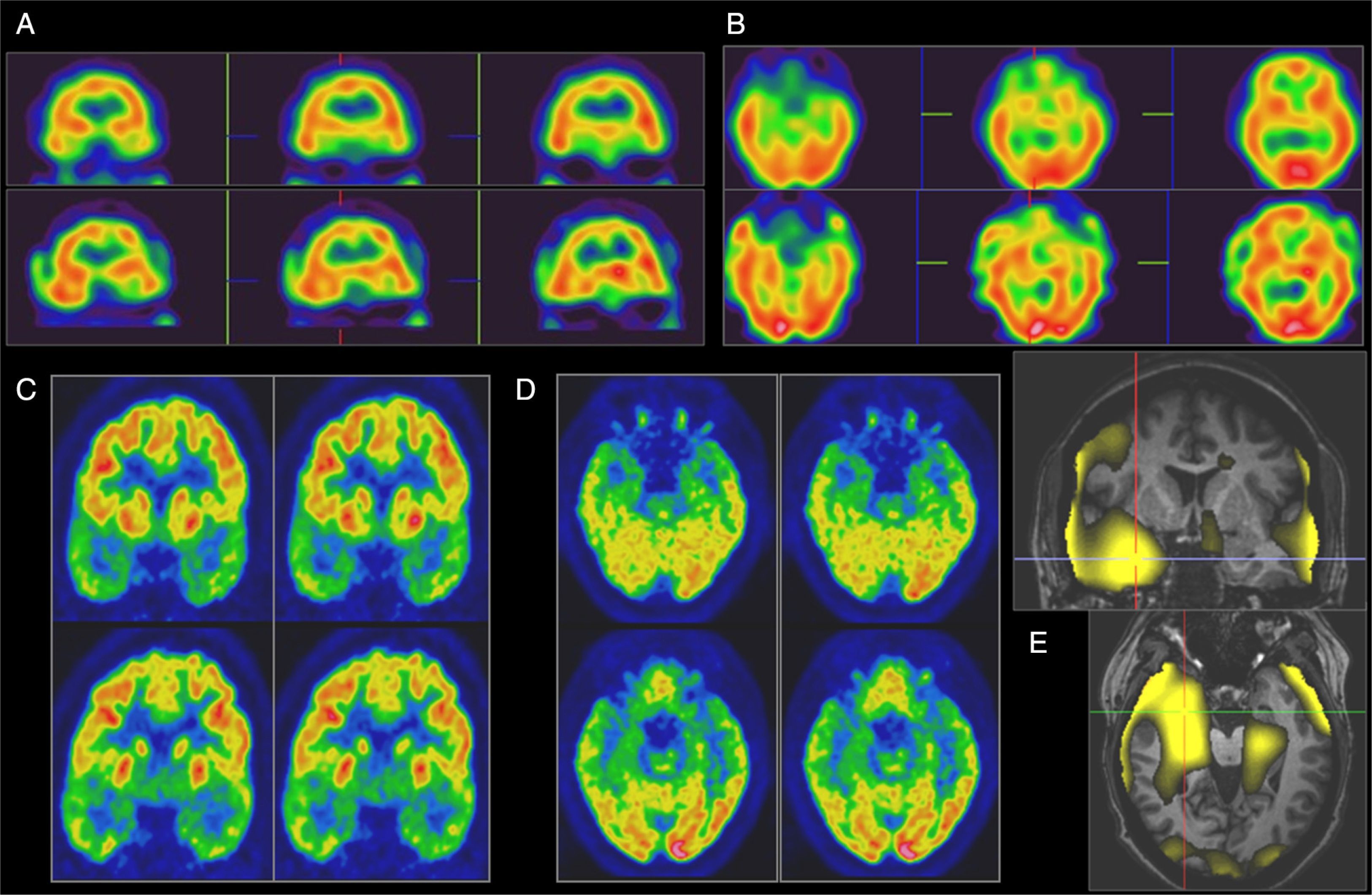
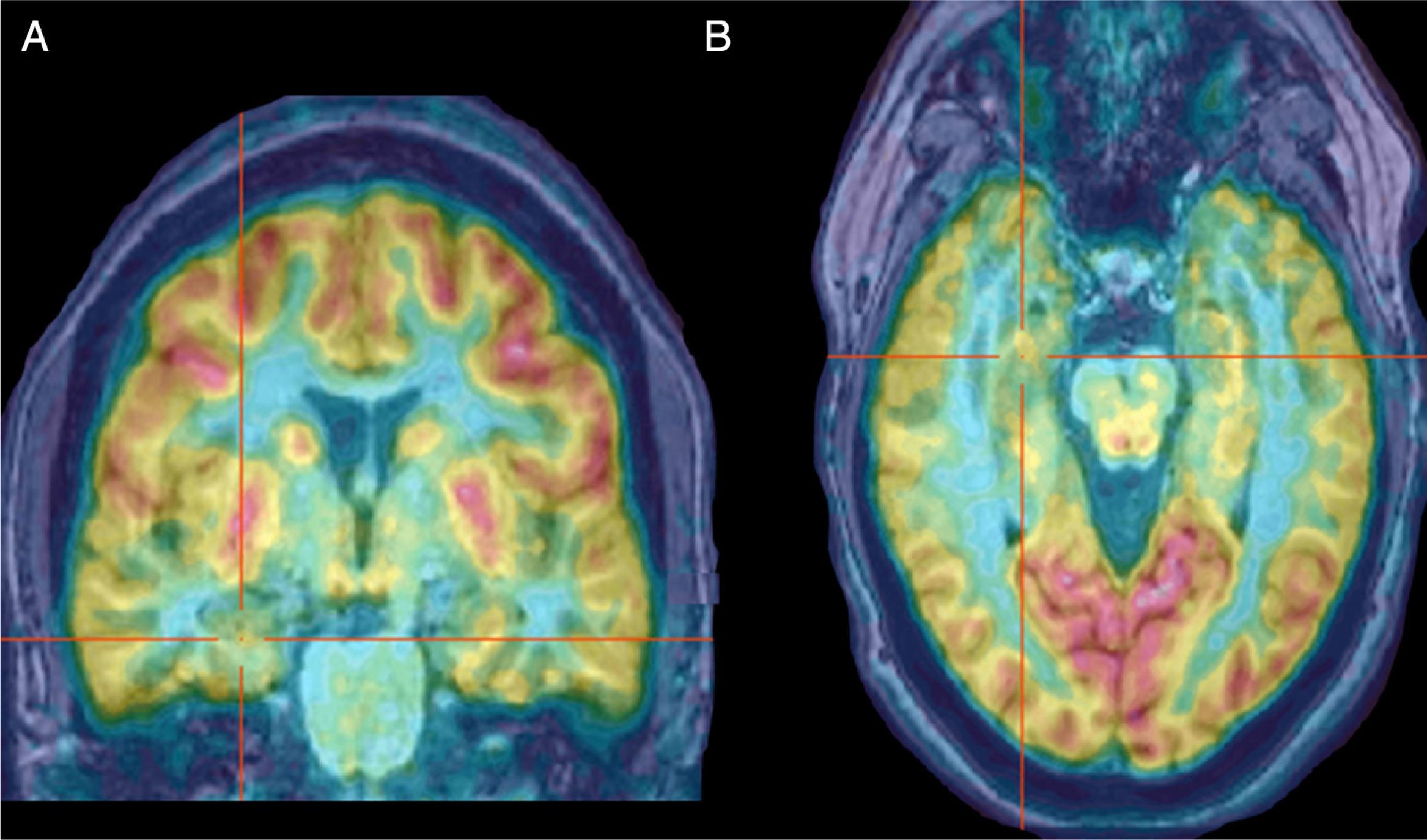
Brain perfusion SPECT (ictal–interictal), SPECT images and subtraction ictal SPECT coregistered to MRI (SISCOM) and 18F-FDG-PET (interictal) play an important role in the pre-surgical diagnosis of patients with medically refractory epilepsy.
This study aimed to establish the reproducibility of visual