Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)
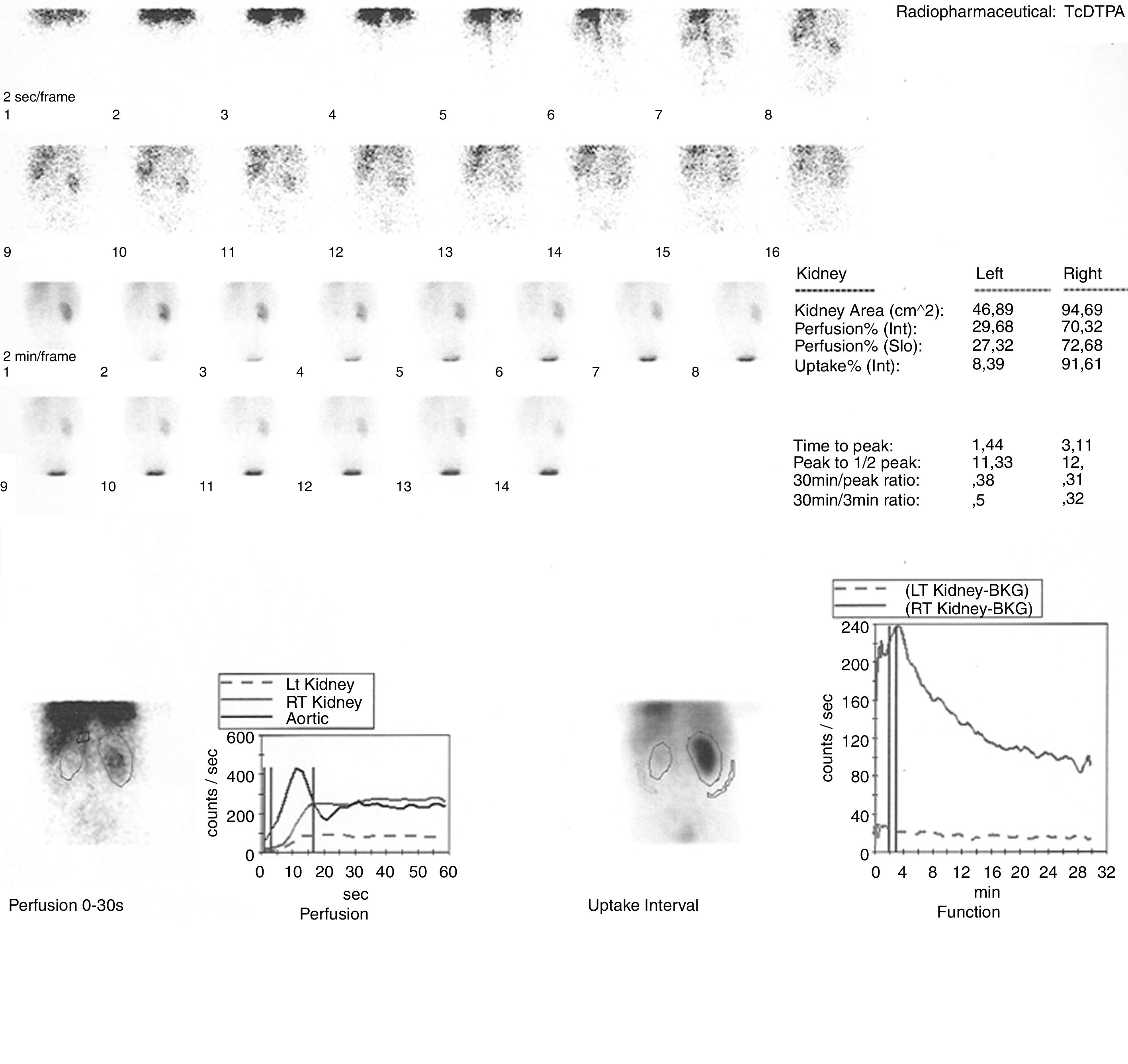
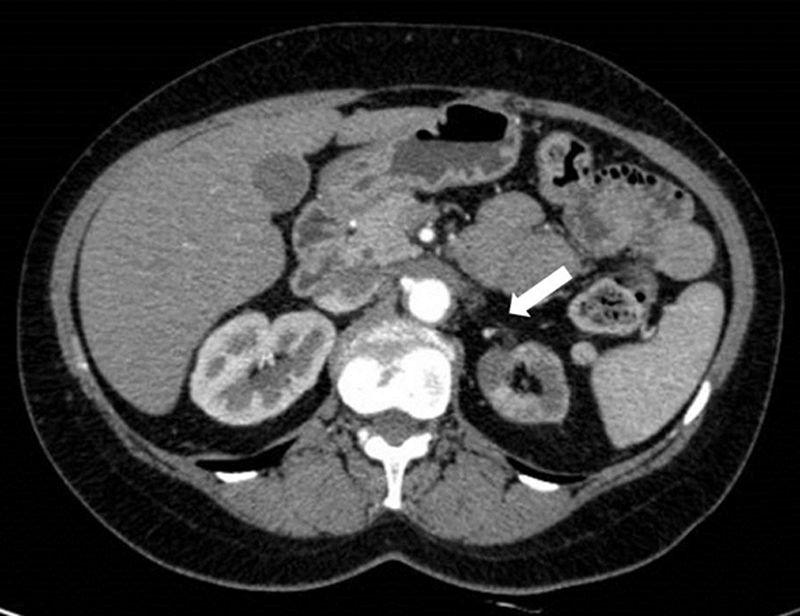
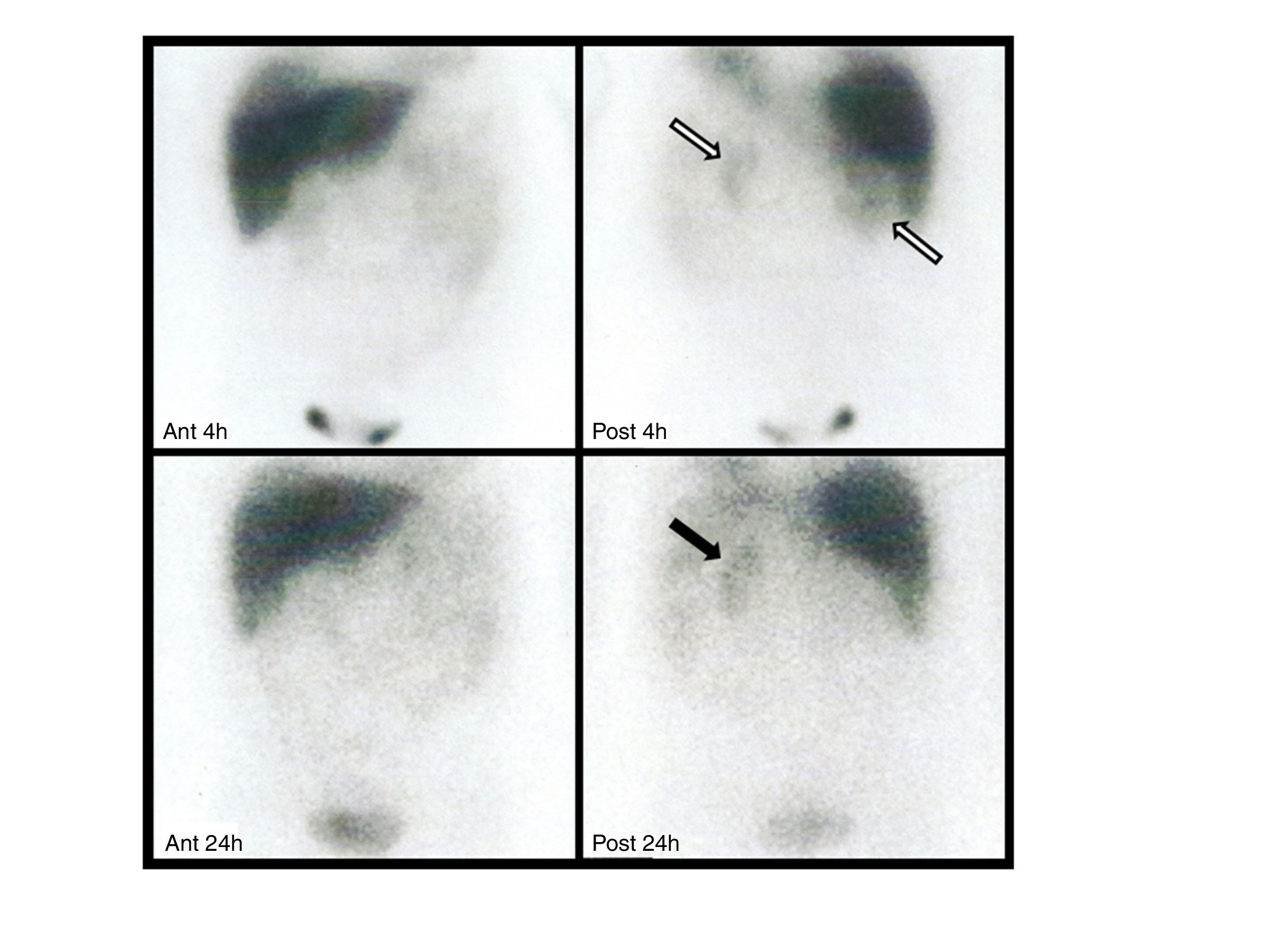
array:24 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300806" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.10.008" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-07-01" "aid" => "1011" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "copyrightAnyo" => "2018" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:247-9" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 1 "HTML" => 1 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18301057" "issn" => "2253654X" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.07.006" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-07-01" "aid" => "1011" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:247-9" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:2 [ "total" => 67 "formatos" => array:2 [ "HTML" => 39 "PDF" => 28 ] ] "es" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Imágenes de interés</span>" "titulo" => "Captación renal difusa de <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG en un paciente con estenosis severa de la arteria renal: una consecuencia de la activación adrenérgica" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "247" "paginaFinal" => "249" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "en" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Diffuse <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG renal uptake in a patient with severe renal artery stenosis: A consequence of adrenergic activation" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figura 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 616 "Ancho" => 800 "Tamanyo" => 59464 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "es" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">La angio-TC de abdomen confirmó la presencia de una estenosis severa al inicio de la arteria renal izquierda, con una placa de pared no calcificada (flecha); el riñón ipsilateral era pequeño y presentaba un adelgazamiento cortical.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "V. Scolozzi, G. Perotti, G. Gambaro, G. Celi, A. Giordano" "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "V." "apellidos" => "Scolozzi" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "G." "apellidos" => "Perotti" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "G." "apellidos" => "Gambaro" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "G." "apellidos" => "Celi" ] 4 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "A." "apellidos" => "Giordano" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253808918300806" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.10.008" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300806?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18301057?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/2253654X/0000003800000004/v1_201906280916/S2253654X18301057/v1_201906280916/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253808918301150" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2018.11.004" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-07-01" "aid" => "1033" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:250-1" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Encrusted cystitis detected by <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG PET/CT" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "250" "paginaFinal" => "251" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Cistitis incrustada detectada por PET/TC con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">18</span>F-FDG" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 1091 "Ancho" => 1300 "Tamanyo" => 107268 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Maximum intensity projection (MIP) showing increased FDG uptake within urinary bladder (A). Axial PET images showing a higher FDG uptake in the posterior part of the bladder, clearly detectable despite urinary FDG outflow (B). Axial non-contrast enhanced CT with a bladder posterior wall thickening with calcifications within (C) and PET/CT fused images (D) with the high bladder FDG uptake corresponding to the lesion detected by CT.