The aim of this study is the implementation in a Hospital Radiopharmacy Unit of a risk analysis methodology in order to proactively identify possible failure modes and prioritize corrective measures.
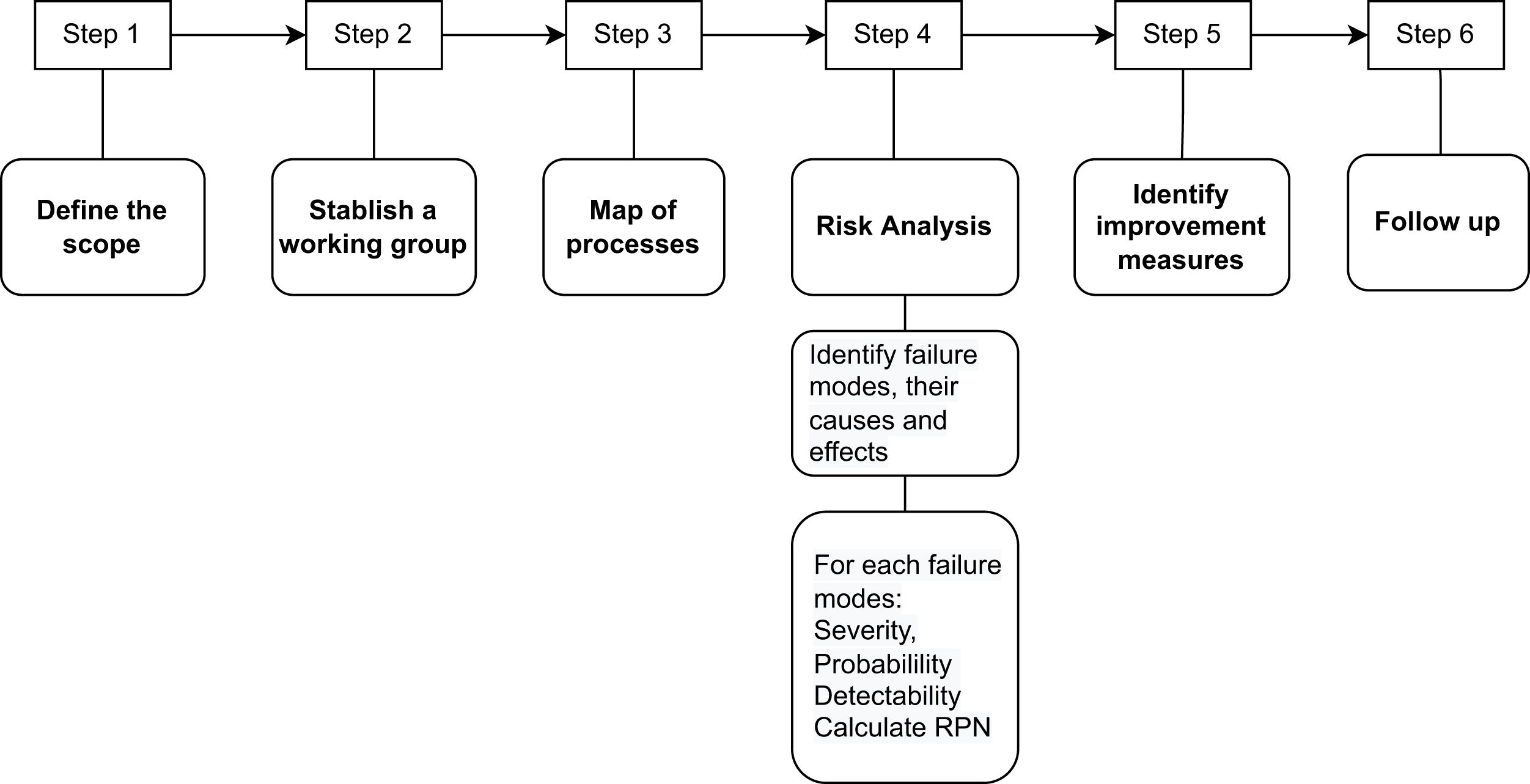
Materials and methodsBy means of the failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA), the possible failure modes of each of the stages of the processes of prescription, preparation, and administration of radiopharmaceuticals for diagnostic and therapy were identified. From the variables of severity, probability and detectability, the risk was quantified using the Risk Priority Number (RPN) for each failure mode, sub-process, and type of radiopharmaceutical. Improvement measures were established and the reduction in the RPN value was calculated.
