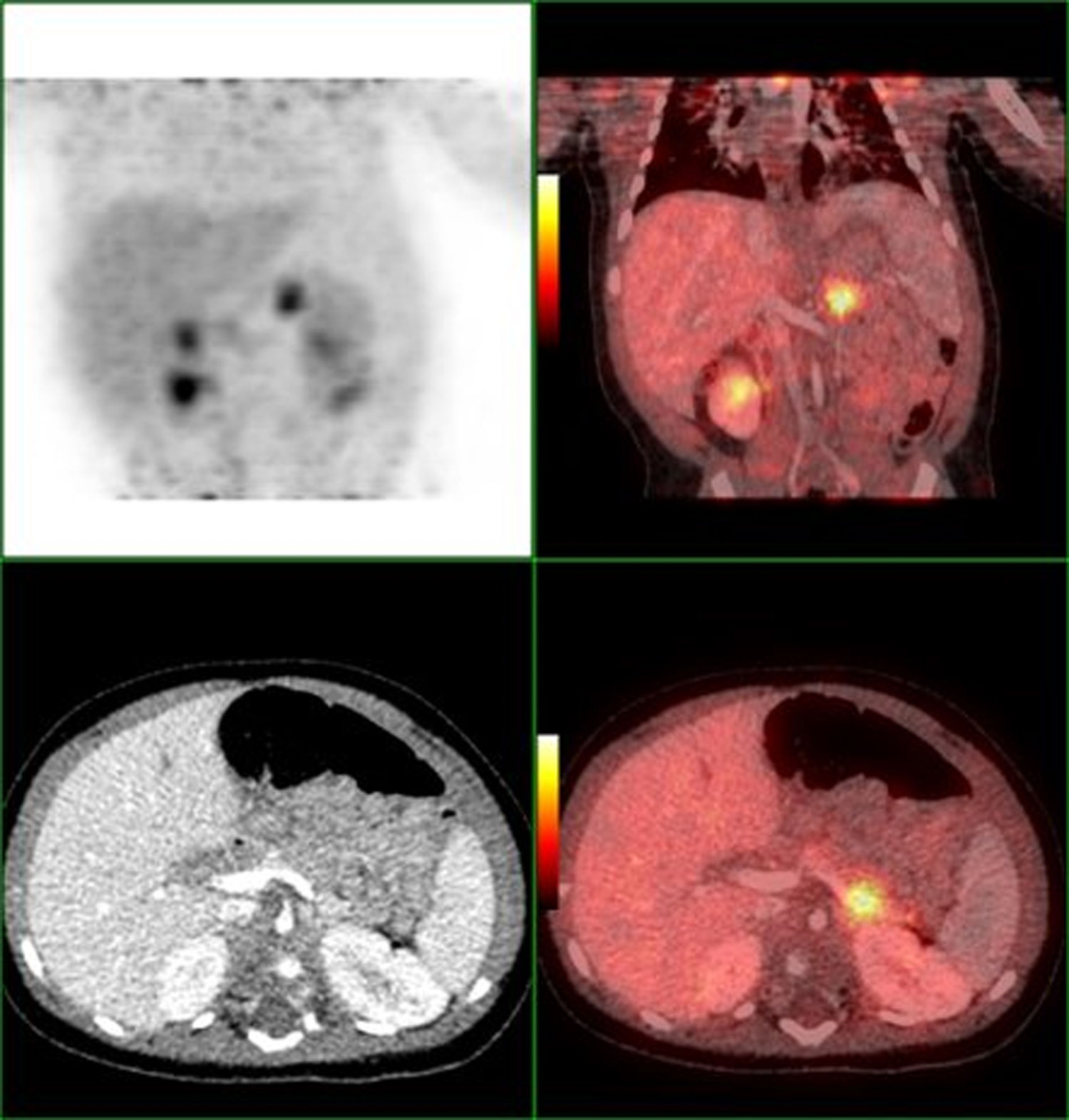
El hiperinsulinismo congénito (HIC) es una enfermedad neuroendocrina con anomalías focales o difusas en el páncreas. Mientras que las formas difusas resistentes a los medicamentos requieren una pancreatectomía casi total o una farmacoterapia prolongada, el HIC focal podría ser tratado por resección quirúrgica dirigida. Por tanto, evaluamos la utilidad del 18F-DOPA PET/TC para identificar la forma pancreática focal.
