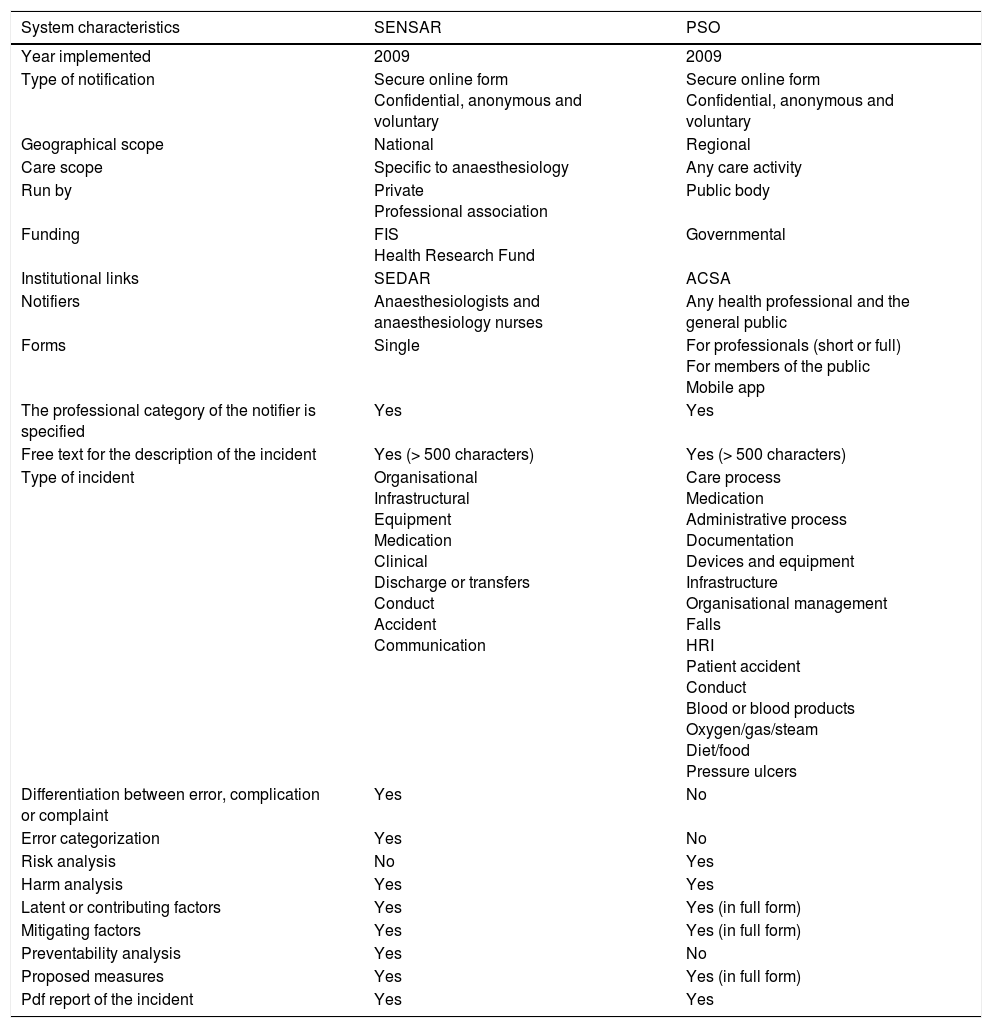
Incident reporting systems (IRS) are considered a tool that facilitates learning and safety culture. Using the experience gained with SENSAR, we evaluated the feasibility and the activity of a multidisciplinary group analyzing incidents in the surgical patient notified to a general community system, that of the Observatory for Patient Safety (OPS).
Material and methodCross-sectional observational study planned for two years. After training in the analysis, a multidisciplinary group was created in terms of specialties and professional categories, which would analyse the incidents in the surgical patient notified to the OPS. Incidents are classified and their circumstances analysed.
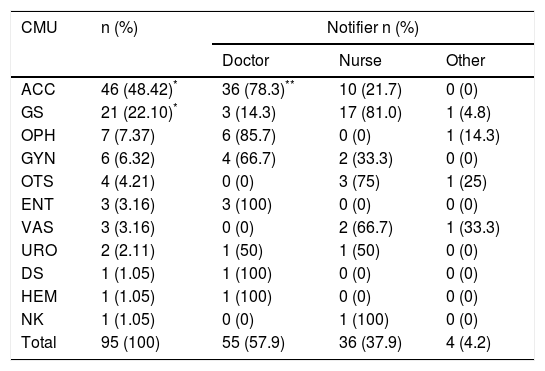
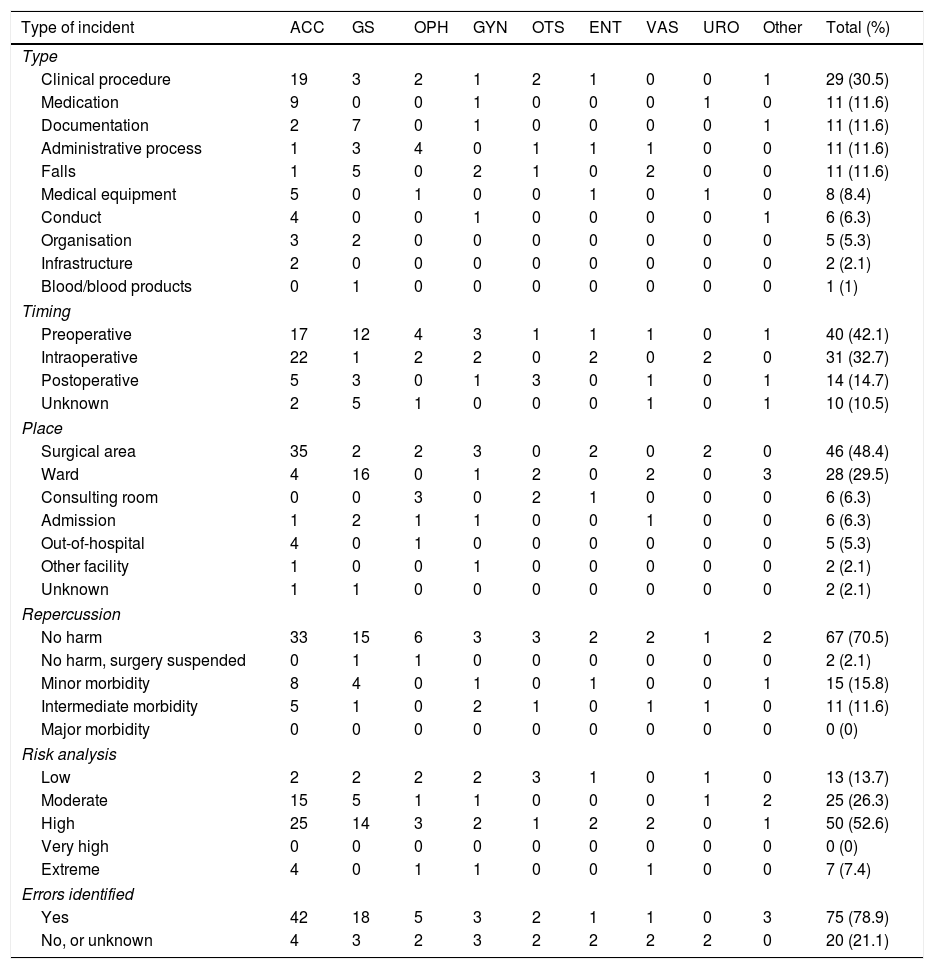
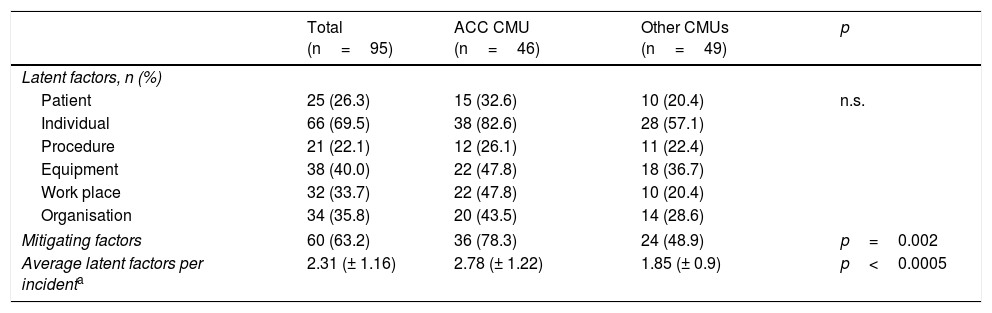
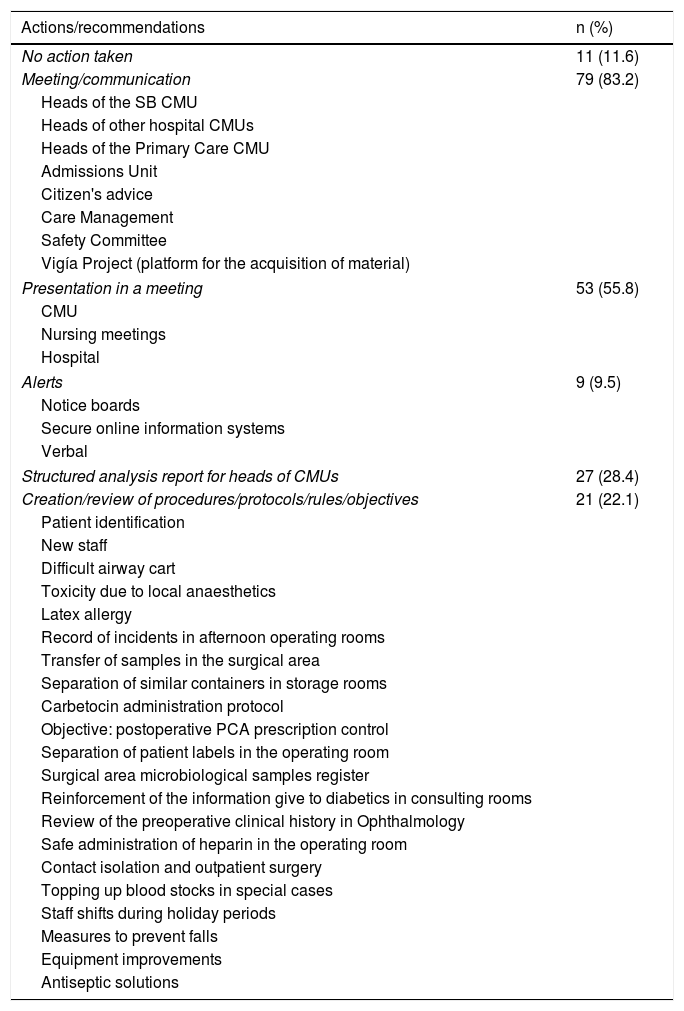
ResultsBetween March 2015 and 2017, 95 incidents were reported (4 by non-professionals). Doctors reported more than nurses, at 54 (56.84%) vs. 37 (38.94%). The anaesthesia unit reported most at 46 (48.42%) (p=0.025). The types of incidents mainly related to the care procedure (30.52%); to the preoperative period (42.10%); and to the place, the surgical area (48.42%). Significant differences were detected according to the origin of the notifier (p=0.03). No harm, or minor morbidity, constituted 88% of the incidents. Errors were identified in 79%. The analysis of the incidents directed the measures to be taken.
ConclusionsThe activity undertaken by the multidisciplinary analytical group during the period of study facilitated knowledge of the system among the professionals and enabled the identification of areas for improvement in the Surgical Block at different levels.
Los sistemas de notificación de incidentes (SNI) se consideran una herramienta que facilita el aprendizaje y la cultura de seguridad. Utilizando la experiencia adquirida con SENSAR, evaluamos la viabilidad y la actividad de un grupo multidisciplinar analizador de incidentes en el paciente quirúrgico notificados a un sistema general comunitario, el del Observatorio para la Seguridad del Paciente (OSP).
