To review the prognostic usefulness of chest X-rays in selecting patients with suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection.
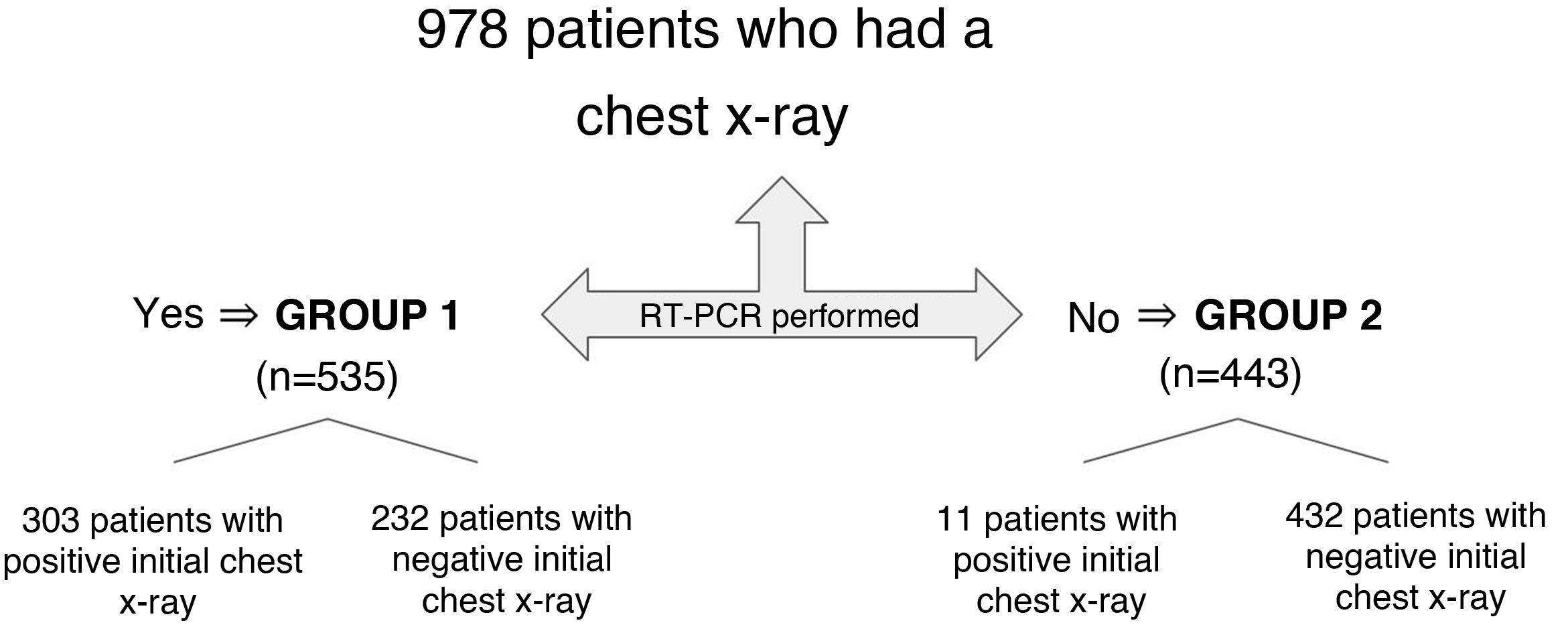
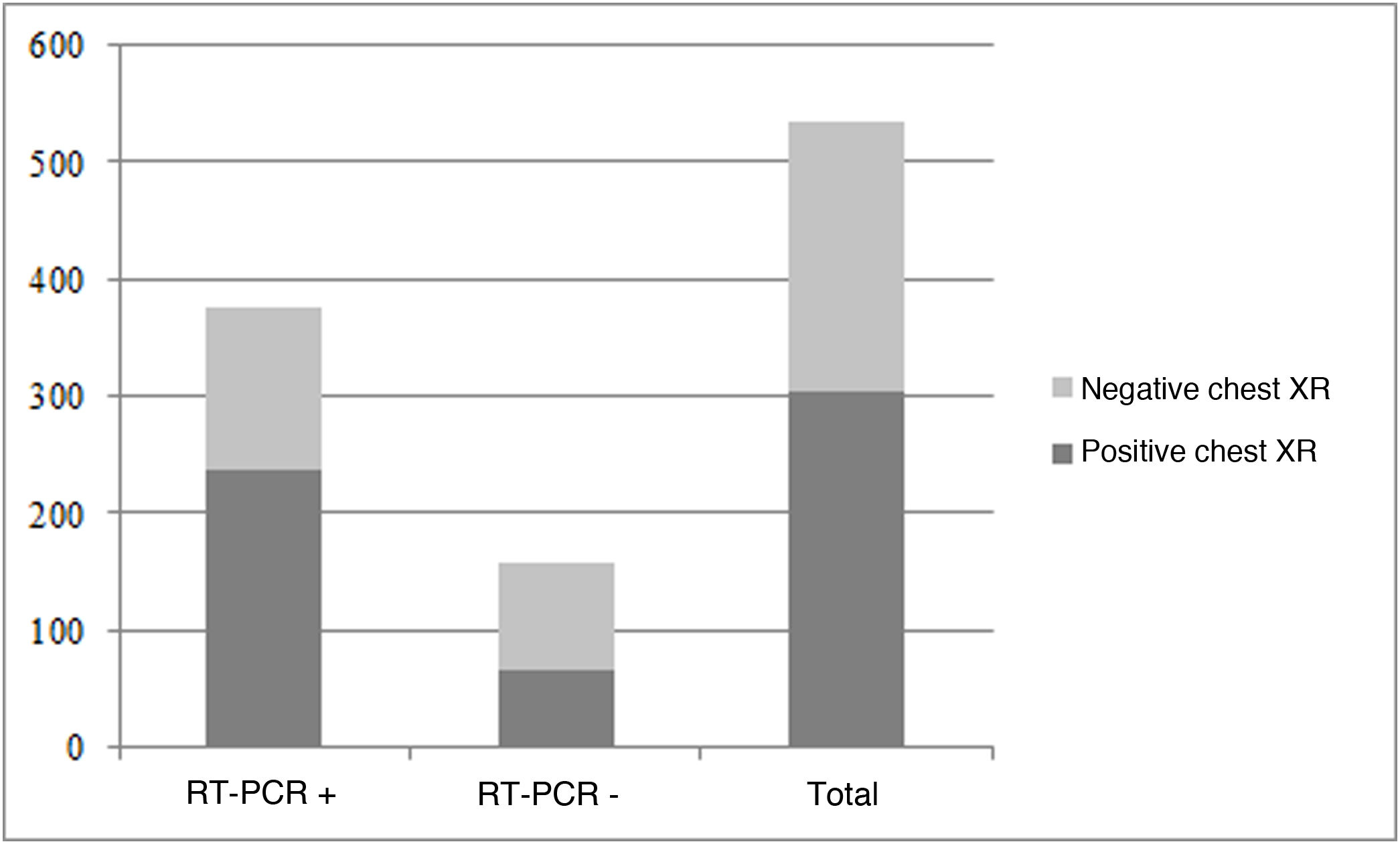
Material and methodsThis cross-sectional descriptive observational study analyzed 978 patients with suspected SARS-CoV-2 infections who underwent chest X-ray examinations in the emergency department of a tertiary hospital in March 2020. We separately analyzed demographic, clinical, and prognostic variables in two groups of patients: those in whom reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was done (n = 535) and those in whom RT-PCR was not done because of low clinical suspicion (n = 443).