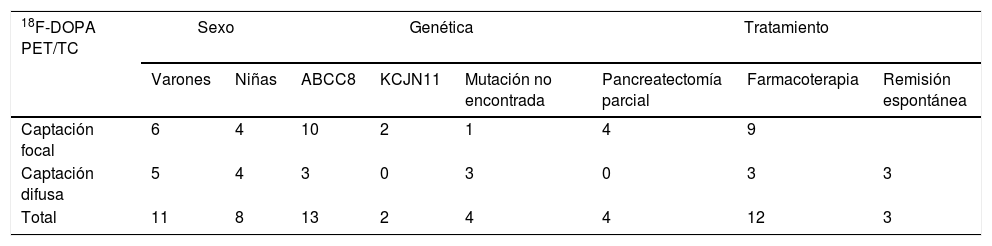
Objetivos y metodologíaDiecinueve niños (11 niños y 8 niñas de 2 a 54meses de edad) con signos clínicos de HIC neonatal y exámenes genéticos positivos fueron registrados en el estudio. Después de la administración intravenosa del 18F-DOPA, una primera PET y posteriormente otra PET/TC cubriendo longitudinalmente la región toracoabdominal fueron llevadas a cabo. Ambas adquisiciones fueron realizadas en modo dinámico para permitir la exclusión de imágenes con artefactos de movimiento. Los valores de absorción estandarizados fueron ajustados al peso corporal (SUVbw). El hallazgo fue considerado como focal cuando la proporción de SUVbwmax entre la región sospechosa y el resto del páncreas fue mayor que 1,2.
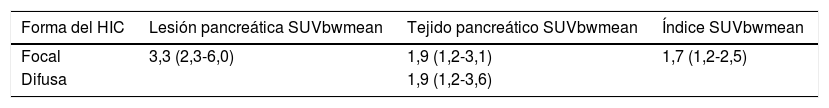
ResultadosLas formas focales fueron registradas en 10/19 niños y 4 de ellos se sometieron a una resección quirúrgica con recuperación completa. La captación focal fue significativamente mayor que la captación en el tejido pancreático normal (p=0,0059). Las formas focales y difusas del HIC no difieren significativamente en la captación del tejido pancreático normal. No encontramos ninguna ventaja en la medición de la relación SUVbwmean en comparación con la relación SUVbwmax (p=0,50).
Conclusiones18F-DOPA PET/TC es una herramienta útil para la localización de HIC focal y la planificación de un tratamiento quirúrgico.
Congenital hyperinsulinism (CHI) is a neuroendocrine disease with focal or diffuse abnormalities in pancreas. While drug-resistant diffuse forms require near-total pancreatectomy or prolonged pharmacotherapy, focal CHI may be treated by targeted surgical resection. We evaluated the usefulness of 18F-DOPA PET/CT to identify the focal pancreatic form.
Subjects and methodsNineteen children (11 boys, 8 girls, aged 2–54 months) with clinical signs of neonatal CHI and positive genetic examinations were enrolled in the study. After i.v. administration of 18F-DOPA, early PET and late PET/CT acquisition covering one-bed length over thoraco-abdominal region were performed. Both acquisitions were done in dynamic mode to allow exclusion of frames with motion artefacts. Standardized uptake values were adjusted to bodyweight (SUVbw). The finding was considered as focal when the ratio of SUVbwmax between the suspicious region and the rest of pancreas was greater than 1.2.
ResultsFocal forms were recorded in 10/19 children and 4 of them underwent surgical resection with complete recovery. Focal uptake was significantly higher than the uptake in the normal pancreatic tissue (p=0.0059). Focal and diffuse forms of CHI did not differ significantly in normal pancreatic tissue uptake. We found no advantage in the measurement of SUVbwmean ratio compared to SUVbwmax ratio (p=0.50).
Conclusion18F-DOPA PET/CT is a useful tool for the localization of focal CHI and planning of surgical treatment.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)