Material y métodoEstudio observacional descriptivo transversal planificado a 2 años. Previa formación en el análisis, se crea un grupo multidisciplinar en cuanto a especialidades y categorías profesionales, que analizarían los incidentes en el paciente quirúrgico notificados al OSP. Se clasifican los incidentes y se analizan sus circunstancias.
ResultadosEntre los meses de marzo de 2015 y 2017 se notificaron 95 incidentes (4 por no profesionales). Los facultativos notificaron más que la enfermería, 54 (56,8%) vs. 37 (38,9%). La unidad que más notificó fue Anestesia con 46 (48,4%) (p=0,025). Los tipos de incidentes se relacionaron principalmente con el procedimiento asistencial (30,5%); el momento, con el preoperatorio (42,1%) y el lugar, con el área quirúrgica (48,4%), detectándose diferencias significativas en función de la filiación del notificante (p=0,03). No daño, o morbilidad menor, presentaron el 88% de los incidentes. Se identificaron errores en el 79%. El análisis de los incidentes dirigió las medidas a tomar.
ConclusionesLa actividad que mantuvo el grupo multidisciplinar de análisis durante el periodo de estudio propició el conocimiento del sistema entre los profesionales y permitió identificar elementos de mejora en el Bloque Quirúrgico a diferentes niveles.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora