Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia worldwide. Previous studies have described that certain clinical characteristics such as age, obesity, the type of AF, and imaging-based factors, such as left atrial (LA) volume, mean density (calculated as the average of Hounsfield Units values in a certain región of interest), and volume of cardiac adipose tissue, may increase the risk of recurrence following pulmonary vein ablation. However, there have been contradictory results regarding radiological variables in previous studies. The objective of this study was to evaluate these clinical and radiological risk factors obtained from computed tomography (CT) studies.
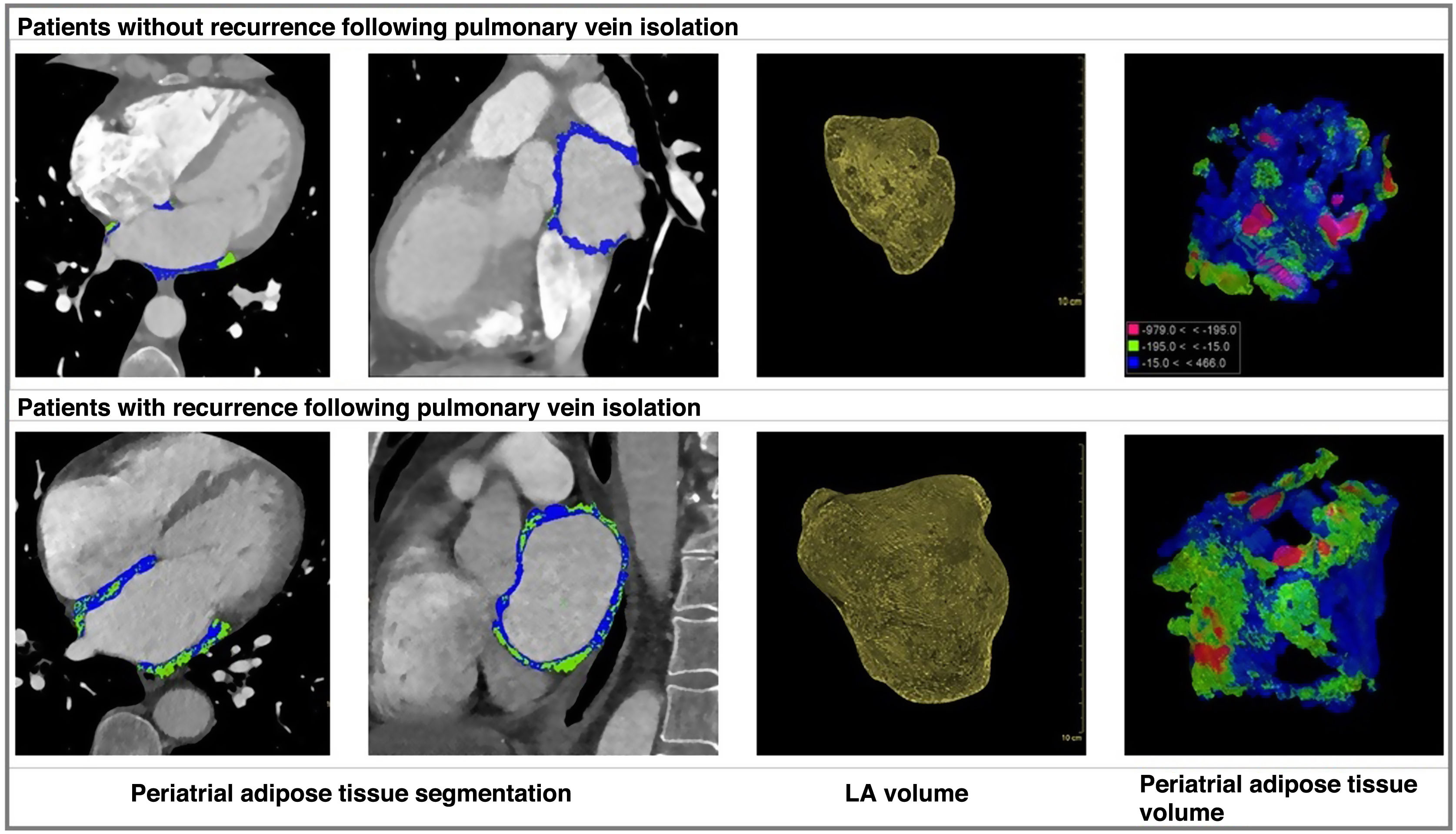
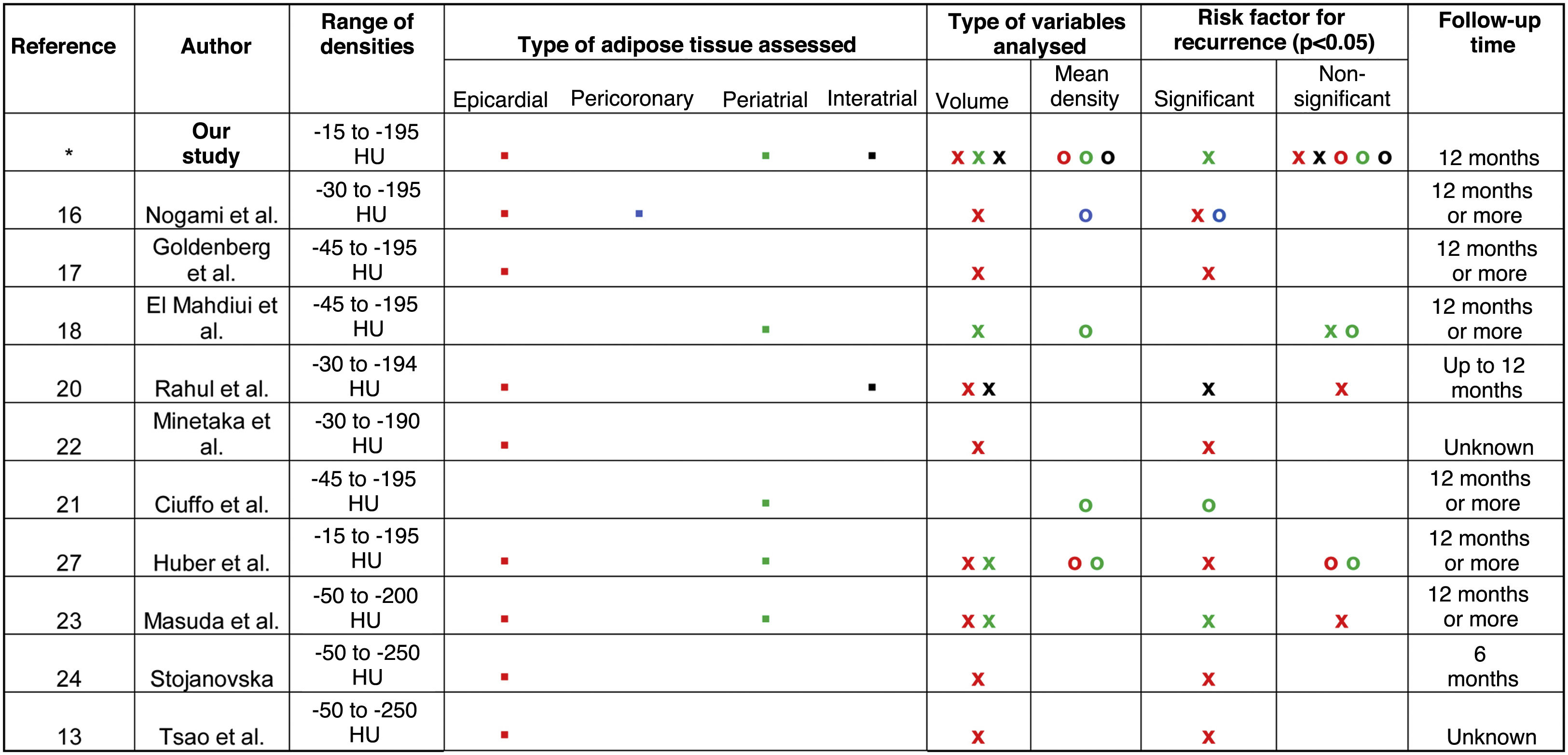
Materials and methodsThis retrospective case-control study included all patients with AF who underwent initial radiofrequency or cryoablation of pulmonary veins after undergoing contrast-enhanced CT between 2017 and 2021. Clinical variables such as age, gender, comorbidities, medications used after ablation, type of AF, and radiological variables obtained from volumetric segmentation of CT studies were collected. Radiological variables included LA volume, mean density, and volume of epicardial, periatrial, and interatrial adipose tissue. The occurrence or absence of AF recurrence within 12 months after ablation was also recorded. These variables were subjected to univariate and multivariate analysis to evaluate the risk of recurrence.
