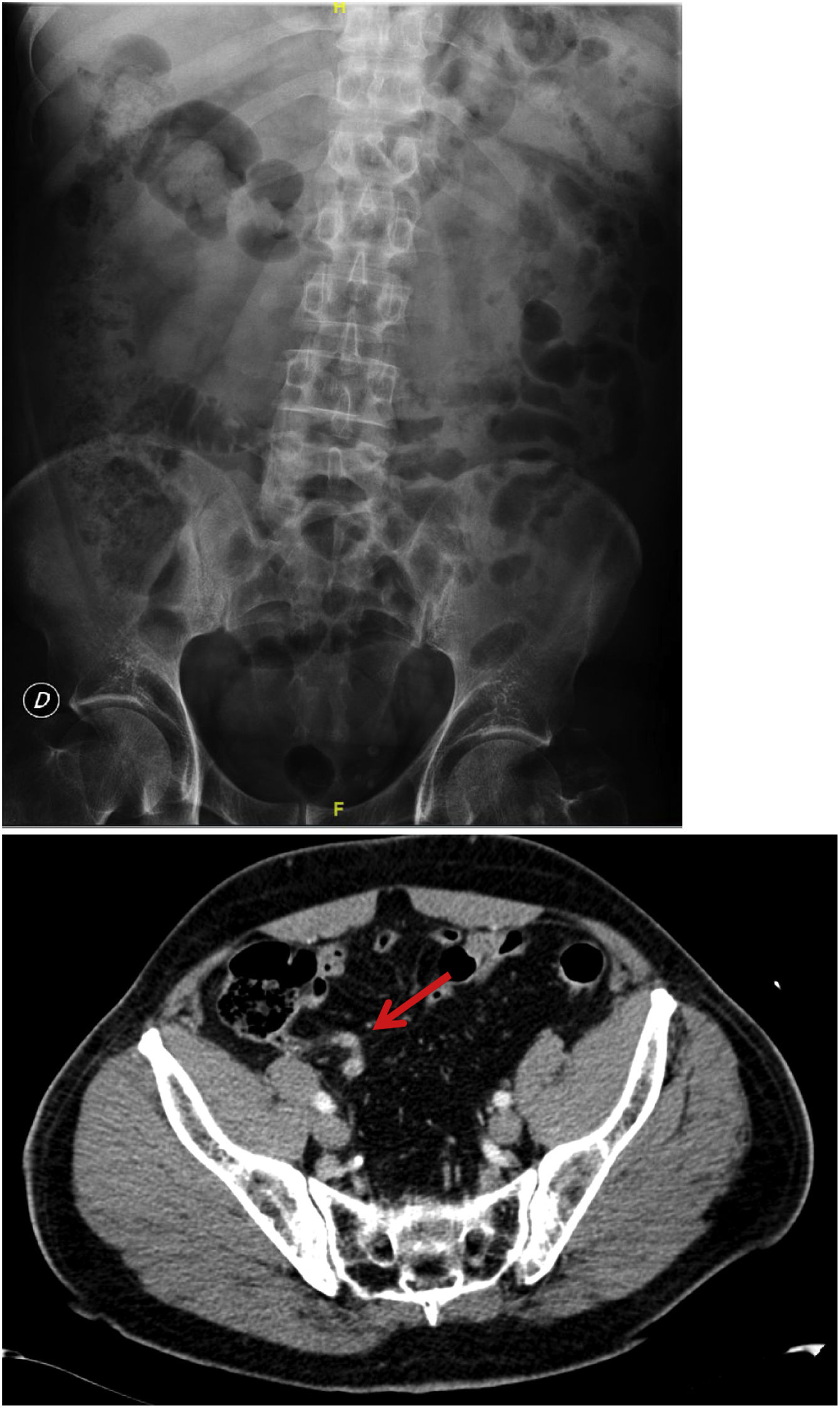
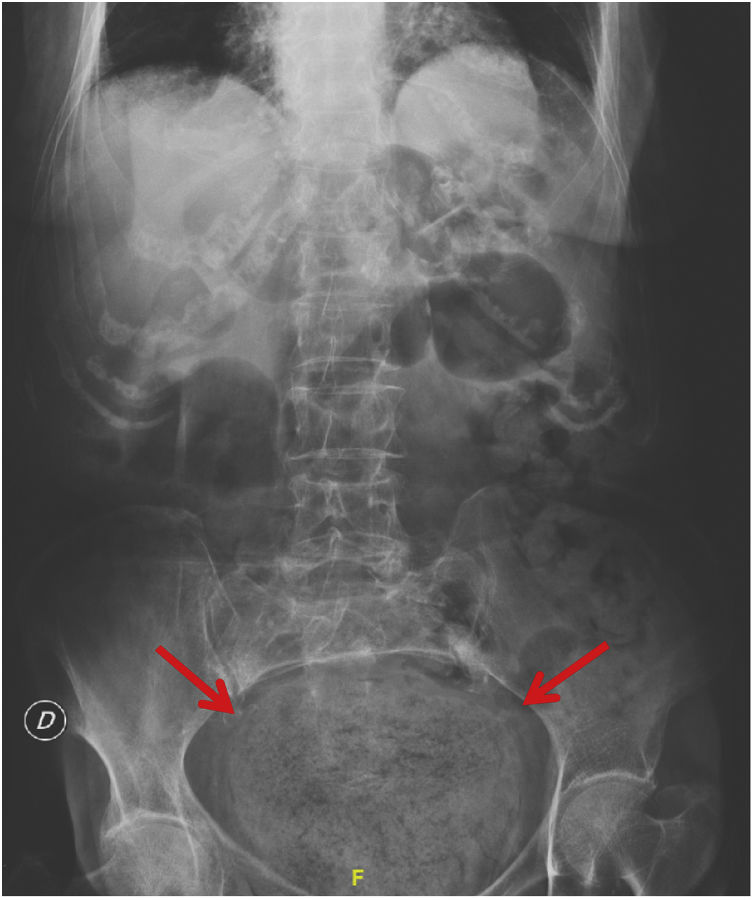
The use of abdominal radiography (AXR) apparently continues to be widespread despite its limited indications, the potential radiation and unnecessary costs associated. In addition, the interpretation and its report seem variable and not always performed by a radiologist. Our objective is to analyze the use, adequacy and usefulness of AXR in the emergency of a tertiary referral hospital.
Material and methodsWe retrospectively reviewed all the AXR performed in January 2020 in the emergency of our centre, as well as the patient’s demographics and medical records, technical quality of the radiographs, indications according to the SERAM (Spanish Society of Radiology) Appropriateness Guidelines, presence of a formal radiology report, and impact on the clinical management of the patient. Of all non-appropriated AXR we calculated the radiation received by the patients and its extra costs.
ResultsIn January 2020, 429 AXR (9.1% of all radiographies) were performed in the emergency of our centre. The most frequent indication was abdominal pain (40%, n = 176), followed by low back pain (21.4%, n = 92). 12.4% of AXR requested did not include any clinical information. Most of the AXR (79.6%) had sufficient technical quality. 61.3% (n = 263) of the AXR performed were not indicated, assuming an average unjustified radiation dose per patient of 0.50 ± 0.33 mSv, and a total additional cost of 6575;. Only 6% of the inadequate AXRs led to a change in the clinical management of the patient, compared to 29% of the adequate AXR (p < 0.001). Only 3% of the AXR had a formal radiology report.
ConclusionsAXR is still common in the emergency setting, although most of them might be inadequate according to the SERAM Appropriateness Guidelines. Its use should be optimized to avoid unnecessary radiation and costs. Radiologists must have a more active participation in the management of AXR.
