To analyse the correlation between 18F-FDG uptake assessed by PET/CT in locally advanced breast tumours and histopathological and immunohistochemical prognostic factors.
Material and methodsThirty-six women with breast cancer were prospectively evaluated. PET/CT was requested in the initial staging previous to adjuvant chemotherapy (multicentric study).
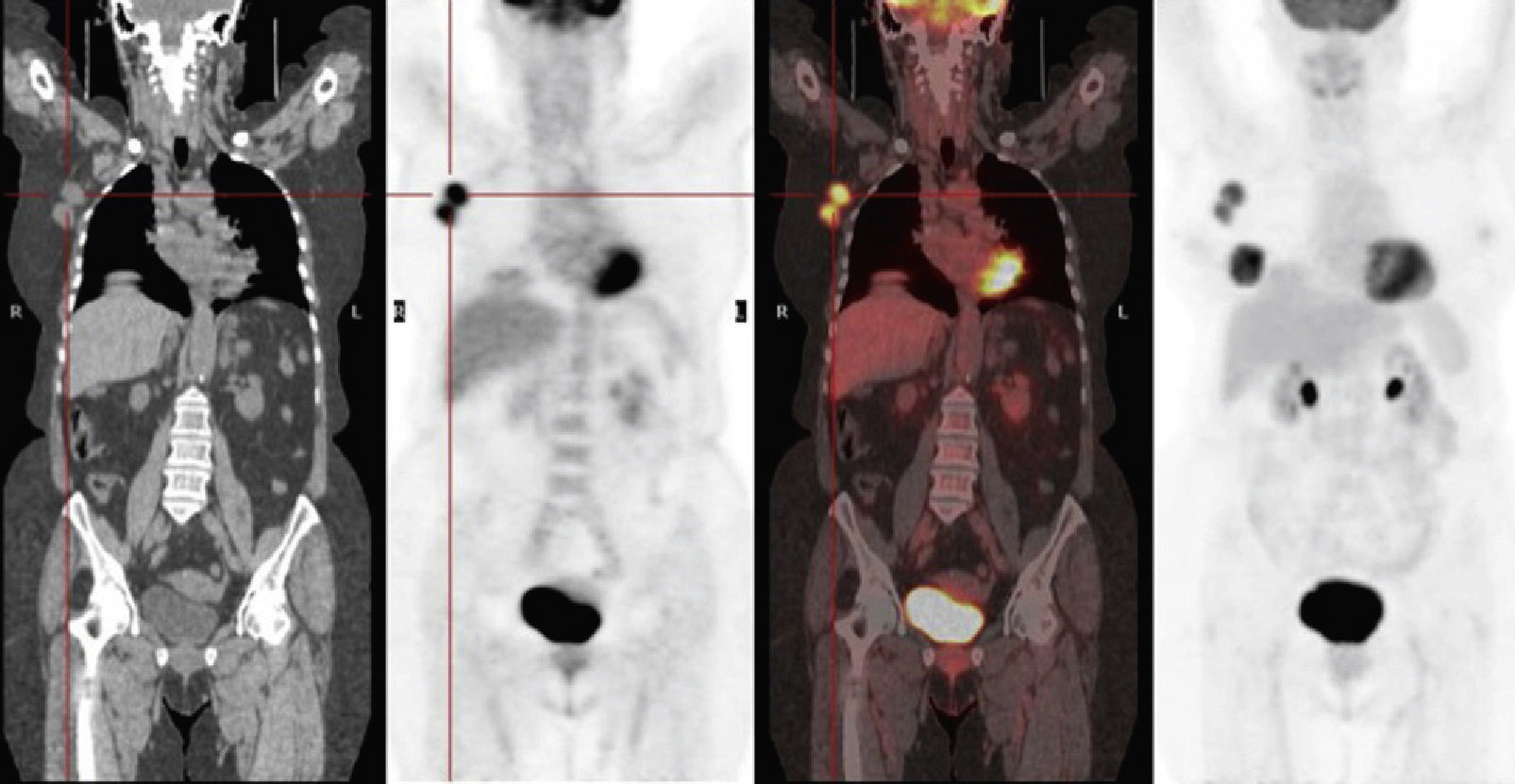
All the patients underwent an 18F-FDG PET/CT with a dual-time-point acquisition. Both examinations were evaluated qualitatively and semiquantitatively with calculation of SUVmax values in PET-1 (SUV-1) and in PET-2 (SUV-2) and the percentage variation of the standard uptake values (retention index) between PET-1 and PET-2.
