To evaluate the impact of the angioscintigrapy of the three phase bone scan as screening method to rule out infection of the hip and knee prosthesis prior to performing the 99mTc-HMPAO leukocyte scintigraphy.
Material and methodsA total of 120 (70 women, 50 men; mean age 71±11years) with clinical suspicion of hip (n=63) or knee (n=57) infection of the prosthesis and clinical suspicion of infection were evaluated prospectively. All patients underwent three-phase bone scan (angioscintigraphy, vascular and bone phase) and 99mTc-HMPAO-labeled white blood cell scintigraphy. Final diagnosis of infection was made by microbiological documentation or clinical follow-up for at least 12 months.
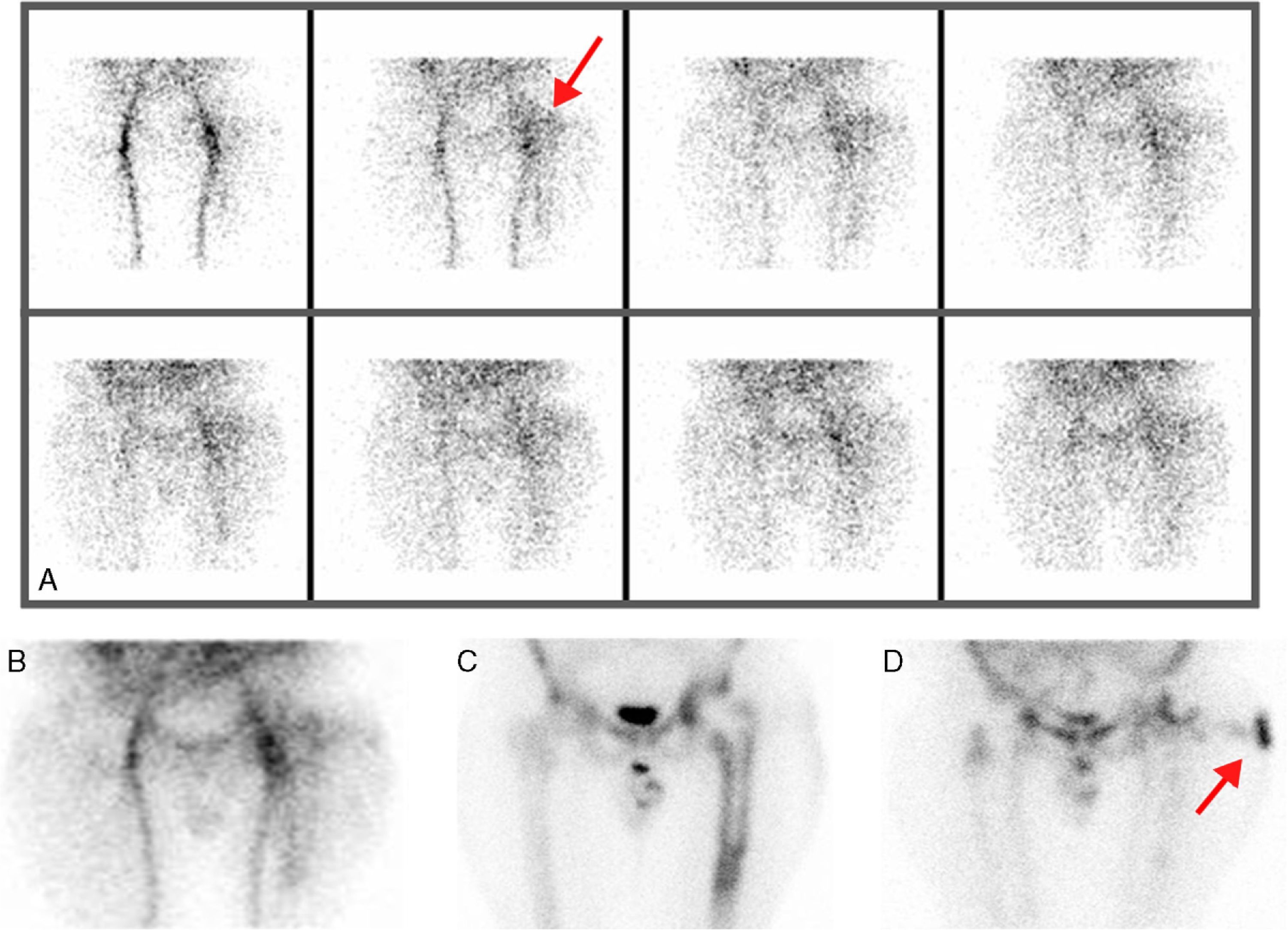
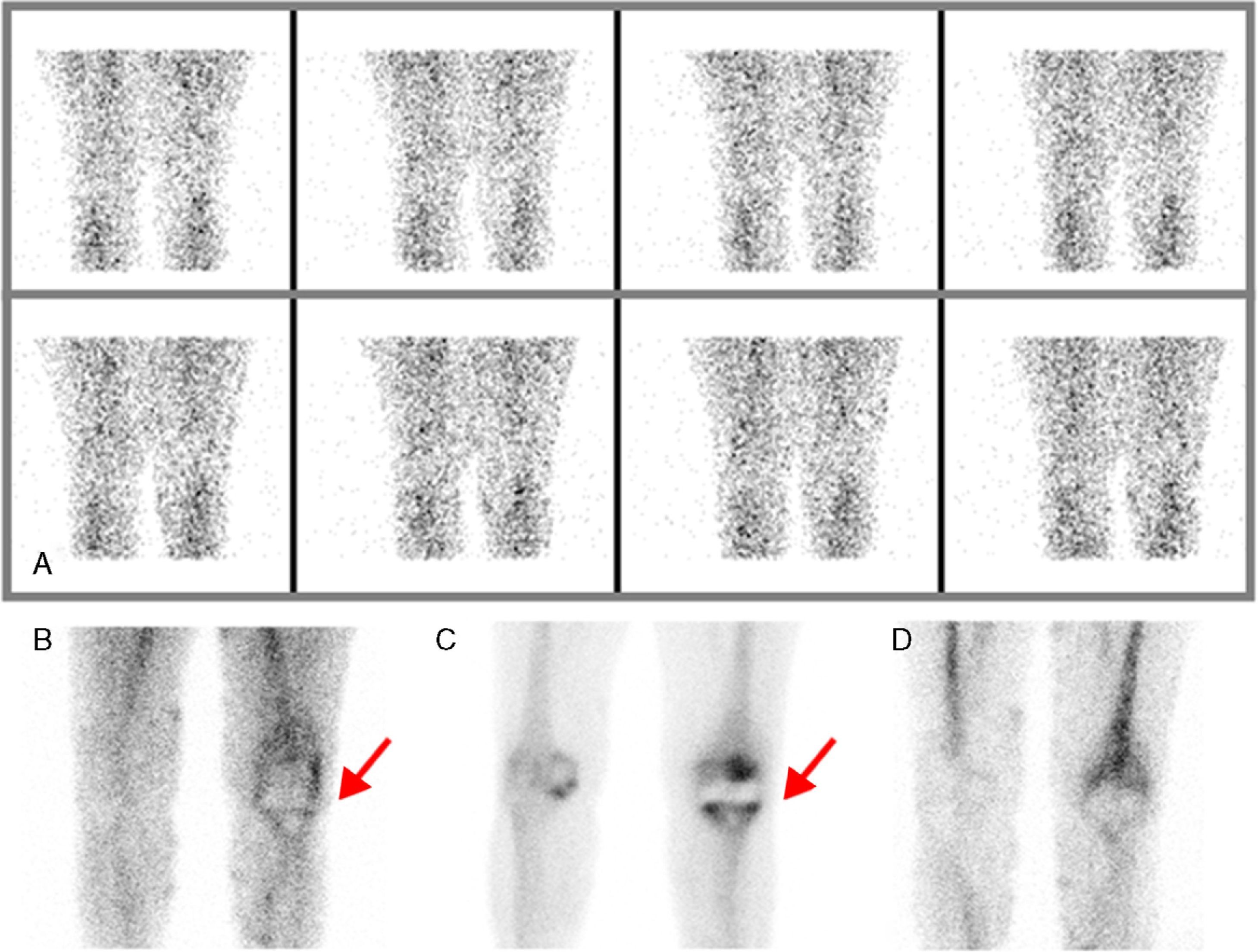
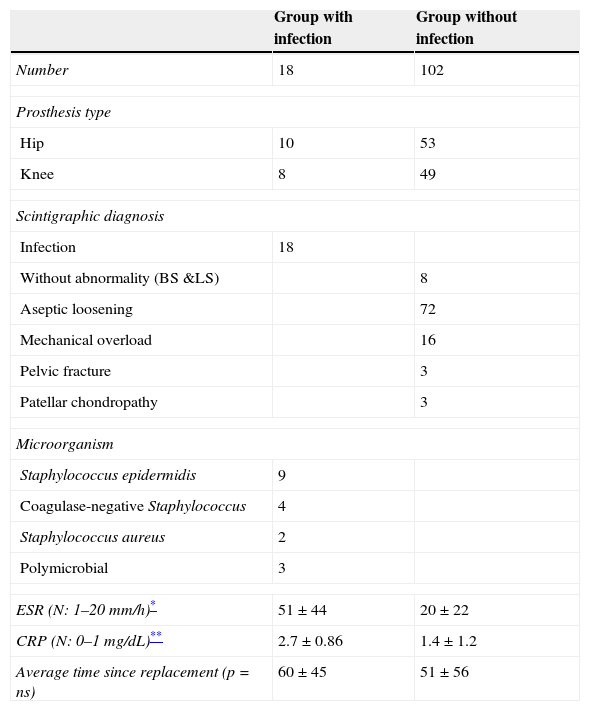
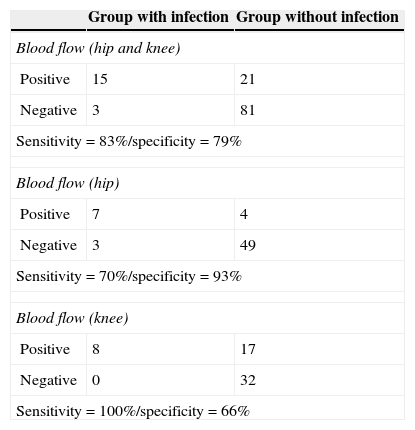
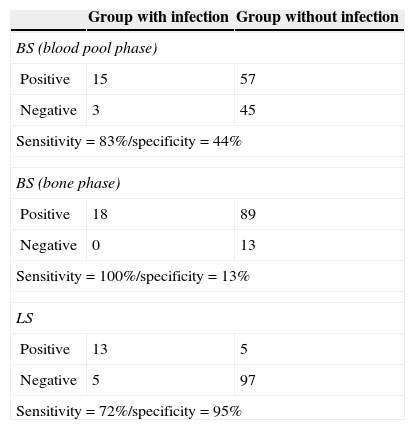
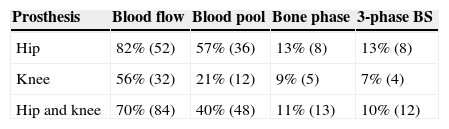
ResultsEighteen out of 120 patients were diagnosed of infection of hip prosthesis (n=10) or knee prosthesis (n=8). The angioscintigraphy was positive in 15/18 infected cases and in 21/102 of the non-infected cases with a sensitivity of 83%, specificity of 79% and negative predictive value of 97%. Sensitivity and specificity of 