To assess image quality and radiation dose in computed tomography (CT) studies of the petrous bone done with a scanner using a tin filter, high-resolution detectors, and iterative reconstruction, and to compare versus in studies done with another scanner without a tin filter using filtered back projection reconstruction.
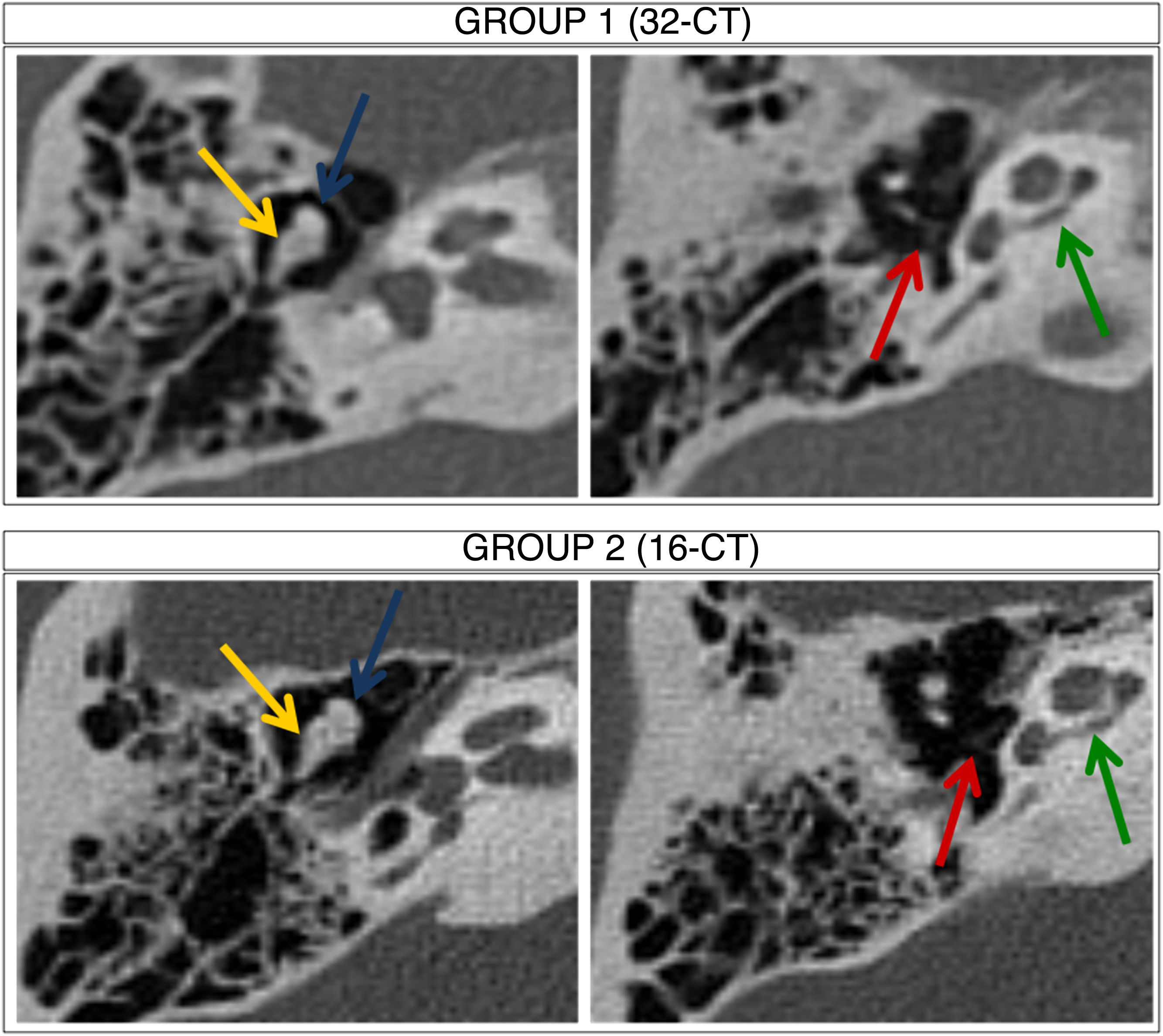
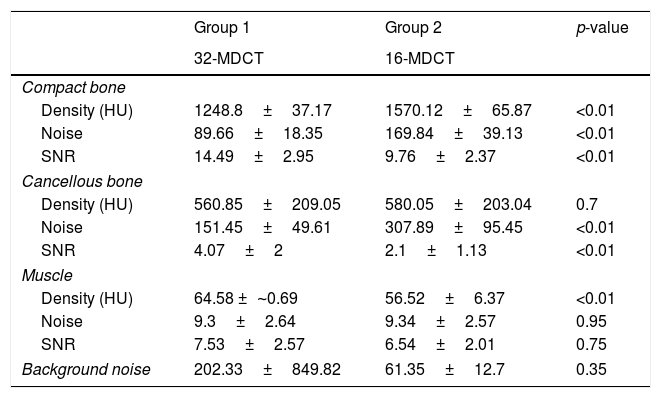
Material and methodsThirty two patients (group 1) were acquired with an ultra-low dose CT (32-MDCT, 130kV, tin filter and iterative reconstruction). Images and radiation doses were compared to 36 patients (group 2) acquired in a 16-MDCT (120kV and filtered back-projection). Muscle density, bone density, and background noise were measured. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was calculated. To assess image quality, two independent radiologists subjectively evaluated the visualization of the different structures of the middle and inner ear (0=not visualized, 3=perfectly identified and delimited). Interobserver agreement was calculated. Effective dose at different anatomical levels with the dose-length product was recorded.