El uso de la radiografía simple de abdomen (RXA) continúa siendo relativamente frecuente en nuestra práctica clínica, a pesar de su limitada utilidad y sus pocas indicaciones, con la potencial radiación y los costes innecesarios asociados. Nuestro objetivo es analizar el uso, la adecuación y la utilidad de la RXA en la urgencia de un hospital universitario de tercer nivel.
Material y métodosRevisamos retrospectivamente todas las RXA realizadas en enero de 2020 en la urgencia de nuestro centro, así como la demografía y las historias clínicas de los pacientes, la calidad técnica de las radiografías, su indicación de acuerdo con las guías de la Sociedad Española de Radiología Médica (SERAM), la presencia de un informe radiológico y el impacto de las radiografías en el manejo clínico del paciente. En el caso de las radiografías no adecuadas a las guías clínicas, calculamos la radiación recibida por los pacientes y su sobrecoste.
ResultadosEn enero de 2020 en la urgencia de nuestro centro se realizaron 429 RXA (el 9,1% del total de las radiografías simples). El principal síntoma guía que motivó su realización fue dolor abdominal (40%, n = 176), seguido de dolor lumbar (21,4%, n = 92). El 12,4% de las peticiones de RXA no incluían ninguna información clínica. La mayoría de las RXA (79,6%) tenían una calidad técnica adecuada. El 61,3% (n = 263) de las RXA realizadas no estaban indicadas, suponiendo una dosis de radiación injustificada promedio por paciente de 0,50 ± 0,33 mSv y un sobrecoste total de 6.575;. Únicamente el 6% de las RXA inadecuadas supusieron un cambio en el manejo clínico del paciente, frente al 29% de las RXA adecuadas (p < 0,001). Solo el 3% de las RXA tenían un informe radiológico.
ConclusionesEl uso de la RXA sigue siendo común en nuestras urgencias, y una mayoría de ellas no se adecúa a las recomendaciones de la SERAM. Debemos optimizar su uso para evitar radiación y costes innecesarios. Los radiólogos deben tener una participación más activa en el manejo y la interpretación de las RXA.