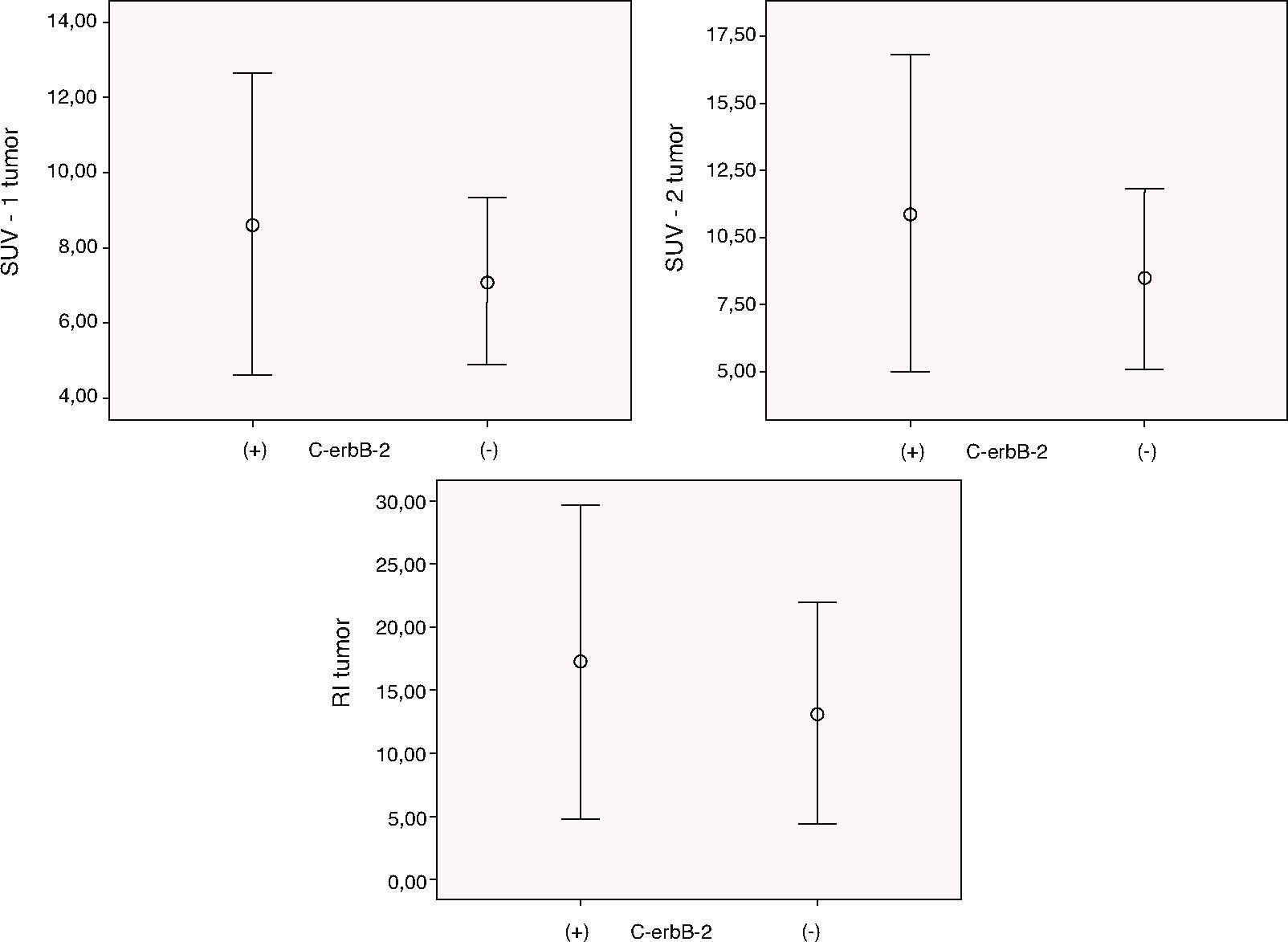
Clinical and metabolic stages were assessed according to TNM classification. The biological prognostic parameters, such as the steroid receptor status, p53 and c-erbB-2 expression, proliferation rate (Ki-67), and grading were determined from tissue of the primary tumour. Metabolic and biological parameters were correlated.
ResultsA positive relationship was found between semiquantitative metabolic parameters and biological parameters. SUV-1 and SUV-2 values did not show significant statistical correlation (p<.05) except for the clinical tumour size.