</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Mattia Bonacina, Domenico Albano, Rexhep Durmo, Fernando Barbera, Francesco Bertagna, Raffaele Giubbini" "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Mattia" "apellidos" => "Bonacina" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Domenico" "apellidos" => "Albano" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Rexhep" "apellidos" => "Durmo" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Fernando" "apellidos" => "Barbera" ] 4 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Francesco" "apellidos" => "Bertagna" ] 5 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Raffaele" "apellidos" => "Giubbini" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18301124" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2018.10.005" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18301124?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918301150?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000004/v1_201907020628/S2253808918301150/v1_201907020628/en/main.assets" ] "itemAnterior" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2253808919300199" "issn" => "22538089" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remnie.2019.02.002" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2019-07-01" "aid" => "1055" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:245-6" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:11 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Subacute cerebral infarction incidentally detected by <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-MDP bone scan" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "245" "paginaFinal" => "246" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Infarto cerebral subagudo detectado accidentalmente mediante gammagrafía ósea con <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>Tc-MDP" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 559 "Ancho" => 900 "Tamanyo" => 50567 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Subsequent MRI images showed slightly high signal intensity on diffusion weighted imaging and obvious enhancement (A and B, arrows).</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "Xun Tian, Rui Su, Chenyang Dai, Wei Lu" "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Xun" "apellidos" => "Tian" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Rui" "apellidos" => "Su" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Chenyang" "apellidos" => "Dai" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "Wei" "apellidos" => "Lu" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2253654X18302646" "doi" => "10.1016/j.remn.2019.01.004" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253654X18302646?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808919300199?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000004/v1_201907020628/S2253808919300199/v1_201907020628/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:14 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Interesting images</span>" "titulo" => "Diffuse <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG renal uptake in a patient with severe renal artery stenosis: a consequence of adrenergic activation" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "247" "paginaFinal" => "249" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "Valentina Scolozzi, Germano Perotti, Giovanni Gambaro, Giuseppe Celi, Alessandro Giordano" "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "Valentina" "apellidos" => "Scolozzi" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "valentina.scolozzi@gmail.