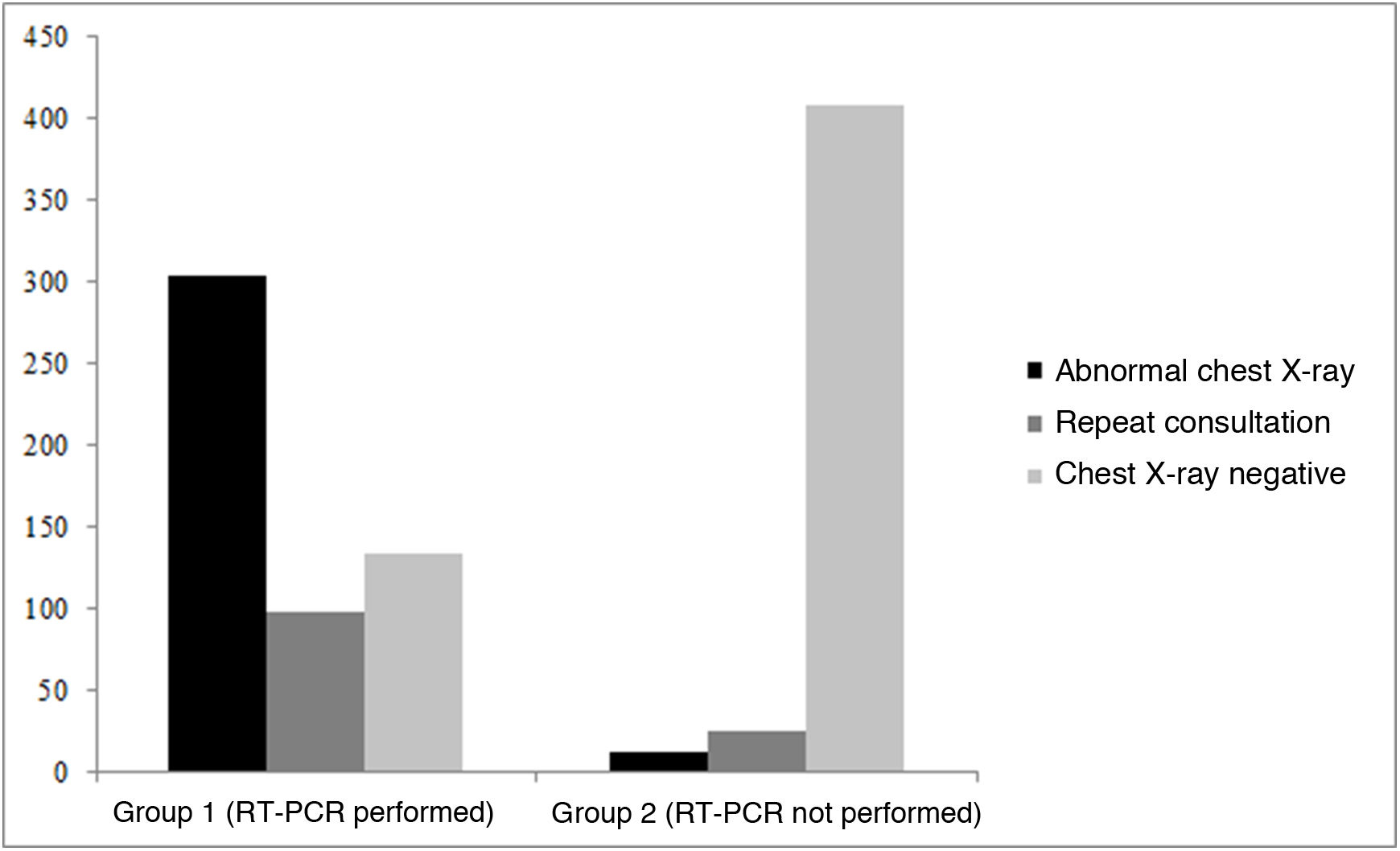
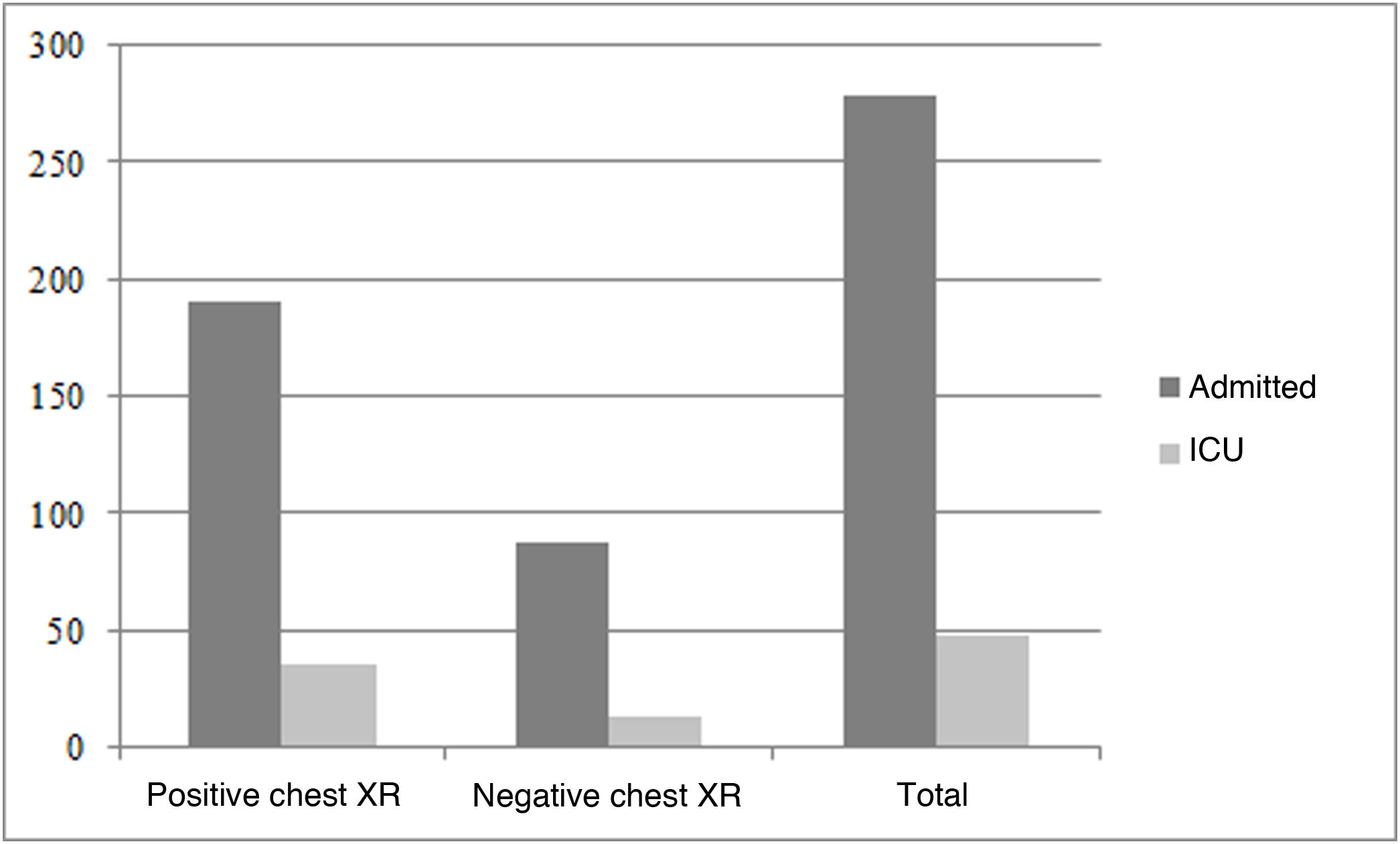
ResultsIn the group of patients with RT-PCR, the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 was 70.4%, and the sensitivity of chest X-rays was 62.8%. In the group of patients without RT-PCR, chest X-rays were negative in 97.5%, corroborating the low clinical suspicion; these patients were discharged, and 5.6% of them reconsulted with mild forms of the disease. In the group of patients with RT-PCR, we observed no statistically significant differences in the percentage of pathologic chest X-rays between patients hospitalized in the ICU (72.9%) and in those hospitalized in other wards (68.3%) (p = 0.22).
ConclusionIn the context of the pandemic, patients with low clinical suspicion and negative chest X-rays can be discharged with a low probability of reconsultation or of developing severe COVID19. In patients with RT-PCR positive for SARS-CoV-2, chest X-rays have no prognostic usefulness.
Revisar la utilidad pronóstica de la radiografía de tórax en la selección de pacientes con sospecha de infección por SARS-CoV-2.