There is still no consensus about whether to perform PET/CT to detect carcinoma in paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (PNS) in patients with or without antibodies. The aim of this study is to determine the diagnostic accuracy of PET/CT and antibodies in patients with PNS.
Material and MethodsA retrospective study was conducted on patients with clinically suspected PNS between 2008 and 2013. The association between histopathological findings, paraneoplastic antibodies, and PET/CT findings were evaluated. Sensitivity and specificity for the detection of underlying malignancy were calculated for PET/CT and paraneoplastic antibodies.
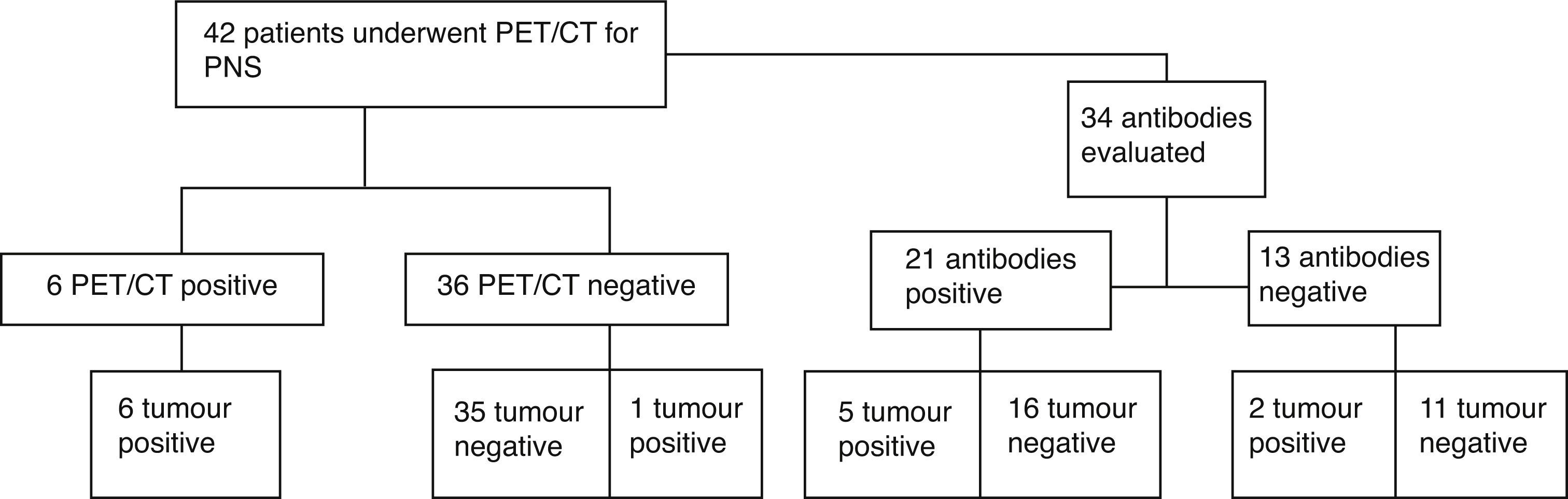
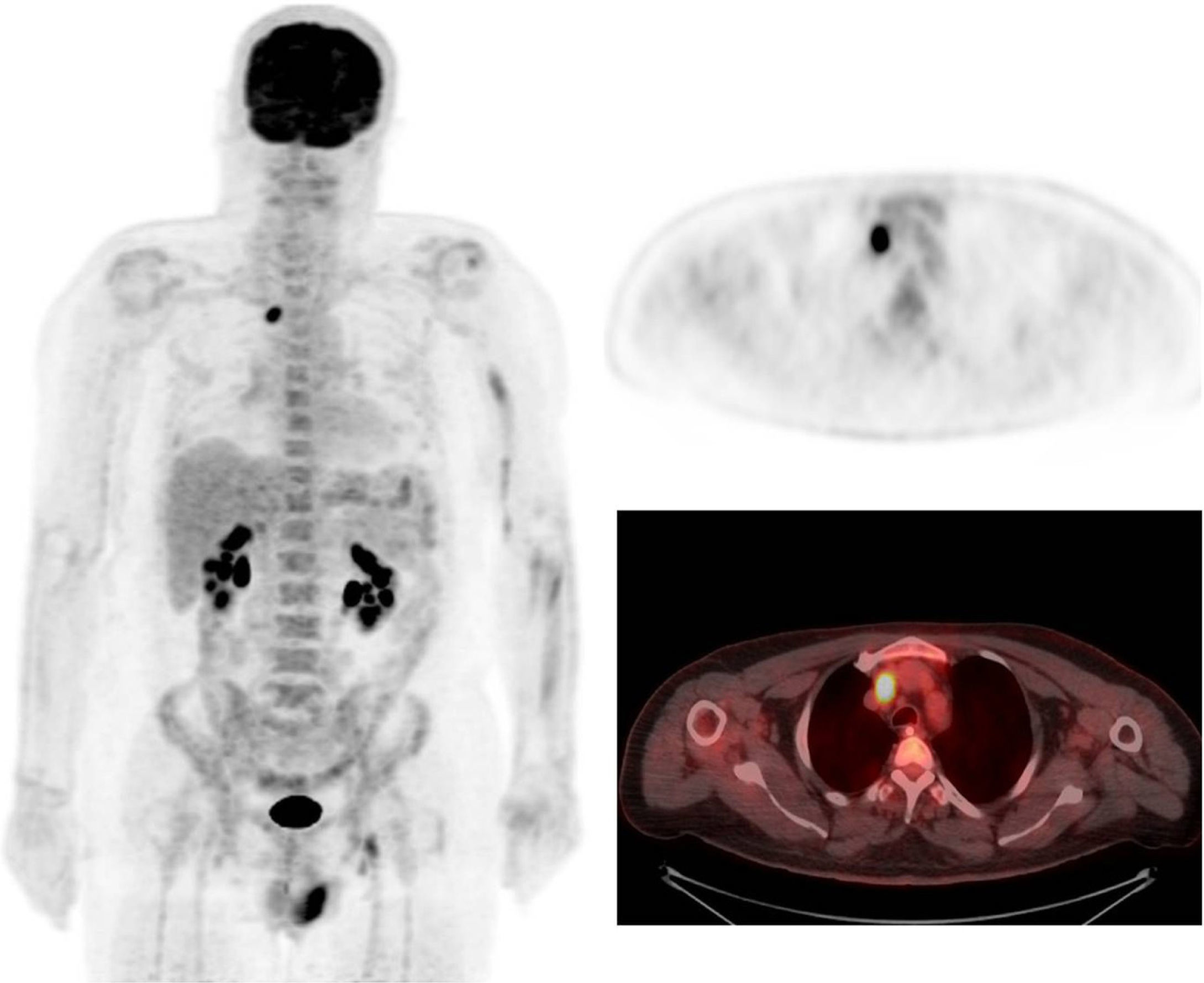
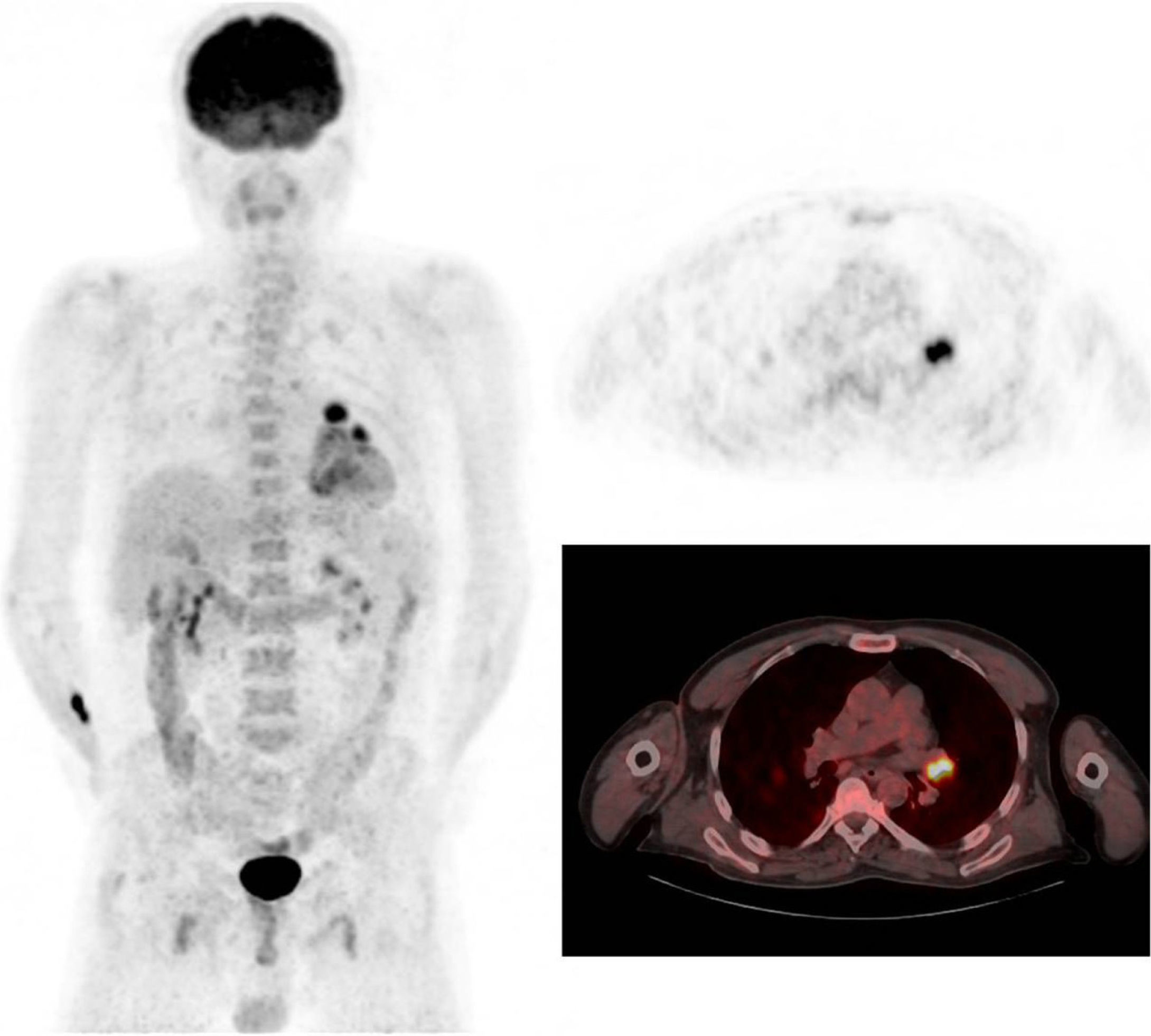
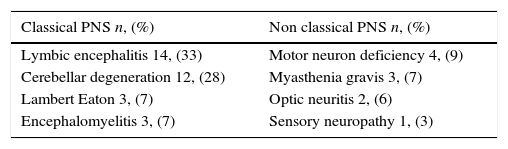
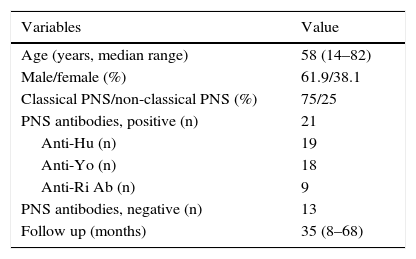
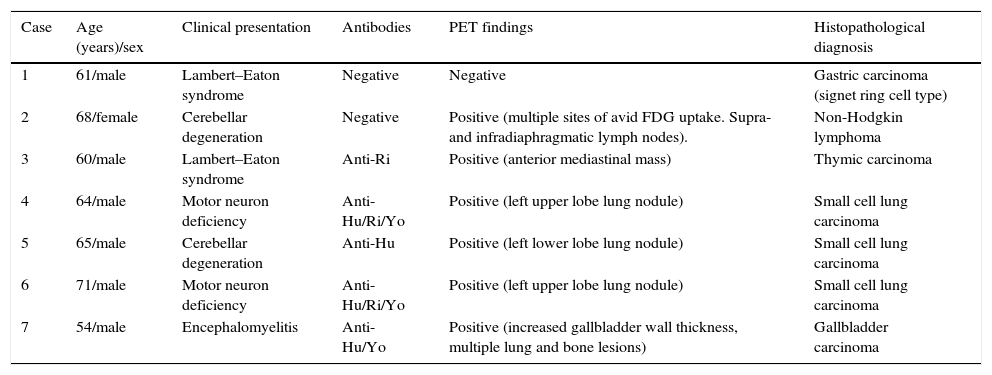