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Germano" "apellidos" => "Perotti" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Giovanni" "apellidos" => "Gambaro" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Giuseppe" "apellidos" => "Celi" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">c</span>" "identificador" => "aff0015" ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "Alessandro" "apellidos" => "Giordano" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">d</span>" "identificador" => "aff0020" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:4 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Nuclear Medicine Unit, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Roma, Italy" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Nefrology Unit, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma, Italy" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] 2 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Radiology Unit, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Roma, Italy" "etiqueta" => "c" "identificador" => "aff0015" ] 3 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Nuclear Medicine Institute, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli IRCCS, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Roma, Italy" "etiqueta" => "d" "identificador" => "aff0020" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Captación renal difusa de <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG en un paciente con estenosis severa de la arteria renal: una consecuencia de la activación adrenérgica" ] ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0015" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 3" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr3.jpeg" "Alto" => 1750 "Ancho" => 2333 "Tamanyo" => 225829 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0015" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG scintigraphy was performed with planar anterior/posterior acquisitions of abdomen, 4 and 24<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h after the intravenous injection of 370<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>MBq of radiopharmaceutical. Early images showed abnormal and diffuse <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG uptake in both renal parenchyma (white arrows), compatible with physiological urinary excretion of the tracer. Delayed images showed increased activity in left kidney (black arrow), probably due to an increased sympathetic activity, whereas the right kidney was not visualized. No focal uptake in the left adrenal gland or other abnormalities were identified.</p>" ] ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A 48-year-old woman was referred to our center for severe hypertension resistant to therapy and ultrasound suspicion of left renal artery stenosis.</p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>TC-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) angioscintigraphy (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0005">Fig. 1</a>) showed a functionally excluded left kidney, consistent with left renal artery stenosis, confirmed by subsequent CT angiogram of abdomen (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0010">Fig. 2</a>). <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) scintigraphy was also performed because of a clinical suspicion of pheochromocytoma (globular aspect of left adrenal gland at CT and borderline level of urinary metanephrines). The scan showed diffuse and increased uptake in the whole left kidney parenchyma at 4 and 24<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h, but no focal uptake in the left adrenal gland (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#fig0015">Fig. 3</a>).</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0005"></elsevierMultimedia><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0010"></elsevierMultimedia><elsevierMultimedia ident="fig0015"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG scintigraphy is usually performed for the evaluation of neuroendocrine tumors such us pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas, due to the specific uptake in sympathetic-adrenal cells,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0020"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> with an extremely low percentage of false-positive results. Focal renal <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG accumulation has already been reported in acute pyelonephritis (in the renal parenchyma)<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0025"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a> and in obstruction (in the renal pelvis). Conversely, diffuse renal <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG uptake is uncommon and has been previously attributed to compromised renal blood flow, as in cases of renal artery stenosis.