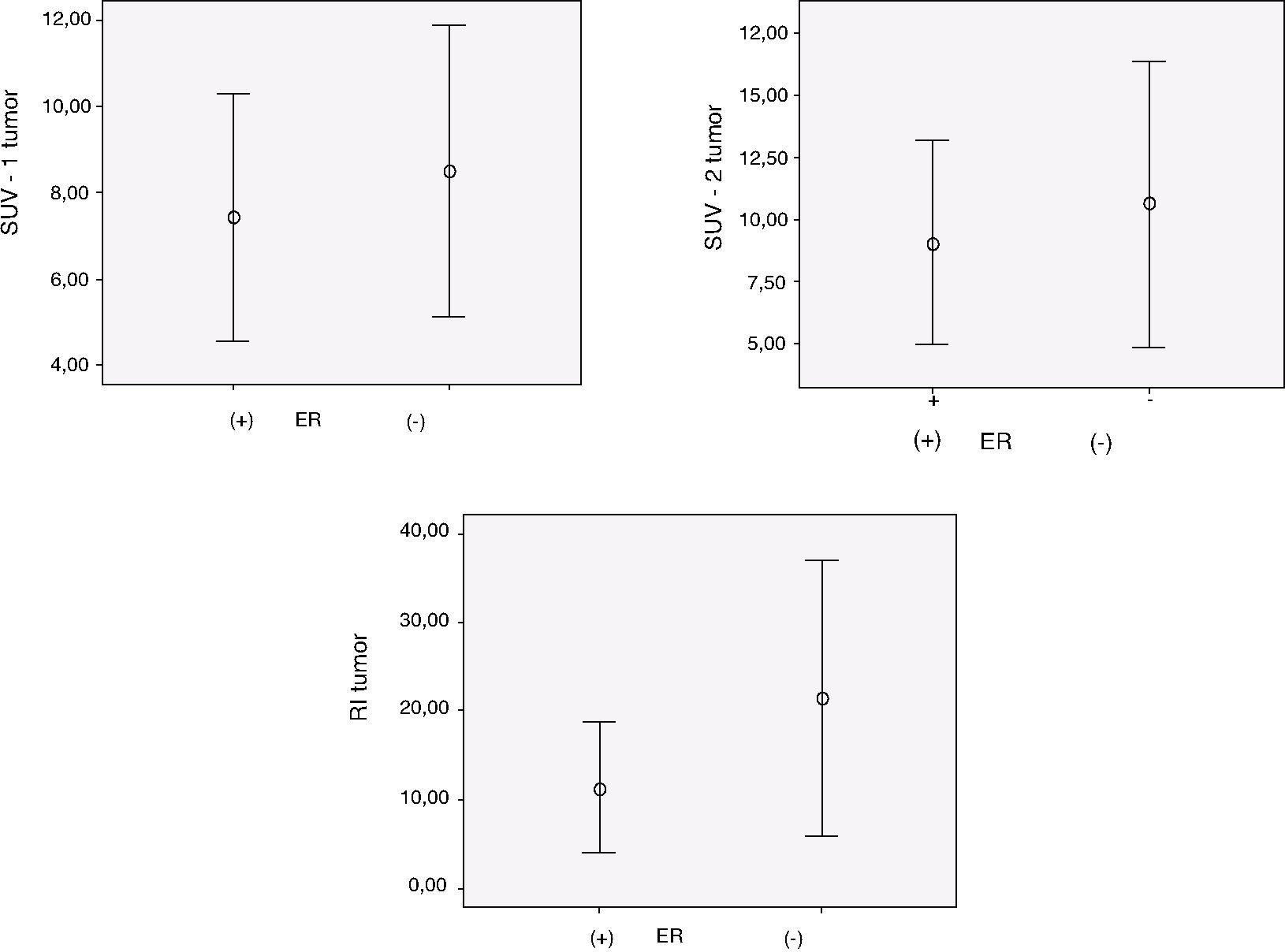
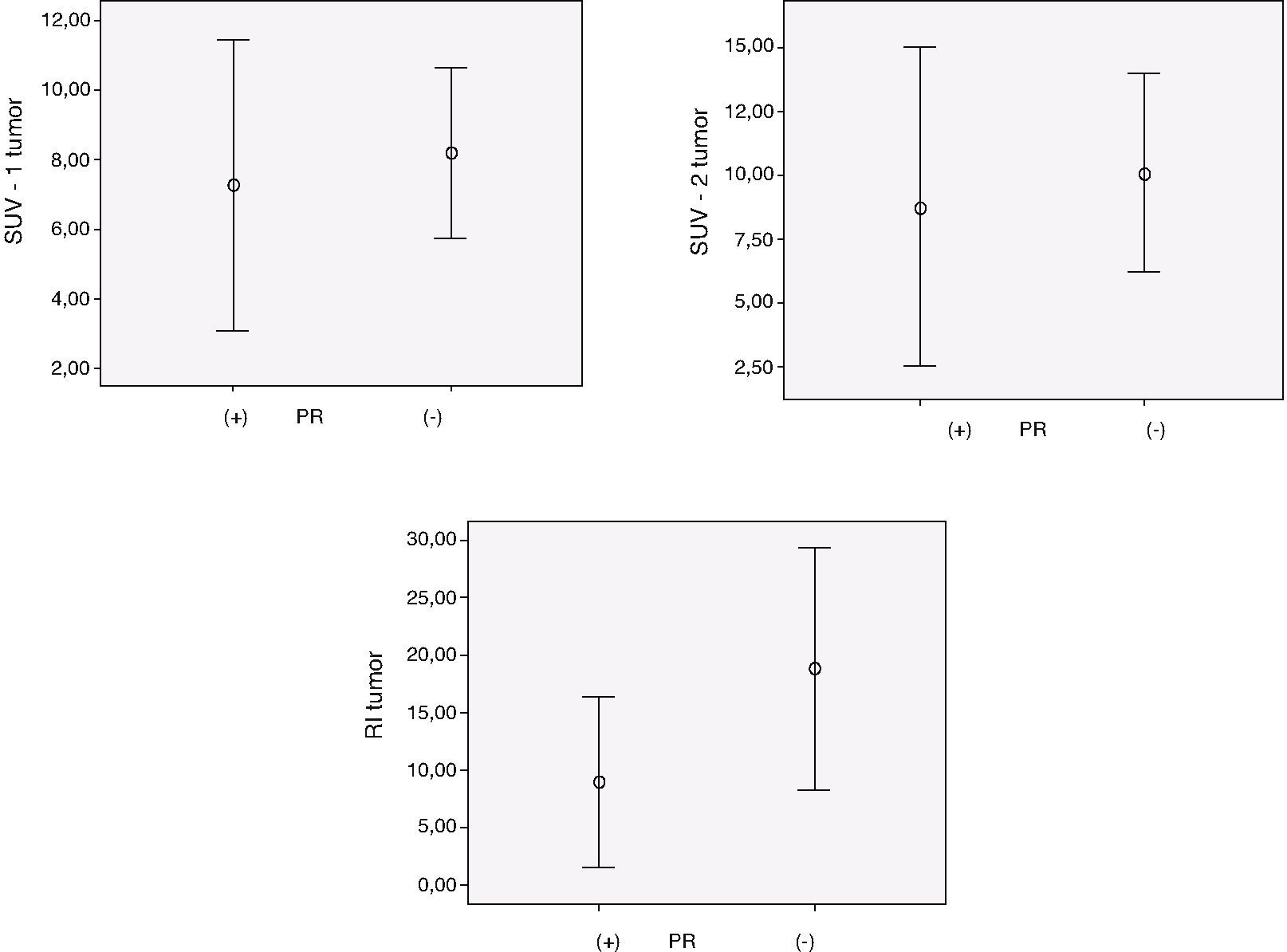
About the biological parameters, retention index showed the best results with positive and significant relation (p<.05) with estrogen and progesterone receptor status and Ki-67. Isolated SUV values did not show significant relation to these parameters.
ConclusionRetention index showed the best relation with biological parameters compared to isolated SUVmax values. These data suggest that SUV change over time is a prognostic marker.
Analizar la correlación entre la captación de 18FFDG valorada por la PET-TC en cáncer de mama localmente avanzado y factores pronósticos histopatológicos e inmunohistoquímicos.
Material y métodosSe valoraron prospectivamente 36 mujeres con cáncer de mama. La PET-TC fue requerida en la estadificación previamente al tratamiento quimioterápico (estudio multicéntrico).
A todas se les realizó una PET-TC con 18FFDG en 2 fases. Ambas fueron valoradas cualitativa y semicuantitativamente con cálculo del SUVmax en la PET-1 (SUV-1) y en la PET-2 (SUV-2) así como el índice de retención.
Los estadios clínicos y metabólicos fueron evaluados siguiendo la clasificación TNM. Se determinaron los parámetros biológicos pronósticos del tumor primario, como el estado de los receptores esteroideos, la expresión del p53 y c-erbB-2, el índice de proliferación (Ki-67) y el grado histológico. Los parámetros biológicos e histológicos fueron correlacionados.
ResultadosSe encontró una relación positiva entre los parámetros metabólicos semicuantitativos y los biológicos. Los valores de SUV-1 y SUV-2 no mostraron una correlación estadísticamente significativa excepto para el tamaño clínico tumoral.
Acerca de los parámetros biológicos, el índice de retención mostró los mejores resultados con relación positiva y significativa (p<0,05) con el estado de los receptores estrogénicos y progestágenos y el Ki-67. Los valores aislados del SUV no mostraron relación significativa con esos parámetros.
ConclusiónEl índice de retención mostró la mayor relación con los parámetros biológicos comparados con los valores aislados de SUVmax. Estos datos sugieren que el cambio del SUV es un marcador pronóstico.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)