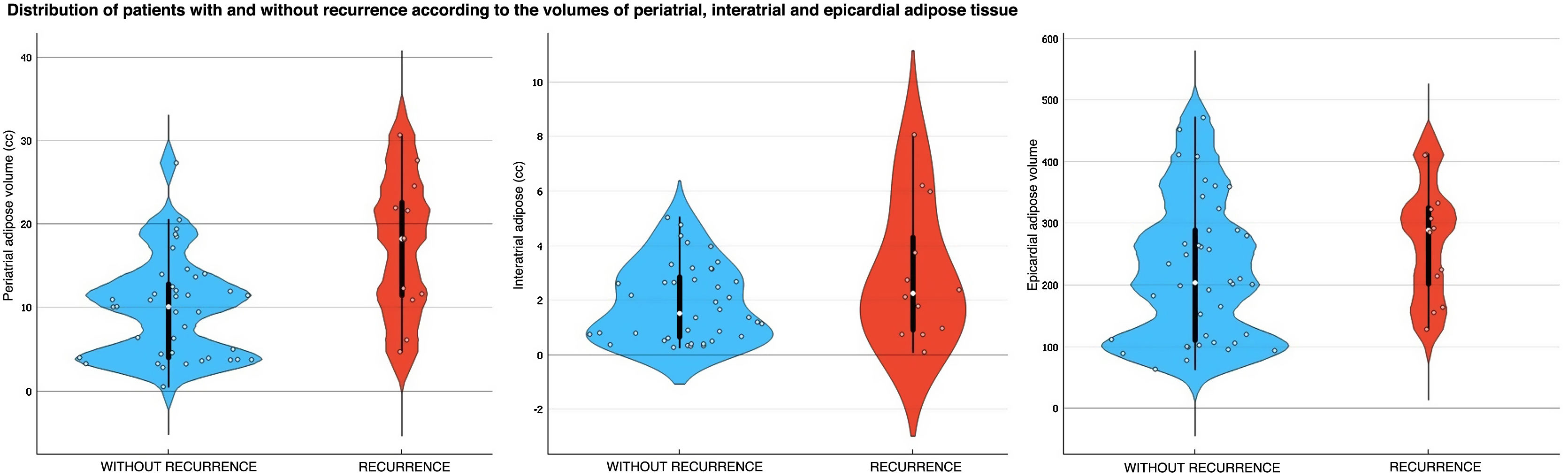
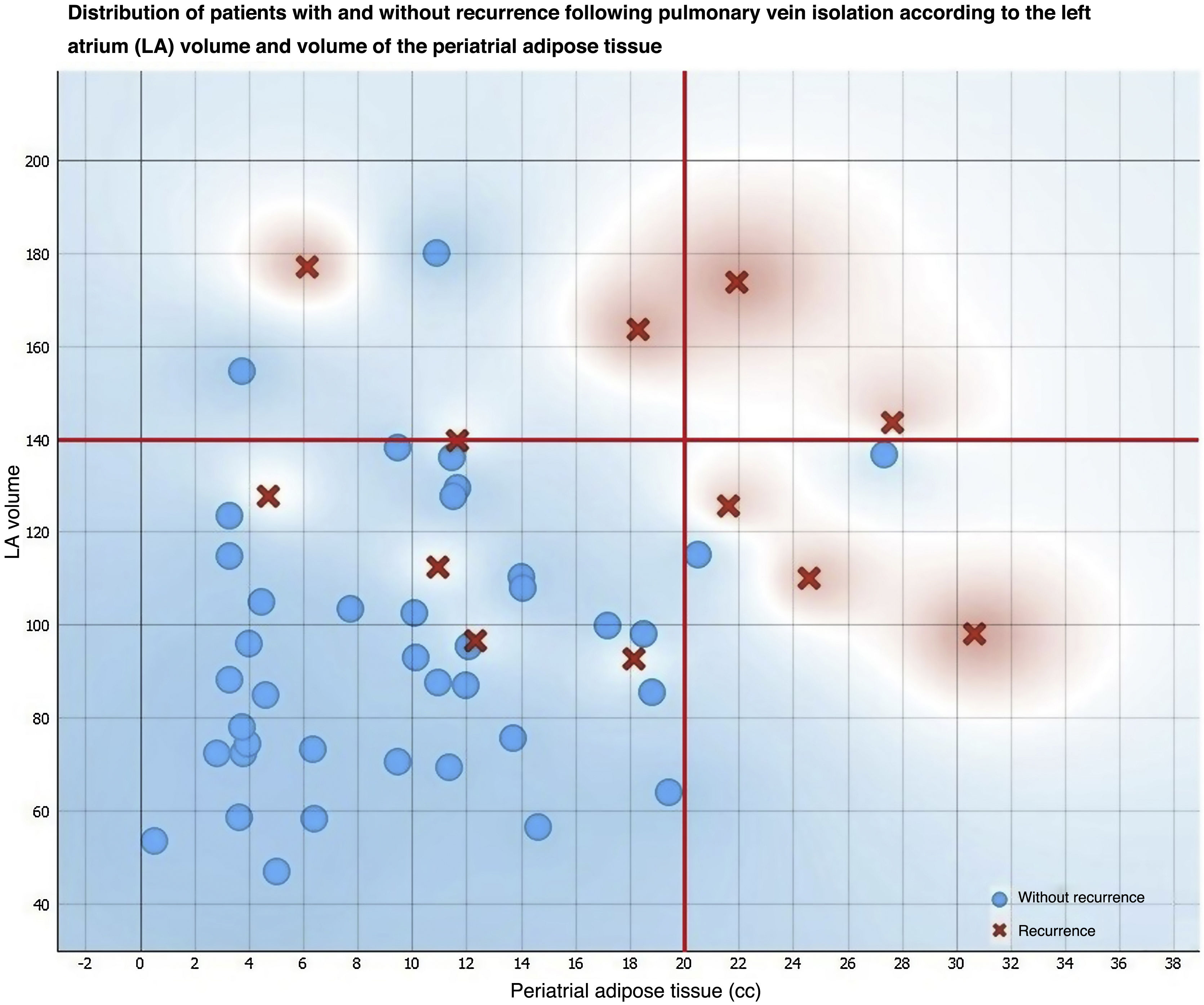
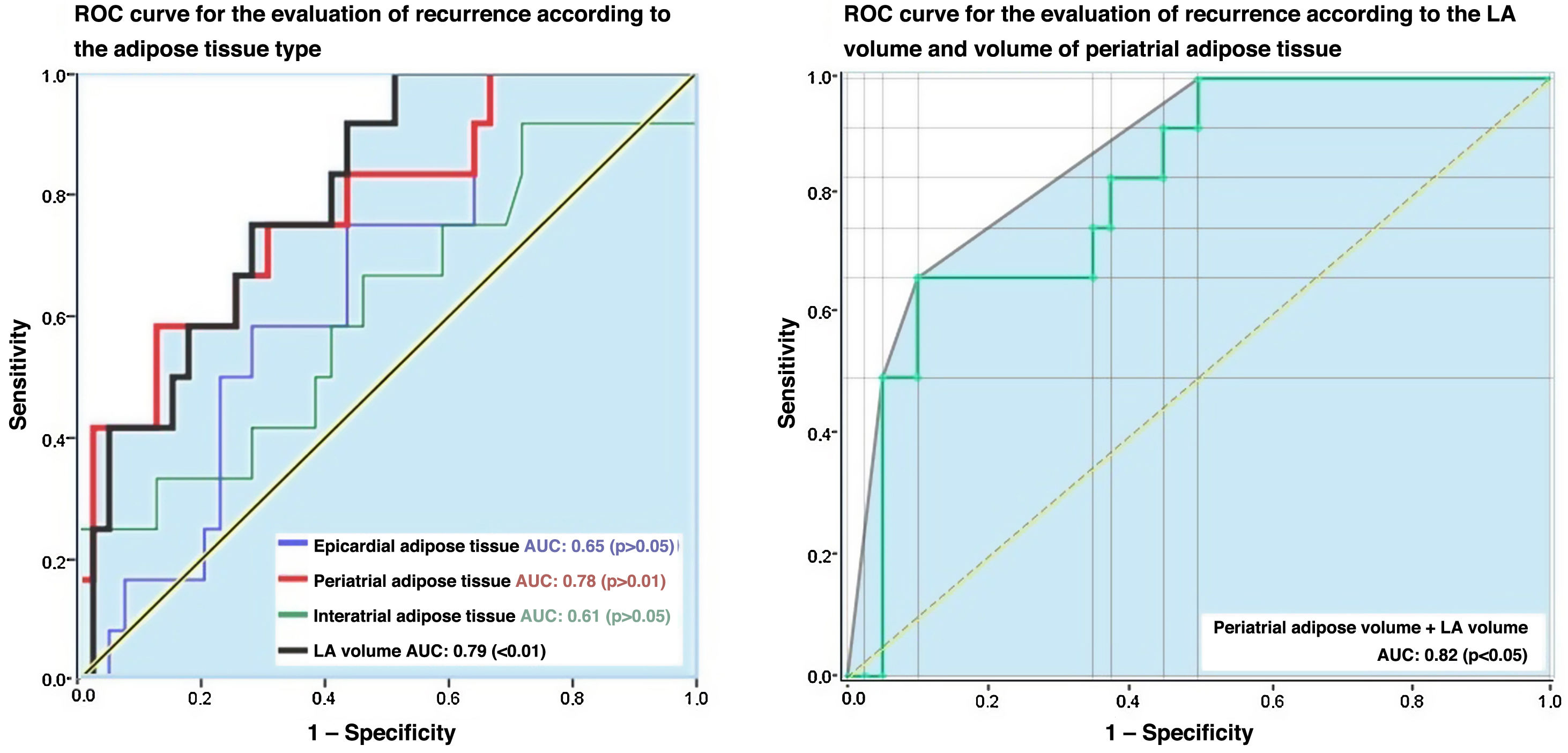
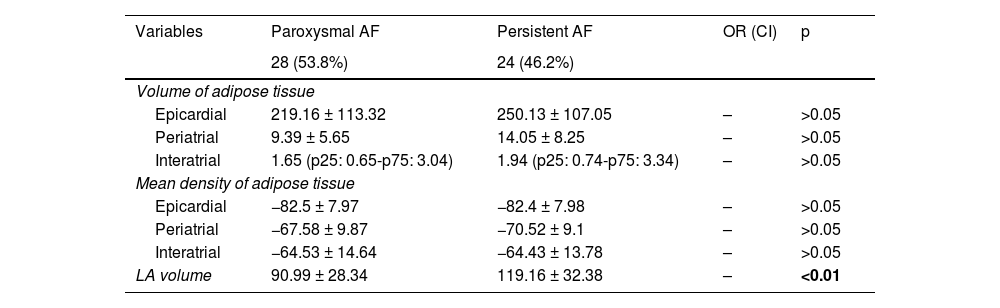
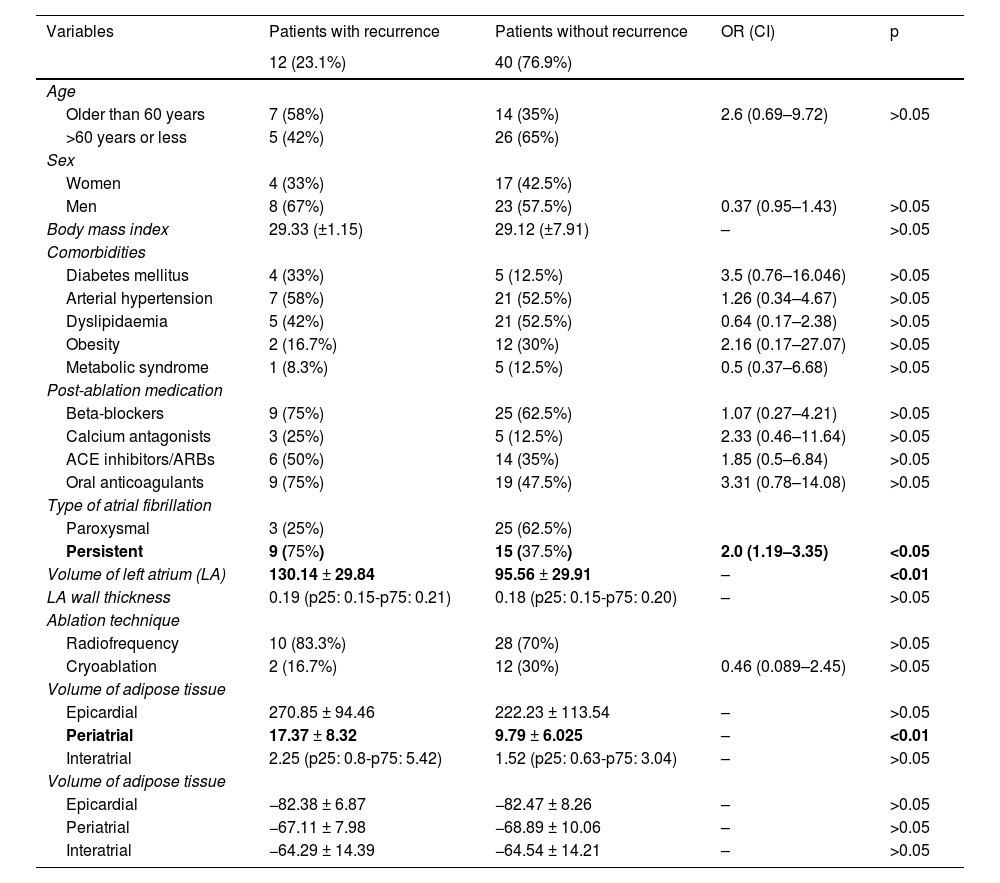
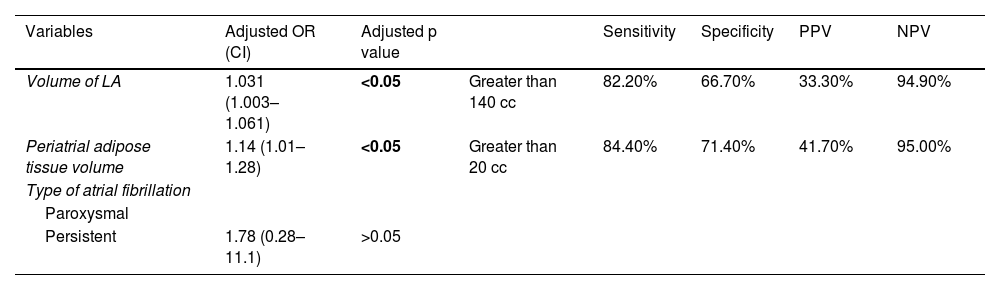
ResultsAmong the total number of included patients, 40 had paroxysmal AF and 12 had persistent AF. During the follow-up period, 12 patients (23.1%) experienced AF recurrence, while 40 patients (76.9%) remained in sinus rhythm. There were statistically significant differences in LA volume based on the type of AF, with higher volumes observed in patients with persistent AF (119.16 +/− 32.38 cc) compared to the rest (90.99 +/− 28.34 cc). Regarding the differences between patients with and without