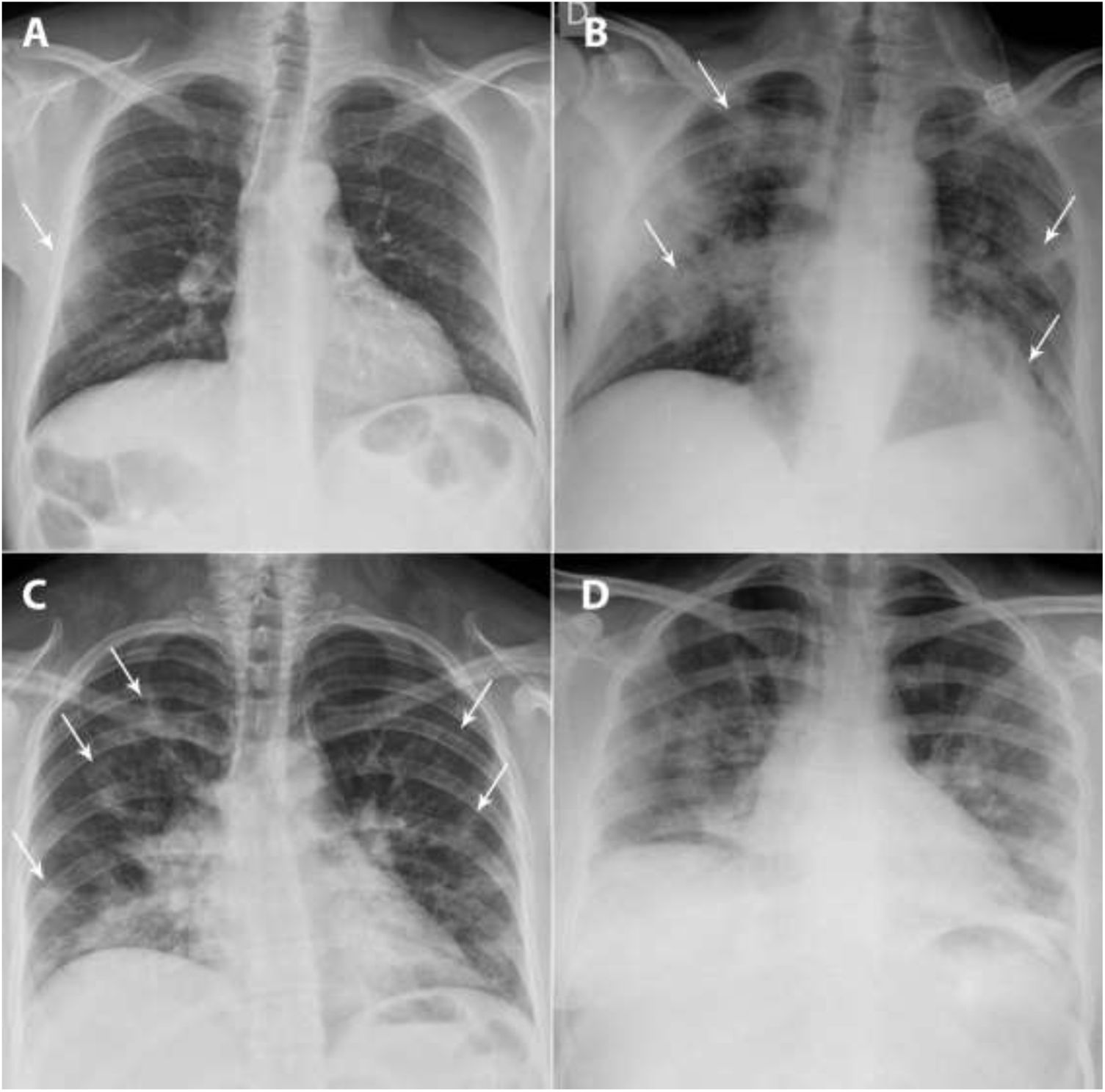
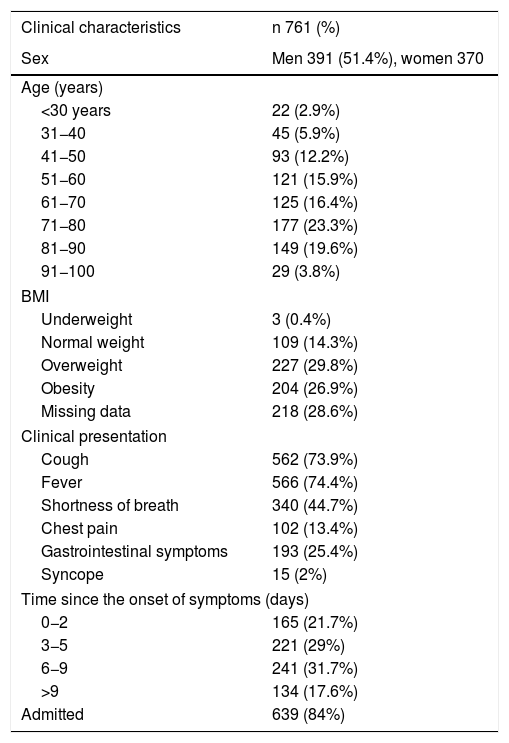
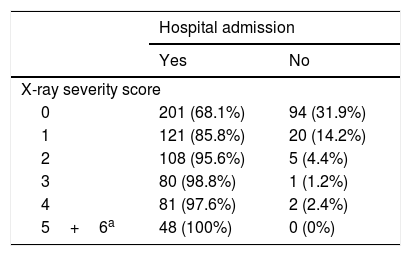
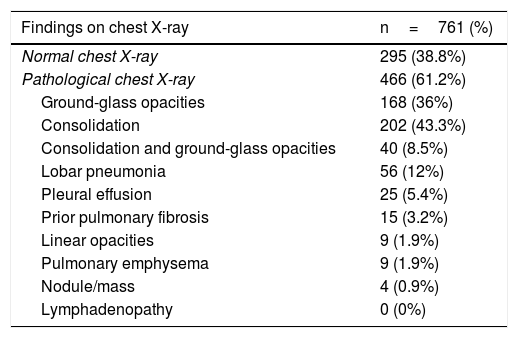
To analyze the initial findings in chest X-rays of patients with RT-PCR positive for SARS-CoV-2, and to determine whether there