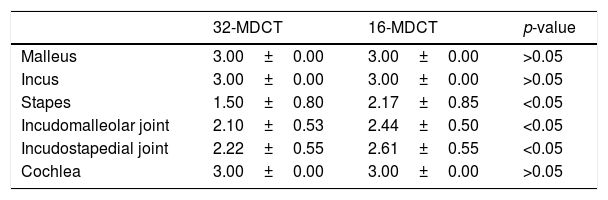
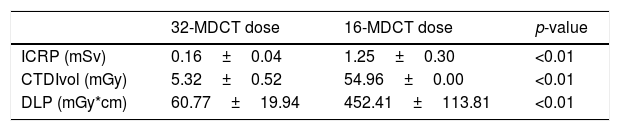
ResultsIn the quantitative analysis, there were no significant differences in image noise between the two groups. In the qualitative analysis, a similar or slightly lower subjective score was obtained in the delimitation of different structures of the ossicular chain and cochlea in the 32-MDCT, compared to 16-MDCT, with statistically significant differences. Mean effective dose (±standard deviation) was 0.16±0.04mSv for the 32-MDCT and 1.25±0.30mSv for the 16-MDCT.
ConclusionsThe use of scanners with tin filters, high-resolution detectors, and iterative reconstruction allows to obtain images with adequate quality for the evaluation of the petrous bone structures with ultralow doses of radiation (0.16±0.04mSv).
Valorar la calidad de imagen y la dosis de radiación en tomografía computarizada (TC) de peñascos adquiridos con una TC multidetector (TCMD) con filtro de estaño, detectores de alta resolución y reconstrucción iterativa, comparándola con otro equipo sin filtro de estaño y con reconstrucción por retroproyección filtrada.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron retrospectivamente 32 pacientes con TC de peñascos, realizadas con dosis ultrabaja en una 32-TCMD (130kV con filtro de estaño y reconstrucción iterativa). Se compararon con 36 estudios realizados en una 16-TCMD (120kV y retroproyección filtrada). Se cuantificó la densidad muscular, ósea y el ruido de fondo, y se calculó la relación señal/ruido. Para valorar la calidad de imagen, dos radiólogos evaluaron de forma subjetiva e independiente la visualización de las diferentes estructuras del oído (0=no se visualiza; 3=se identifica y delimita perfectamente). Se calculó el coeficiente de concordancia interobservador kappa. Utilizando un software comercial, se cuantificó a diferentes niveles anatómicos la dosis efectiva con el producto dosis-longitud.
ResultadosEn el análisis cuantitativo de las imágenes no se observaron diferencias significativas en el ruido de fondo. En el análisis cualitativo se obtuvo una puntuación subjetiva similar o ligeramente menor en la delimitación de las diferentes estructuras de la cadena osicular y cóclea en la 32-TCMD, con diferencias estadísticamente significativas. La dosis media efectiva fue de 0,16±0,04 mSv para la 32-TCMD frente a 1,25±0,30 mSv para la 16-TCMD.
ConclusionesLa utilización de equipos con filtro de estaño, detectores de alta resolución y reconstrucción iterativa permiten obtener TC con dosis de radiación ultrabaja (0,16±0,04 mSv) con una calidad de imagen adecuada para valorar las estructuras de los peñascos.