To compare the haemodynamic response and effectiveness of tracheal intubation with Airtraq® device and Macintosh laryngoscope, for airway management of patients between 2 and 8 years undergoing elective surgery.
MethodsA prospective, comparative, randomised and blind clinical trial where the effectiveness of tracheal intubation in 80 paediatric patients undergoing elective surgery was determined. Patients were divided into 2 groups of 40 subjects each: group A, intubated with Airtraq® optical laryngoscope; and group M, intubated with Macintosh laryngoscope. Haemodynamic changes, time and number of attempts at intubation and its complications were evaluated in both.
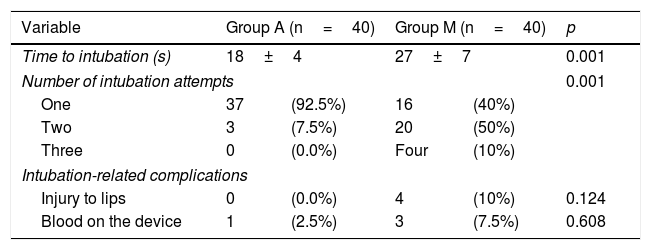
ResultsHeart rate was higher in group M from minute 1 to 5 with statistically significant difference (p: 0.001). The mean, systolic and diastolic blood pressure and EtCO2 values were higher in group M. There were no statistically significant differences in SO2. There was a statistically significant difference in time (group A: 18±4s, group M: 27±7s) and the number of attempts for intubation were lower for group A (p: 0.001). Seven patients in group M had post-intubation complications while only one subject had in group A.
ConclusionIntubation with Airtraq® device is more effective than Macintosh laryngoscope in terms of reduction of haemodynamic changes, SO2, EtCO2, time and number of attempts for intubation and complications in paediatric patients undergoing elective surgery.
Comparar la respuesta hemodinámica y efectividad de la intubación orotraqueal mediante los dispositivos Airtraq® y laringoscopio Macintosh, para asegurar la vía aérea de pacientes entre 2 y 8 años sometidos a cirugía electiva.
MétodosEstudio con diseño prospectivo, comparativo, aleatorizado y ciego, donde se determinó la efectividad de la intubación orotraqueal en 80 pacientes pediátricos programados para cirugía electiva. Los pacientes fueron divididos en dos grupos de 40 pacientes cada uno: grupo A, intubados con laringoscopio óptico Airtraq®; y, grupo M, intubados con laringoscopio Macintosh. Se evaluó en ambos la respuesta hemodinámica, tiempo y número de intentos para la intubación y sus complicaciones.
ResultadosLa frecuencia cardíaca fue mayor en el grupo M del minuto 1 al 5 con diferencia estadísticamente significativa (p: 0,001). Los valores de presión arterial media, sistólica y diastólica y de EtCO2 fueron mayores en el grupo M. No hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas en cuanto a la saturación de oxígeno. Hubo diferencia estadísticamente significativa en cuanto al tiempo de intubación (grupo A: 18±4 segundos; grupo M: 27±7 segundos) y el número de intentos siendo menor para el grupo A (grupo A: 92,7% y grupo M: 40% al primer intento; p: 0,001). Siete pacientes del grupo M y uno del grupo A presentaron complicaciones posteriores a la intubación.
ConclusiónLa intubación con dispositivo Airtraq® es más efectiva que con laringoscopio Macintosh en cuanto a reducción de cambios hemodinámicos, SO2, EtCO2, tiempo y número de intentos para la intubación y complicaciones, en pacientes pediátricos sometidos a cirugía electiva.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora