To analyse the efficacy of the procedure for withdrawing an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter and the clinical and radiological factors associated with difficult withdrawal.
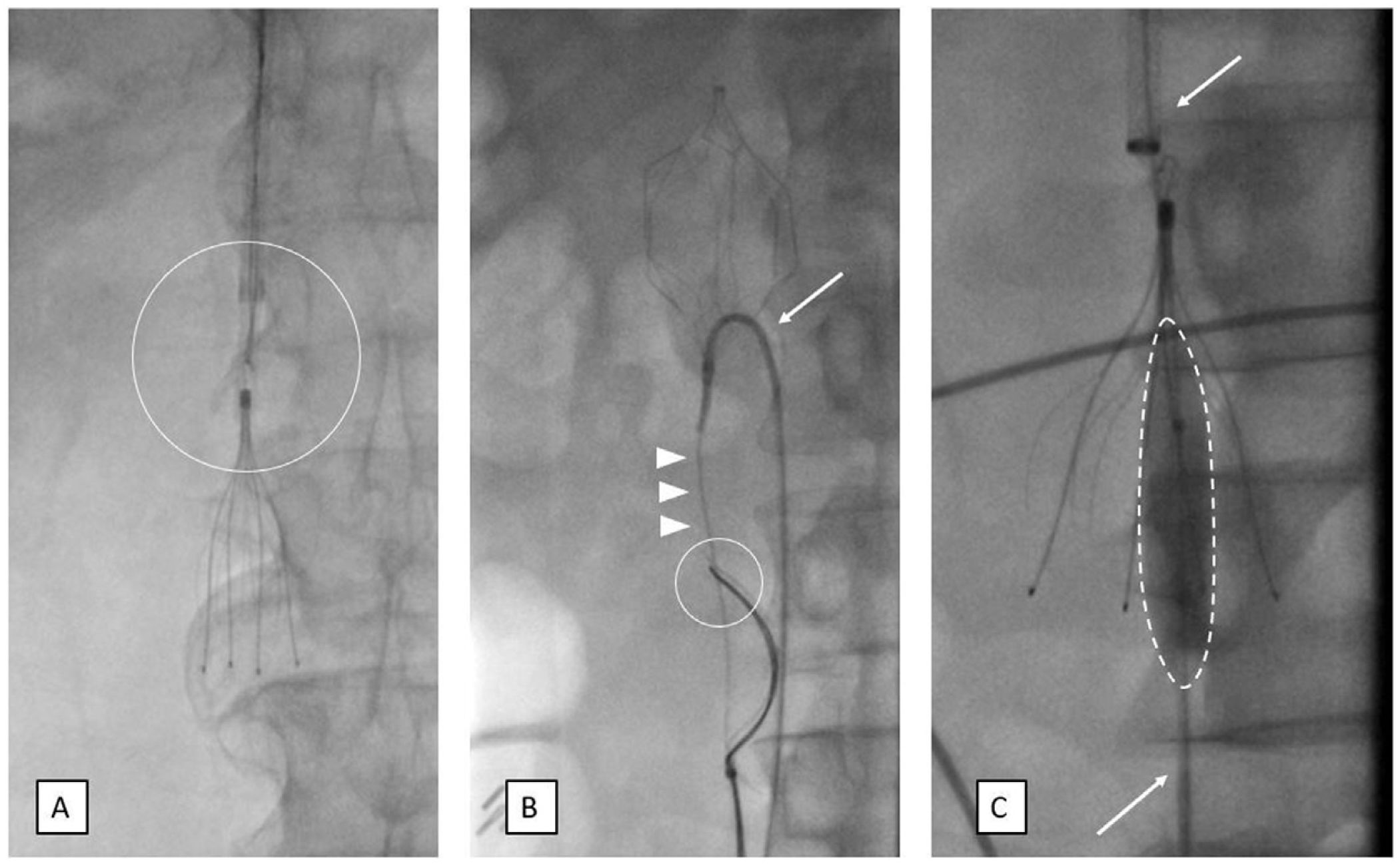
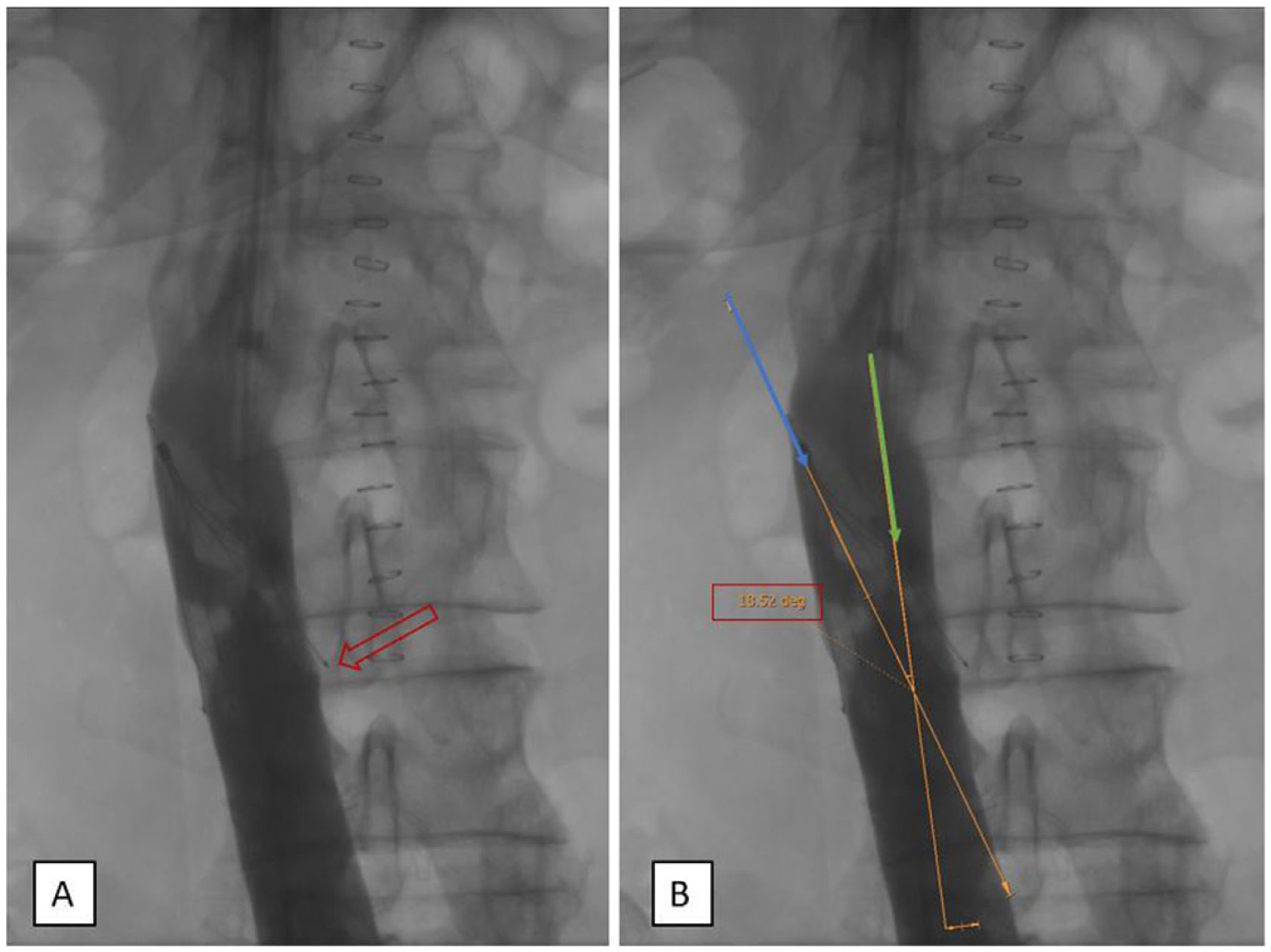
Material and methodsThis retrospective observational study included patients who underwent IVC filter withdrawal at a single centre between May 2015 and May 2021. We recorded demographic, clinical, procedural, and radiological variables: type of IVC filter, angle with the IVC > 15°, hook against the wall, and legs embedded in the IVC wall > 3 mm. The efficacy variables were fluoroscopy time, success of IVC filter withdrawal, and number of attempts to withdraw the filter. The safety variables were complications, surgical removal, and mortality. The main variable was difficult withdrawal, defined as more than 5 min fluoroscopy or more than 1 attempt at withdrawal.