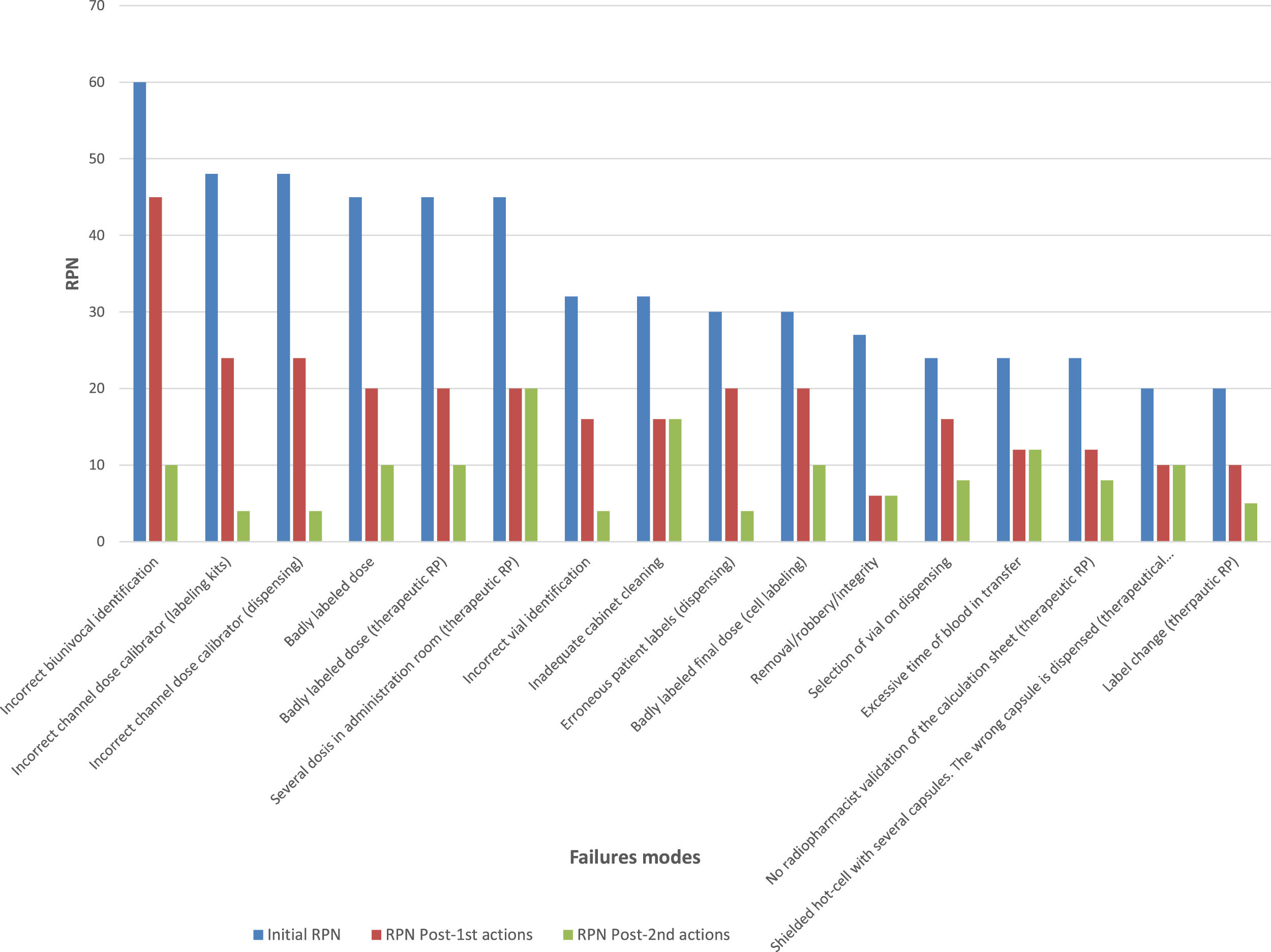
ResultsA total of 96 failure modes were identified (58 for diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals and 38 for therapy). Biunivocal identification of the patient with the radiopharmaceutical is the failure mode with the highest RPN (60) and the radiolabeling cell sub-process the one that has the highest risk (RPN 286). As a result of the improvement measures, the overall RPN was reduced by 22% for diagnostic radiopharmaceuticals and 20% for therapy. This reduction would be 46% and 31% respectively if radiopharmacy software and a barcode technology in the administration were implemented.
ConclusionsThe application of the FMEA methodology as a risk analysis tool allows to identify the critical points of the processes related to radiopharmaceuticals and prioritize measures to reduce the risk.
El objetivo de este estudio es la implementación en una Unidad de Radiofarmacia Hospitalaria de una metodología de análisis de riesgos para poder identificar de forma proactiva los posibles modos de fallo y priorizar medidas correctivas.
Material y métodosMediante el análisis modal de fallos y efectos (AMFE) se identificaron los posibles modos de fallo de cada una de las etapas de los procesos de prescripción, preparación y administración de los radiofármacos de diagnóstico y de terapia. A partir de las variables de severidad, probabilidad y detectabilidad se cuantificó el riesgo mediante el Número de Prioridad de Riesgo (NPR) para cada modo de fallo, subproceso y tipo de radiofármaco. Se establecieron medidas de mejora y se calculó la reducción en el NPR.
ResultadosSe identificaron 96 modos de fallos (58 para los radiofármacos de diagnóstico y 38 para los de terapia). La identificación biunívoca del paciente con el radiofármaco es el modo de fallo con mayor NPR (60) y el subproceso de marcaje celular el que presenta mayor riesgo (NPR 286). Como resultado de las medidas de mejora se disminuyó el NPR global en un 22% para los radiofármacos de diagnóstico y 20% para los de terapia. Esta reducción sería del 46% y 31% respectivamente si se implantara un software de radiofarmacia y tecnología de código de barras en la administración.
ConclusionesLa aplicación de la metodología AMFE como herramienta de análisis de riesgos permite identificar los puntos críticos de los procesos relacionados con los radiofármacos y priorizar medidas para disminuir el riesgo.
Artículo

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)