99mTc-HMPAO leukocyte scintigraphy were 72% and 95%, respectively. If the leukocyte labeled scintigraphies had been used exclusively for patients with positive angioscintigraphy, this would have saved up to 70% of the 99mTc-HMPAO leukocyte scintigraphies performed. There were no cases of infection with positive labeled leukocyte scintigraphy and negative angioscintigraphy.
ConclusionAngioscintigraphy (blood flow phase of bone scan) is a useful technique for screening for hip and knee joint prosthesis infection, significantly reducing the need for 99mTc-HMPAO leukocyte scintigraphy without affecting the sensitivity of the technique.
Analizar la utilidad de la fase angiogammagráfica de la gammagrafía ósea en 3fases como posible método de cribado en el diagnóstico de infección de prótesis de cadera y de rodilla, previa a la realización de la gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados.
Material y métodosSe analizaron prospectivamente 120 pacientes (70 mujeres y 50 hombres) con edad media de 71±11años y sospecha clínica de infección de prótesis de cadera (n=63) o rodilla (n=57), a los que se realizó gammagrafía ósea en 3fases (angiogammagrafía, fase vascular y fase ósea) y gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados con 99mTc-HMPAO. El diagnóstico definitivo se realizó mediante estudio microbiológico o seguimiento clínico mínimo de 12meses.
ResultadosSe estableció el diagnóstico de infección de la prótesis articular en 18/120 pacientes: 10 pacientes con prótesis de cadera y 8 pacientes con prótesis de rodilla. La angiogammagrafía fue positiva en 15/18 pacientes infectados y en 21/102 pacientes no infectados, mostrando una sensibilidad del 83%, una especificidad del 79% y un valor predictivo negativo del 97%. La gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados mostró una sensibilidad y una especificidad del 72 y del 95%, respectivamente. Si se realizara la gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados exclusivamente a los pacientes con angiogammagrafía positiva, se reduciría un 70% de gammagrafías con leucocitos practicadas. No hubo ningún caso de infección con gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados positiva y angiogammagrafía negativa.
ConclusionesLa angiogammagrafía es una buena técnica de cribado de infección de prótesis articulares de cadera y rodilla, disminuyendo significativamente el número de gammagrafías con leucocitos marcados, sin afectar la sensibilidad de la técnica.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora