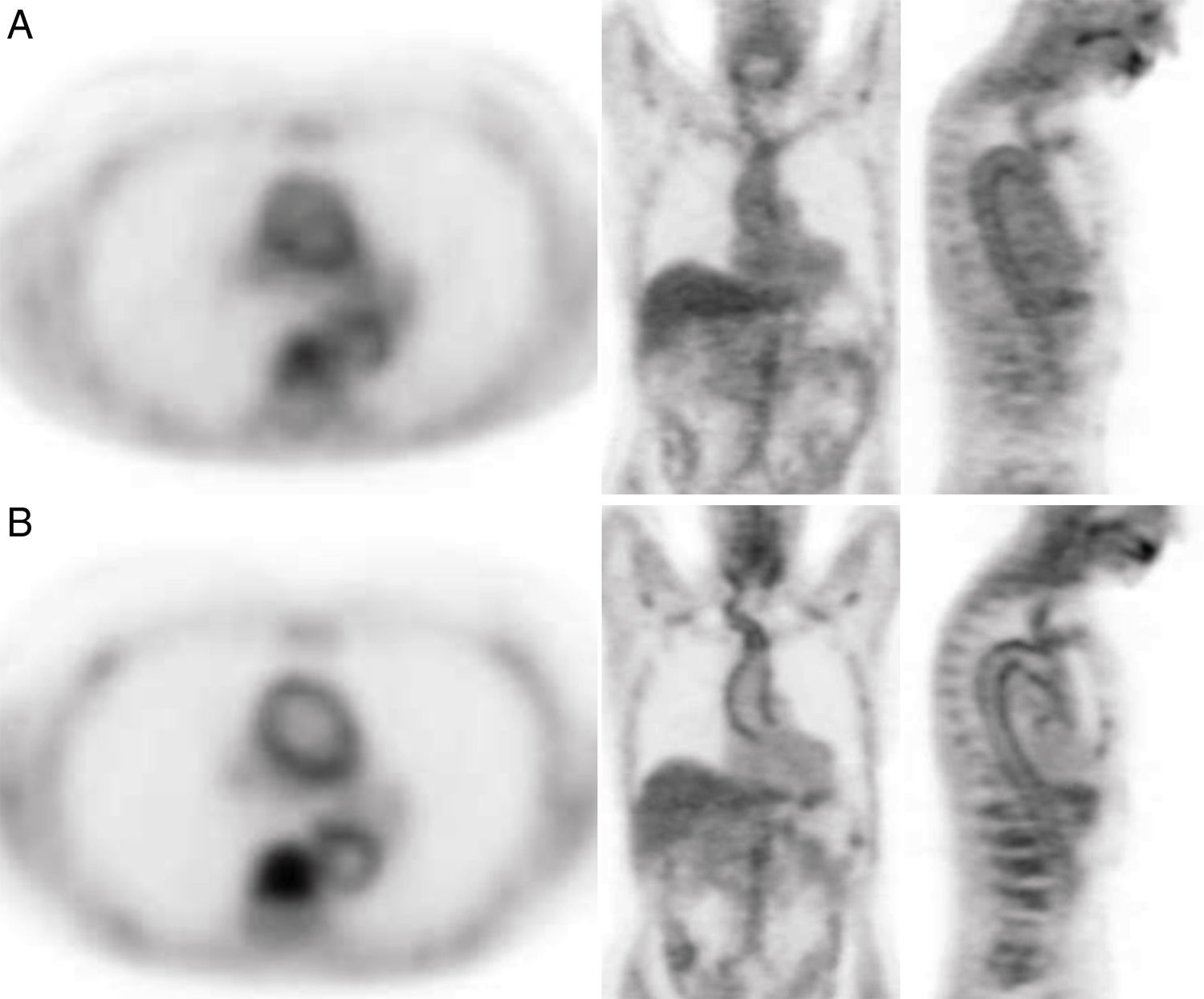
To compare the contribution of the 18F-FDG-PET/CT acquisition at 180min and at 60min in suspicion of large vessel vasculitis (LVV).
Material and methodsA prospective study including 23 patients was performed. PET/CT was acquired at 60 and 180min (early and delayed scan) after 18F-FDG injection. A visual analysis was performed at the supra-aortic trunks (SAT), thoracic aorta (TA), abdominal aorta (AA), iliac arteries (IA) and femoral/tibioperoneal arteries (FTA). Intensity (0–3) and uptake pattern (diffuse/linear) were assessed in the 115 vascular regions.
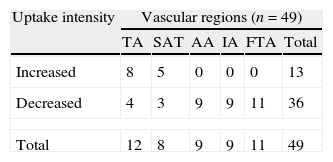
ResultsThere was no FDG uptake in the early and delayed acquisition in 20/115 vascular regions (17.4%). Of the 95 regions (82.6%) showing FDG uptake at the early, delayed or both acquisitions, intensity did not change in the delayed acquisition in 46 and changed in 49. Of the 49 regions in which the intensity changed, it decreased in 36 and increased in 13 (TA:8, SAT:5). AA, IA and FTA intensity did not increase in any of the cases. Uptake pattern at the TA in the early acquisition was diffuse in 16 patients. In 7, it changed to linear and in 9 the uptake disappeared. The early pattern was linear in 7 patients and 6 of them showed increased intensity in the delayed acquisition and in 1 remained the same.
ConclusionThe 180min delayed FDG-PET/CT acquisition provides a more detailed visualized of the vessel wall, showing the washout of the blood pool activity. Therefore, it may contribute to a more accurate diagnosis of LVV.
Comparar la contribución de la adquisición con 18F-FDG-PET/TC a 180min con la de 60min en sospecha de vasculitis de grandes vasos (VGV).
Material y métodosEste estudio prospectivo incluyó 23 pacientes. El estudio PET/TC fue adquirido a 60 y 180min (precoz y tardío) tras la administración de 18F-FDG. Se realizó un análisis visual de las imágenes valorando los troncos supraaórticos (TSA), la aorta torácica (AT), la abdominal (AA), las arterias ilíacas (AI) y las femoro/tibioperoneas (AFT). En las 115 regiones vasculares se evaluó la intensidad (0-3) y el patrón de captación (difuso/lineal).
ResultadosEn 20/115 regiones vasculares (17,4%) no hubo captación en la adquisición precoz y tardía. De las 95 regiones (82,6%) con captación en la adquisición precoz la intensidad no cambió en la tardía en 46 y cambió en 49. De esas 49 regiones en las que la intensidad cambió, esta disminuyó en 36 y aumentó en 13 (AT: 8, TSA: 5). En ningún caso la intensidad aumentó en la AA, las AI y las AFT. El patrón de captación en la AT fue difuso en la adquisición precoz en 16 pacientes, en 7 de ellos cambió a lineal en la tardía y desapareció en 9. El patrón precoz fue lineal en 7 pacientes, 6 de ellos mostraron un aumento de intensidad en la tardía y en uno permaneció igual.
ConclusiónLa adquisición tardía de 180min con FDG-PET/TC proporciona una más detallada visualización de la pared vascular, mostrando la desaparición de la actividad del pool vascular y contribuyendo a un más correcto diagnóstico de VGV.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)