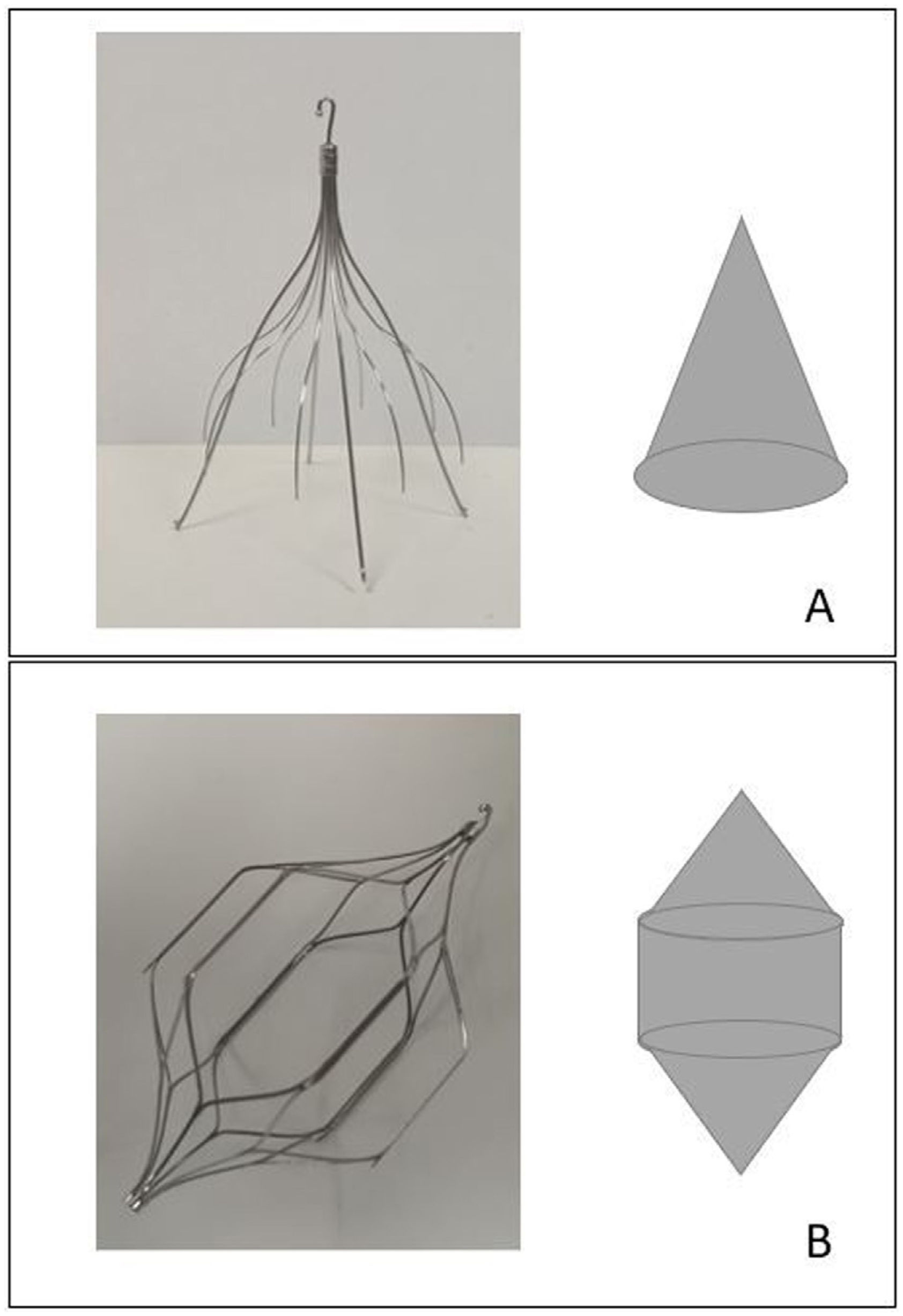
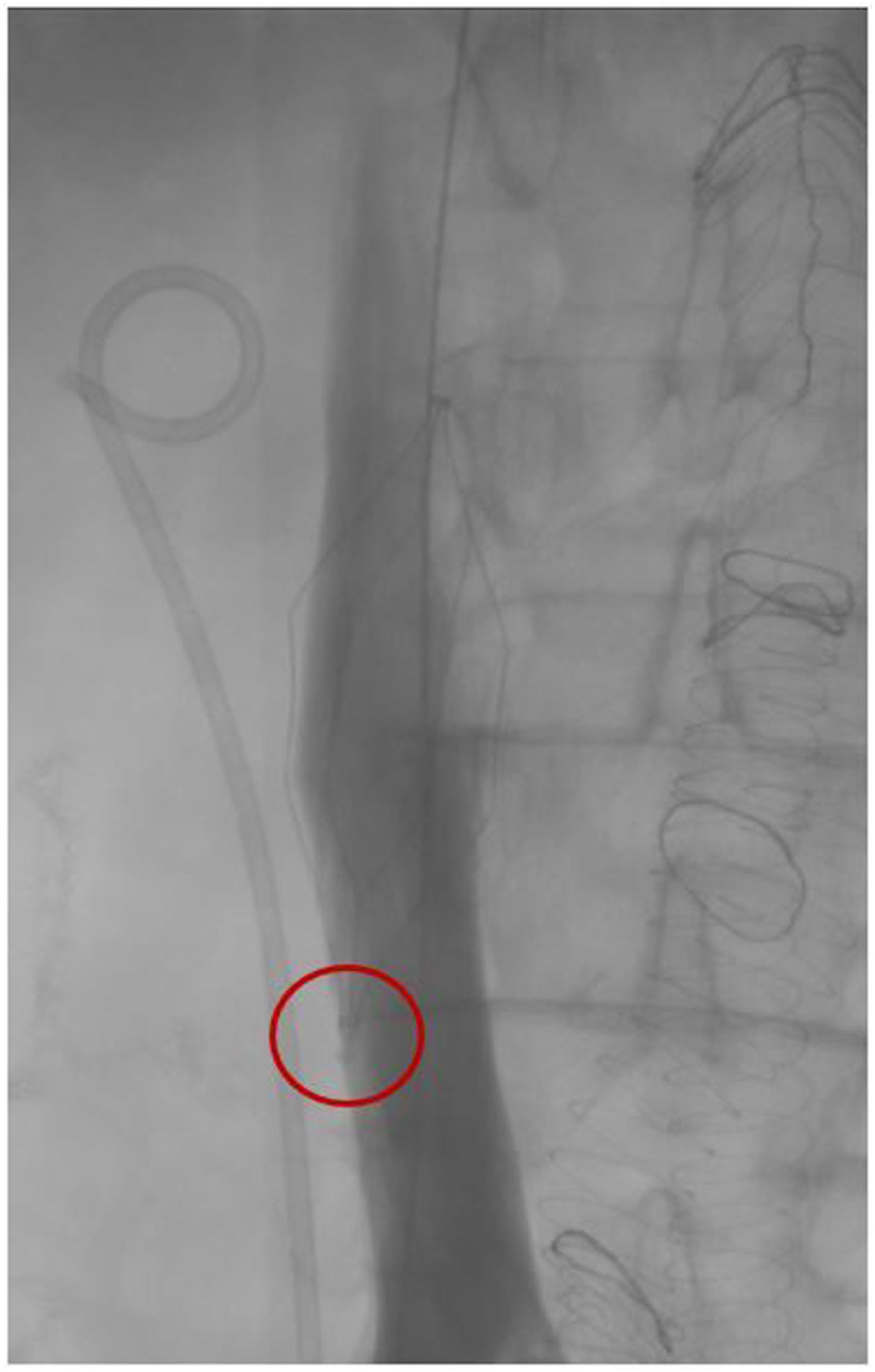
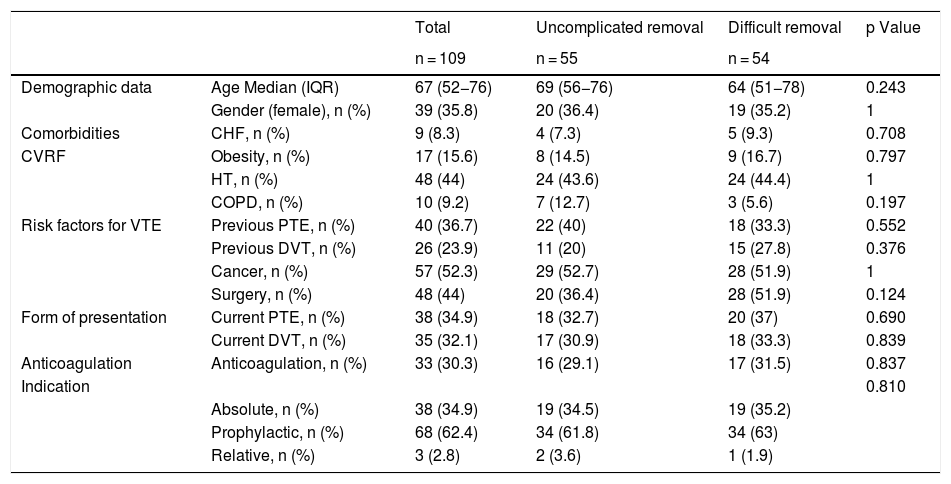
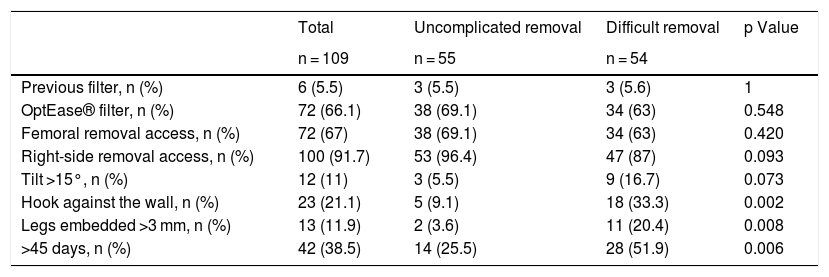
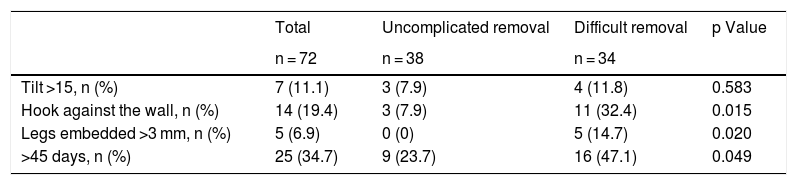
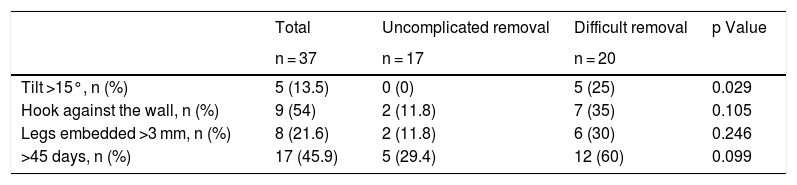
ResultsA total of 109 patients were included; withdrawal was considered difficult in 54 (49.5%). Three radiological variables were more common in the difficult withdrawal group: hook against the wall (33.3% vs. 9.1%; p = 0.027), embedded legs (20.4% vs. 3.6%; p = 0.008), and >45 days since IVC filter placement (51.9% vs. 25.5%; p = 0.006). These variables remained significant in the subgroup of patients with OptEase IVC filters; however, in the group of patients with Celect IVC filters, only the inclination of the IVC filter >15 ° was significantly associated with difficult withdrawal (25% vs 0%; p = 0.029).
ConclusionDifficult withdrawal was associated with time from IVC placement, embedded legs, and contact between the hook and the wall. The analysis of the subgroups of