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0030"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a> In our patient, the diffuse activity of the renal parenchyma, in the images acquired at 4<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h, is attributable to physiological urinary excretion of the tracer, being evident in both kidneys. Nevertheless, the diffuse uptake of the left kidney at 24<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h may be probably due to increased sympathetic activity, already described in patients with resistant hypertension and renal artery stenosis. Indeed, the activation of the sympathetic nervous system determines exacerbation of hypertension by enhancing renin release, decreasing renal blood flow, and increasing tubular sodium retention. In these cases, renal denervation is sometimes used to resolve hypertension and associated comorbidities.</p></span>" "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "NotaPie" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "☆" "nota" => "<p class="elsevierStyleNotepara" id="npar0005">Please cite this article as: Scolozzi V, Perotti G, Gambaro G, Celi G, Giordano A. Captación renal difusa de <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG en un paciente con estenosis de la arteria renal grave: una consecuencia de la activación Adrenérgica. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2019;38:247–249.</p>" ] ] "multimedia" => array:3 [ 0 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0005" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr1.jpeg" "Alto" => 2673 "Ancho" => 2833 "Tamanyo" => 326341 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>TC-DTPA renal angioscintigraphy did not show abnormalities in right kidney: morphology and size were normal; perfusion, uptake and excretion of the radiopharmaceutical were regular with a normal renogram curve. The left kidney showed an extremely low <span class="elsevierStyleSup">99m</span>TC-DTPA uptake, with poor visualization during the entire dynamic acquisition and a renogram characterized by typical “plateau”. The relative percentage of radiopharmaceutical uptake was 92% for the right kidney and 8% for the left kidney. These findings were suggestive of functionally excluded left kidney, in agreement with the suspicion of left renal artery stenosis.</p>" ] ] 1 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 616 "Ancho" => 800 "Tamanyo" => 62075 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">CT-angiogram of abdomen confirmed the presence of a severe stenosis at the beginning of the left renal artery with a non-calcified wall plaque (arrow); the ipsilateral kidney was small with low cortical thickness.</p>" ] ] 2 => array:7 [ "identificador" => "fig0015" "etiqueta" => "Fig. 3" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr3.jpeg" "Alto" => 1750 "Ancho" => 2333 "Tamanyo" => 225829 ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0015" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG scintigraphy was performed with planar anterior/posterior acquisitions of abdomen, 4 and 24<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>h after the intravenous injection of 370<span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>MBq of radiopharmaceutical. Early images showed abnormal and diffuse <span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I-MIBG uptake in both renal parenchyma (white arrows), compatible with physiological urinary excretion of the tracer. Delayed images showed increased activity in left kidney (black arrow), probably due to an increased sympathetic activity, whereas the right kidney was not visualized. No focal uptake in the left adrenal gland or other abnormalities were identified.