El Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) es un cuestionario extendido internacionalmente para patología de pie y tobillo. El propósito del estudio fue desarrollar y validar la versión española de 29 ítems del cuestionario FAAM para las subescalas de Actividades de la Vida Diaria (AVD) y DEPORTE en el área de rehabilitación.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un estudio observacional en dos fases. Primero, se hizo una adaptación transcultural del cuestionario FAAM con una traducción doble al español y doble traducción inversa al inglés. Posteriormente, se validaron las propiedades psicométricas. Los participantes (n = 147), con patología de pie y tobillo, completaron la versión española del FAAM para AVD y DEPORTE, el cuestionario SF-36 y la Escala Analógica Visual de Dolor (EVA). La muestra se empleó para determinar la estructura factorial, consistencia interna y validez convergente y, un subgrupo (n = 46), para determinar la fiabilidad a las 48-72 h.
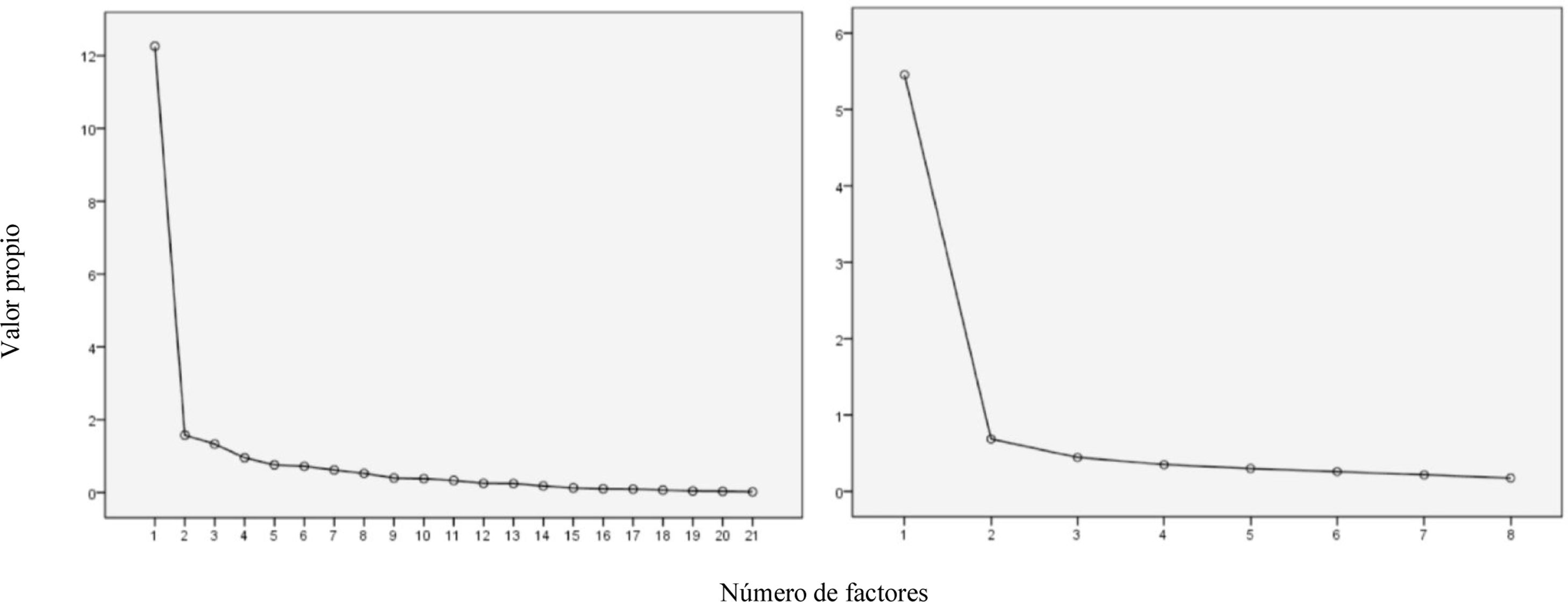
ResultadosLa estructura factorial de la versión española del FAAM para AVD y DEPORTE fue unidimensional demostrando alta consistencia interna en ambas subescalas (AVD y DEPORTE, α = 0,97 y α = 0,93, respectivamente). Los valores de fiabilidad fueron de ICC = 0,90 y ICC = 0,76, respectivamente. La validez convergente del cuestionario FAAM con la EVA dolor (r = 0,50) y con la función física de la SF-36 (r = 0,64) se correlacionó moderadamente.
ConclusionesLa versión española del FAAM de 29 ítems es un instrumento de medida válido para patologías de pie y tobillo con unas propiedades psicométricas similares a la versión original y a las versiones en otros idiomas.
The Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) is an internationally widely used outcome measure of foot and ankle disorders available in several languages. The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a FAAM Spanish-version with 29 items of Activities of Daily Living (ADL) and SPORT subscales in rehabilitation setting.
Materials and methodsA two-stage observational study was conducted. The FAAM was cross-culturally adapted to Spanish through a double-forward translation and a double-backward translation; the psychometric properties were then validated. The participants (n = 147), with various chronic foot and ankle disorders, completed the Spanish version of the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure ADL and SPORT, SF-36, and a pain intensity visual analogue scale (Pain VAS). The full sample was used to determine the factor structure, the internal consistency, and the convergent criterion validity, and a subgroup (n = 46) was used to determine the reliability at 48–72 h.
ResultsThe factor structure of Spanish version of FAAM ADL and SPORT subscales were both one-dimensional, demonstrating high internal consistency (α = 0.97 and α = 0.93, respectively). The reliability values were ICC = 0.90 and ICC = 0.76, respectively. The convergent validity criterion of Spanish version of FAAM with the Pain VAS (r = 0.50) and Physical Function of SF-36 (r = 0.64) were moderately correlated.
ConclusionsThe Spanish version of FAAM with 29 items are a valid foot and ankle disorder outcome measure with similar psychometric properties to the original version and versions in other languages.