recurrence after ablation, only LA volume (p < 0.05) and periatrial adipose tissue volume (p < 0.01) were significantly higher in patients with recurrence.
ConclusionThe type of atrial fibrillation, increased left atrial volume, and increased periatrial adipose tissue volume are risk factors for recurrence in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing pulmonary vein ablation using cryoablation or radiofrequency.
La fibrilación auricular (FA) es la arritmia cardíaca más frecuente globalmente. Se ha descrito previamente que algunas características clínicas como la edad, obesidad, el tipo de FA y otras, obtenidas mediante estudios de imagen, como el volumen de la aurícula izquierda (AI), la densidad media (calculada a partir del promedio de los valores de Unidades Hounsfield en una región de interés) y volumen del tejido graso cardiaco podrían aumentar el riesgo de recurrencia tras la ablación de venas pulmonares, existiendo resultados contradictorios entre algunos estudios previos con respecto a las variables radiológicas. El objetivo de este estudio fue el de evaluar estos factores de riesgo clínicos y radiológicos obtenidos a partir de estudios de tomografía computarizada.
Materiales y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de casos y controles incluyendo a todos los pacientes con FA sometidos a una primera ablación por radiofrecuencia o crioablación de venas pulmonares posterior a la realización de una tomografía computarizada (TC) con