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, descriptivo y transversal, realizado en 978 pacientes con sospecha de infección por SARS-CoV-2 a los que se les hizo una radiografía de tórax en el servicio de urgencias de un hospital terciario, en marzo de 2020. Se analizaron variables demográficas, clínicas y pronósticas por separado en pacientes con RT-PCR (reacción en cadena de la polimerasa por transcriptasa inversa) hecha (grupo 1, n = 535) o no hecha por baja sospecha clínica (grupo 2, n = 443).
ResultadosEn el grupo 1 se observó una prevalencia de SARS-CoV-2 del 70,4%. La radiografía mostró una sensibilidad del 62,8%. En el grupo 2, la radiografía fue negativa en el 97,5%, corroborando la baja sospecha clínica, y fueron dados de alta; de ellos, el 5,6% volvió a consultar con formas leves de la enfermedad. En el grupo 1 no se observaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en el porcentaje de radiografías de tórax patológicas entre los pacientes ingresados en plantas hospitalarias (68,3%) y los ingresados en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (72,9%), (p = 0,22).
ConclusiónEn situación de pandemia, los pacientes con baja sospecha clínica y radiografía negativa pueden ser dados de alta con baja probabilidad de volver a consultar o de desarrollar formas graves de la enfermedad. En los pacientes con SARS-CoV-2 positivo, la radiografía de tórax inicial no tiene utilidad pronóstica.