste, especialmente en pacientes con insuficiencia renal previa. Para prevenir la lesión renal aguda post-contraste debemos mantener una hidratación adecuada del paciente por vía oral o parenteral, evitando periodos de ayuno de líquidos prolongados.
Por otra parte, las reacciones de hipersensibilidad son independientes de dosis y clínicamente pueden presentarse desde un cuadro cutáneo leve hasta una anafilaxia. En el artículo se propone un algoritmo que permitiría diferenciar una reacción inespecífica de una verdadera reacción de hipersensibilidad, así como identificar su gravedad. Asimismo, se plantea un esquema de tratamiento de las reacciones inmediatas ajustado al nivel de gravedad, incidiendo en el manejo de la anafilaxia y la administración precoz de adrenalina intramuscular. Finalmente, se detallan recomendaciones sobre el manejo de los pacientes con reacciones de hipersensibilidad previa que precisan la administración de un contraste de forma electiva o urgente, favoreciendo el uso de contrastes alternativos con tolerancia confirmada en lugar del uso indiscriminado de la premedicación.