patients with different types of IVC filters found that these variables remained significant in those with OptEase filters; however, in those with cone-shaped devices (Celect), the inclination of the IVC filter >15° was significantly associated with difficult withdrawal.
Analizar la eficacia del procedimiento de retirada de filtro de vena cava inferior (FVCI), así como los factores clínico-radiológicos asociados a retirada difícil.
Material y métodoEstudio retrospectivo, observacional y unicéntrico de pacientes tratados mediante retirada de FVCI entre mayo del 2015 y mayo del 2021. Se recogieron variables clínico-demográficas, del procedimiento y radiológicas: tipo de FVCI, angulación respecto a la vena cava inferior (VCI) > 15 °, gancho contra pared y patas del dispositivo incrustadas en la pared de VCI > 3 mm. Las variables de eficacia fueron: tiempo de fluoroscopia, éxito en la retirada del FVCI y número de intentos a retirada. Como variables de seguridad: presencia de complicaciones, retirada quirúrgica y mortalidad. La variable principal fue la retirada difícil, definida como más de 5 min de fluoroscopia o más de un intento de retirada.
ResultadosSe incluyó a 109 pacientes, 54 (49,5%) fueron considerados retirada difícil. Las variables radiológicas gancho contra pared (33,3% vs. 9,1%; p = 0,027), patas incrustadas (20,4% vs. 3,6%; p = 0,008) y > 45 días desde la colocación (51,9% vs. 25,5%; p = 0,006) fueron significativamente más frecuentes en el grupo retirada difícil. Estas variables mantienen la asociación al analizar los FVCI Optease®. En los FVCI Celect® solo se asoció con retirada difícil la inclinación del FVCI > 15 ° (25% vs. 0%; p = 0,029).
ConclusiónSe ha encontrado asociación entre retirada difícil y las variables: tiempo desde colocación del FVCI, patas incrustadas y contacto del gancho con pared de VCI. Al analizar según el tipo de FVCI, estas variables se mantienen en el tipo Optease®, en cambio, la variable inclinación más de 15° dificulta la retirada de los dispositivos de morfología cónica (Celect®).