ResultsA total of 42 patients were analyzed. Of these 42 patients, 32 (75%) had a classical PNS, 6 (14%) had positive PET/CT findings, and 34 were tested for the presence of antibodies (anti-Hu Ab, anti-Yo Ab, and anti-Ri Ab). Twenty one of 34 patients had positive antibodies. Of the 6 patients with positive PET/CT findings, 6 had positive histopathological results. Among 21 patients with positive biomarkers, carcinoma was confirmed only in 5 patients. One patient with negative antibodies, but positive PET/CT findings, was diagnosed with a tumor. Gastric carcinoma was detected in 1 patient with negative PET/CT findings and antibodies during follow-up. Based on the results, PET/CT was found to have 85.71% sensitivity, 100% specificity, 100% positive and 97.22% negative predictive values in the detection of tumors.
ConclusionPET/CT has a certain diagnostic accuracy for detecting underlying malignancy in patients with PNS, regardless of the presence of paraneoplastic antibodies.
No hay un criterio unánime para realizar PET/TC en la detección de carcinoma en pacientes de síndrome neurológico paraneoplásico (PNS), con o sin anticuerpos. Nuestro objetivo es buscar la utilidad diagnóstica de la PET/TC y los anticuerpos en pacientes con PNS.
Material y métodosSe examinaron retrospectivamente los pacientes con sospecha clínica de PNS estudiados entre 2008 y 2013. Se evaluó la asociación entre los resultados histopatológicos, los anticuerpos y los resultados de la PET/TC. Se calcularon la sensibilidad y la especificidad de la PET/TC y de los anticuerpos paraneoplásicos para la detección de malignidad.
ResultadosSe analizaron un total de 42 pacientes. De ellos 32 pacientes (el 75%) tenían un PNS clásico. A todos se les había realizado PET/TC y 6 (el 14%) tuvieron resultados positivos. Se determinó la presencia de anticuerpos en 34 pacientes (anticuerpos anti-Hu, anticuerpos anti-Yo y anticuerpos anti-Ri). Veintiuno de los cuales dieron positivo. Los 6 pacientes con resultados PET/TC positivos tuvieron resultados histopatológicos positivos. Entre los 21 pacientes con biomarcadores positivos, el carcinoma se confirmó solo en 5 pacientes. A un paciente con resultado negativo para anticuerpos, pero positivo en la PET/TC, se le diagnosticó un tumor. Se detectó carcinoma gástrico en un paciente con resultados negativos en la PET/TC y anticuerpos en el periodo de seguimiento. Según los resultados, se comprobó que la PET/TC tiene un 85,71% de sensibilidad, un 100% de especificidad, con valor predictivo positivo de 100% y valor predictivo negativo de 97,22% en la detección de tumores.
ConclusiónLa PET/TC tiene un cierto grado de exactitud diagnóstica para detectar malignidad subyacente en pacientes con PNS, sin importar la presencia de anticuerpos paraneoplásicos.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)