</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0015" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:3 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0020" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "The evolution in the use of MIBG scintigraphy in pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "V. Rufini" 1 => "G. Treglia" 2 => "G. Perotti" 3 => "A. Giordano" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:5 [ "tituloSerie" => "Hormones (Athens)" "fecha" => "2013" "volumen" => "12" "paginaInicial" => "58" "paginaFinal" => "68" ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0025" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Unusual Tc-99m MDP and I-123 MIBG images in focal pyelonephritis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "A. Jacobs" 1 => "P. Lenoir" 2 => "M. Delree" 3 => "J. Ramet" 4 => "A. Piepsz" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Clin Nucl Med" "fecha" => "1990" "volumen" => "15" "paginaInicial" => "821" "paginaFinal" => "824" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2292157" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0030" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">123</span>I MIBG appearance of severe renal artery stenosis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "A. Jordan" 1 => "M. Seltzer" 2 => "A. Siegel" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1097/RLU.0000000000000510" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Clin Nucl Med" "fecha" => "2014" "volumen" => "39" "paginaInicial" => "1003" "paginaFinal" => "1004" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25243940" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/22538089/0000003800000004/v1_201907020628/S2253808918300806/v1_201907020628/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "47121" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Interesting image" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/22538089/0000003800000004/v1_201907020628/S2253808918300806/v1_201907020628/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2253808918300806?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Consulte los artículos y contenidos publicados en éste medio, además de los e-sumarios de las revistas científicas en el mismo momento de publicación
Esté informado en todo momento gracias a las alertas y novedades
Acceda a promociones exclusivas en suscripciones, lanzamientos y cursos acreditados
The Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (Spanish Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging), was founded in 1982, and is the official journal of the Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, which has more than 700 members. The Journal, which publishes 6 regular issues per year, has the promotion of research and continuing education in all fields of Nuclear Medicine as its main aim. For this, its principal sections are Originals, Clinical Notes, Images of Interest, and Special Collaboration articles. The works may be submitted in Spanish or English and are subjected to a peer review process. In 2009, it became the leading Spanish journal in the field of Medical Imaging on having an Impact Factor , awarded by the Journal Citation Reports.
Science Citation Index Expander, Medline, IME, Bibliomed, EMBASE/Excerpta Medica, Healthstar, Cancerlit, Toxine, Inside Conferences, Scopus
See moreThe Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years.
© Clarivate Analytics, Journal Citation Reports 2022
SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact.
See moreSNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field.
See more
Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)

¿Es usted profesional sanitario apto para prescribir o dispensar medicamentos?
Are you a health professional able to prescribe or dispense drugs?
Você é um profissional de saúde habilitado a prescrever ou dispensar medicamentos