is a relationship between the severity of these findings and the clinical and laboratory findings.
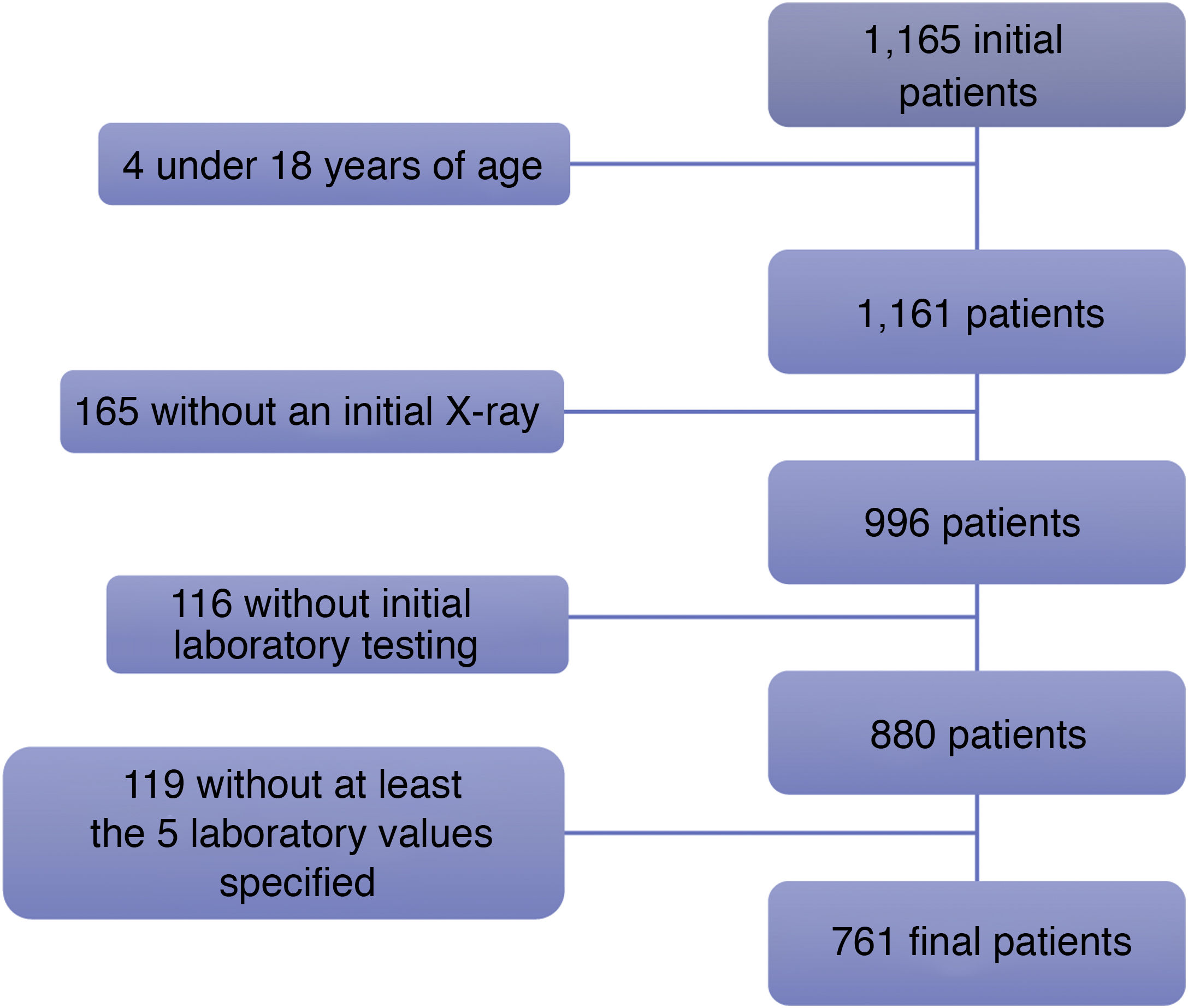
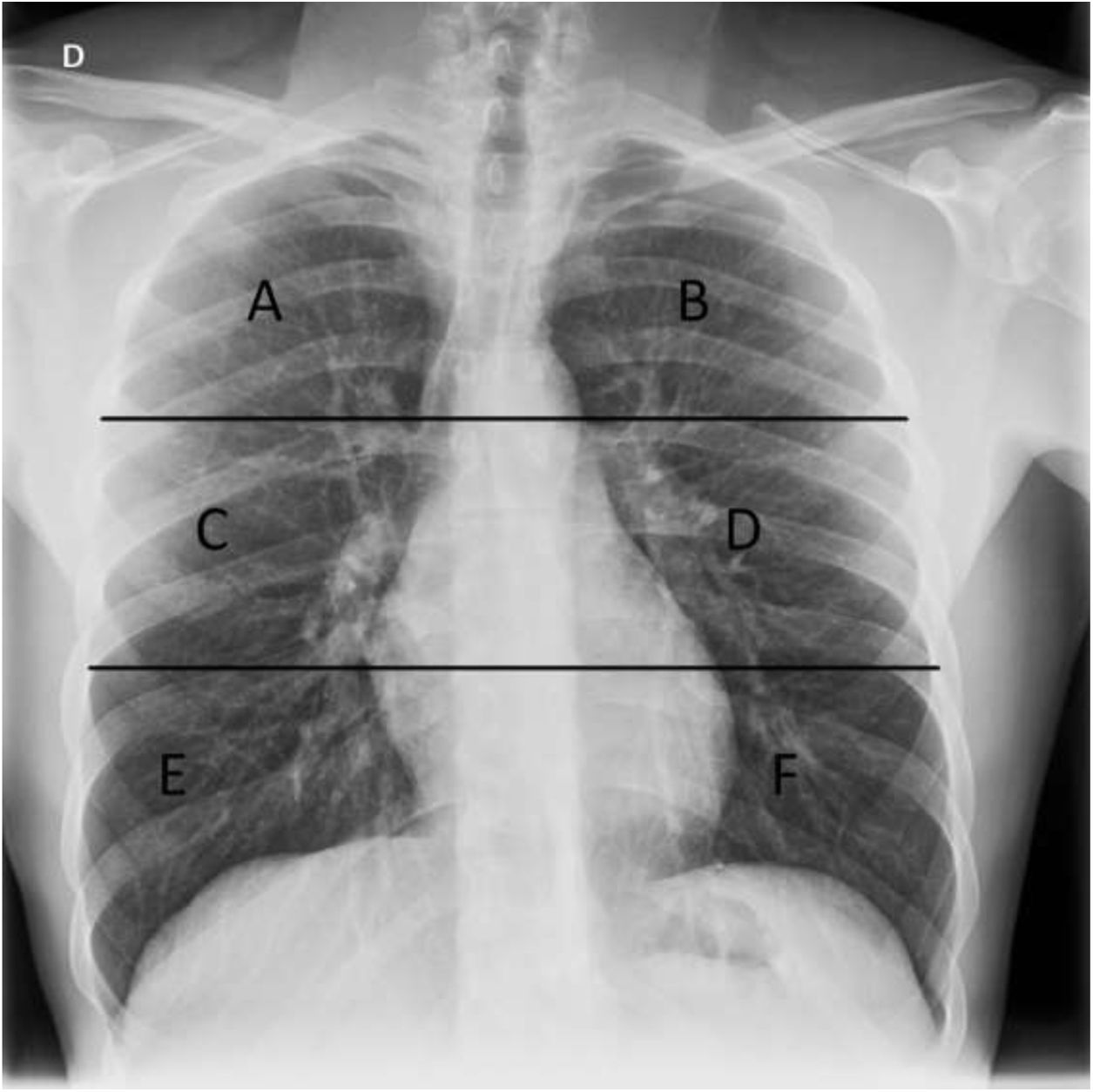
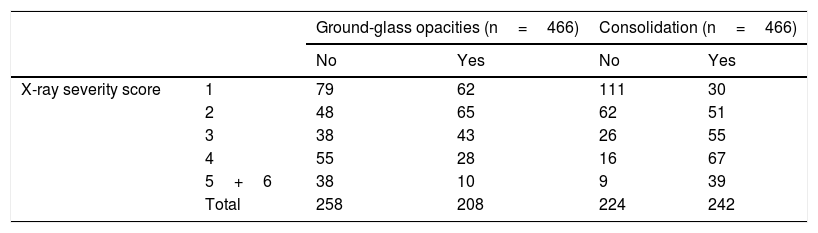
Materials and methodsThis retrospective study analyzed the relationship between initial chest X-rays and initial laboratory tests in symptomatic adults with nasopharyngeal RT-PCR results positive for SARS-CoV-2 seen at our center between February 29 and March 23, 2020. Among other radiologic findings, we analyzed ground-glass opacities, consolidations, linear opacities, and pleural effusion. We also used a scale of radiologic severity to assess the distribution and extent of these findings. Among initial laboratory findings, we analyzed leukocytes, lymphocytes, platelets, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and C-reactive protein.