contraste entre 2017 y 2021. Se recopilaron variables clínicas como la edad, sexo, comorbilidades, medicaciones empleadas tras la ablación, tipo de FA y radiológicas obtenidas a partir segmentación volumétrica de los estudios de TC, como volumen de AI, la densidad media y volumen del tejido graso epicárdico, periatrial e interatrial, así como la aparición o no de recurrencia de la FA tras 12 meses desde la ablación. Estas variables fueron sometidas a un análisis univariante y multivariante para evaluar el riesgo de recurrencia.
ResultadosDel total de pacientes incluidos, 40 tenían FA paroxística y 12 persistente. 12 (23,1%) mostraron recurrencia durante el periodo de seguimiento y 40 (76,9%) se mantuvieron con ritmo sinusal. Existieron diferencias estadísticamente significativas para el volumen de la AI según el tipo de FA, siendo mayor en los pacientes con FA persistente (119,16 +/− 32,38 cc), respecto al resto (90,99 +/− 28,34 cc). En cuanto a las diferencias entre los pacientes con y sin recurrencia tras la ablación, únicamente el volumen de la AI (p < 0.05) y el volumen del tejido graso periatrial (p < 0.01) fueron significativamente mayores en los pacientes con recurrencia.
ConclusiónEl tipo de fibrilación auricular, el aumento del volumen de la aurícula izquierda y del tejido graso periatrial son factores de riesgo para la recurrencia en pacientes con fibrilación auricular sometidos a ablación de venas pulmonares mediante crioablación o radiofrecuencia.