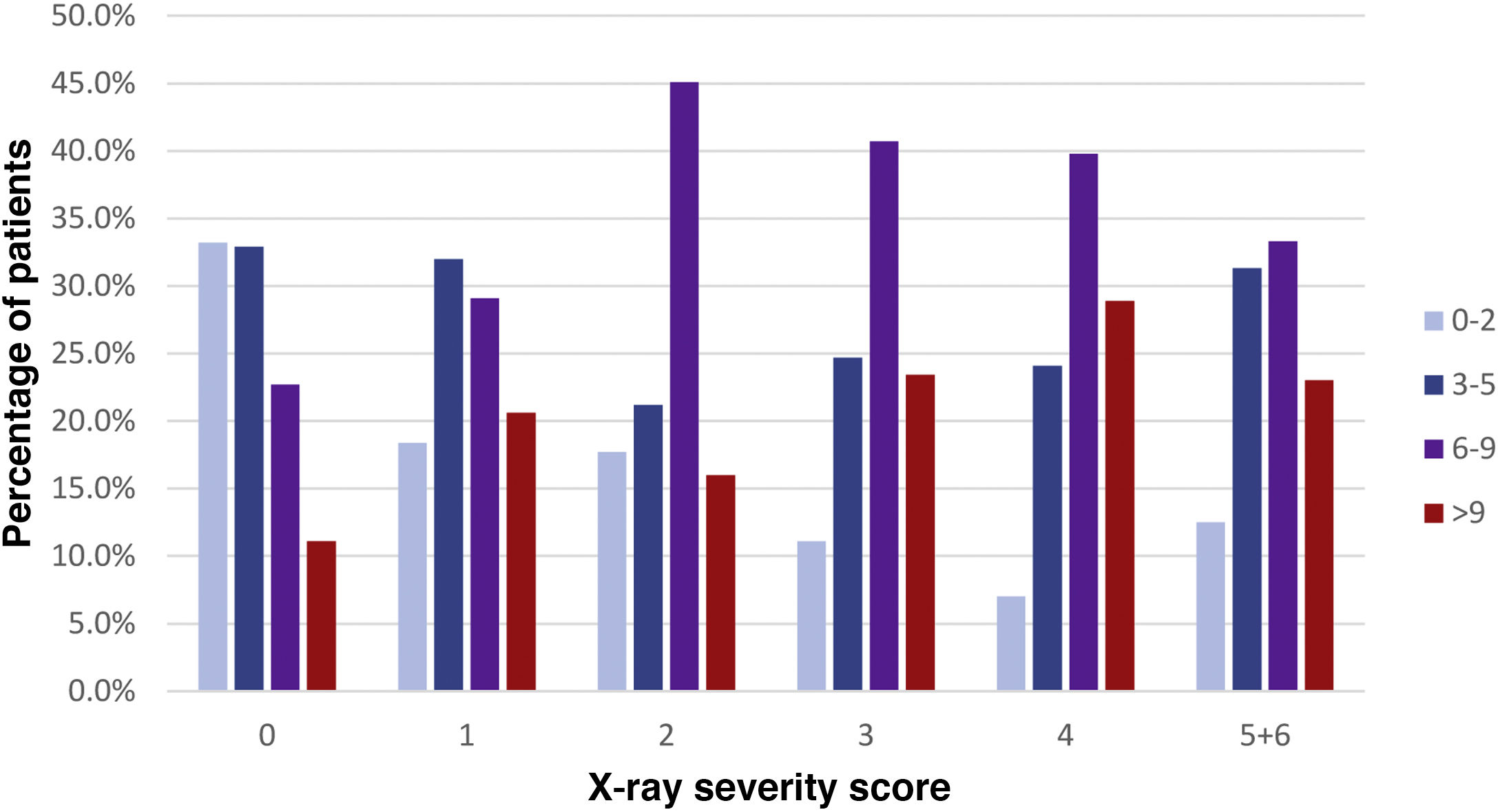
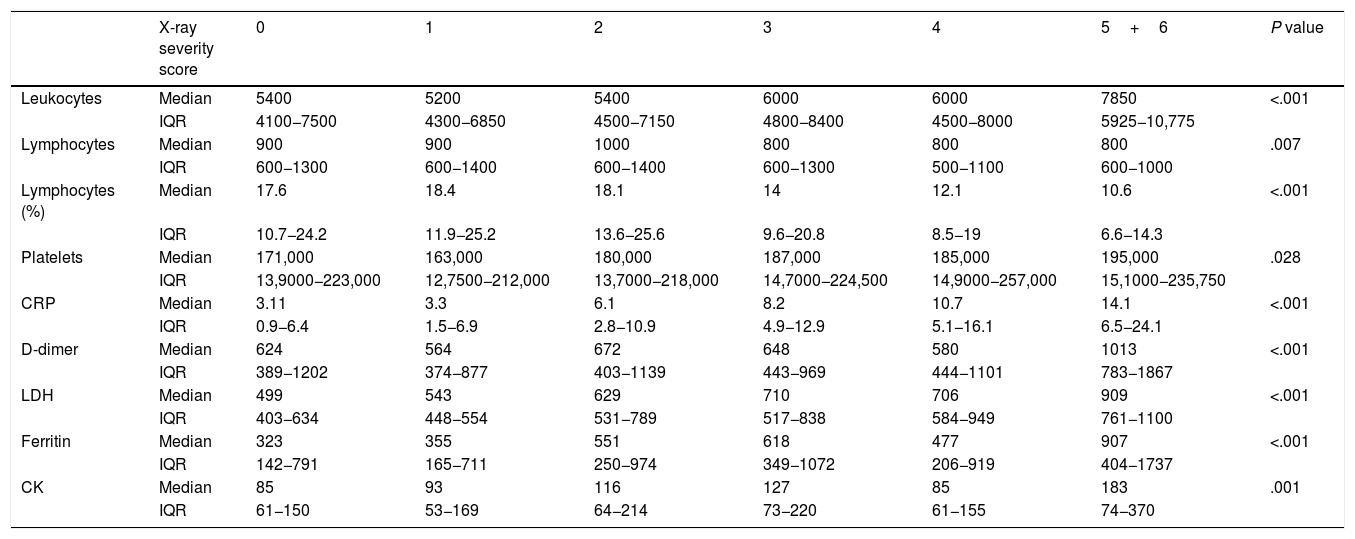
ResultsOf 761 symptomatic patients, 639 (84%) required hospitalization and 122 were discharged to their homes. The need for admission increased with increasing scores on the scale of radiologic severity. The extent of initial lung involvement was significantly associated with the laboratory parameters analyzed (P<.05 for platelets, P<.01 for lymphocytes, and P<.001 for the remaining parameters), as well as with the time from the onset of symptoms (P<.001).
ConclusionIt can be useful to use a scale of radiologic severity to classify chest X-ray findings in diagnosing patients with COVID-19, because the greater the radiologic severity, the greater the need for hospitalization and the greater the alteration in laboratory parameters.
Analizar los hallazgos radiológicos iniciales en las radiografías de tórax de pacientes con RT-PCR positiva para SARS-CoV-2 y valorar si existe una relación entre la graduación de los mismos y los datos clínicos y analíticos.
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo donde se analizaron las radiografías de tórax iniciales de pacientes adultos sintomáticos entre el 29 de febrero y el 23 de marzo de 2020 con una prueba RT-PCR nasofaríngea positiva para SARS-CoV-2 y una analítica inicial que incluía: leucocitos, linfocitos, plaquetas, cociente linfocitos/leucocitos y PCR. Entre otros hallazgos radiológicos se valoraron: opacidades en vidrio deslustrado, consolidaciones, opacidades lineales y derrame pleural. También la distribución y la extensión de estos hallazgos mediante un índice de gravedad radiográfico.
ResultadosDe 761 pacientes sintomáticos, 639 precisaron ingreso hospitalario (84%) y 122 fueron dados de alta con aislamiento domiciliario. La necesidad de ingreso fue mayor cuanto más alto el índice de gravedad radiográfico. Existió una relación estadísticamente significativa entre la extensión de la afectación pulmonar inicial y los parámetros analíticos estudiados (P<,05 para plaquetas, P<,01 para linfocitos y P<,001 para el resto), así como con los días de evolución desde el inicio de los síntomas (P<,001).
ConclusiónLa graduación de los hallazgos radiológicos al diagnóstico y su relación con los datos analíticos podría ser útil a la hora de valorar la evolución de pacientes con COVID-19, pues a mayor índice de gravedad radiográfico, mayor incidencia de ingreso hospitalario y parámetros analíticos más alterados.