ictal–interictal SPECT and SISCOM analysis altogether with the capacity of SPECT, SISCOM and PET to determine the epileptogenic zone.
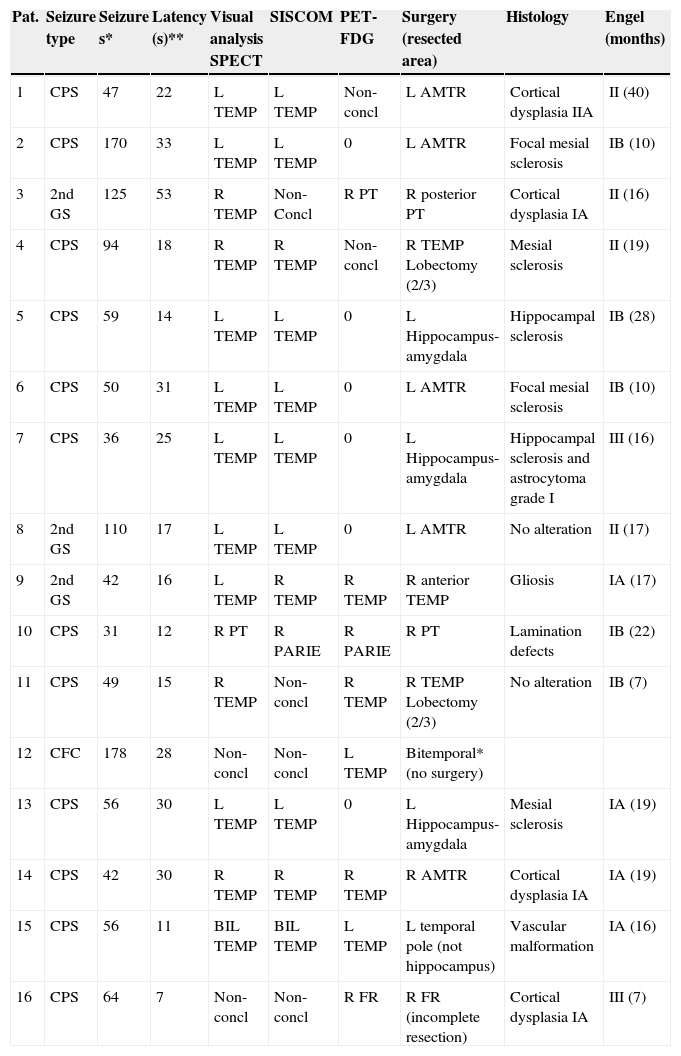
Material and methods99mTc-HMPAO SPECT ictal–interictal and SISCOM (Analyze 7.0) were performed on 47 refractory epilepsy patients (24 F, 19–60 yrs). In 13 patients, SISCOM was also performed using a new programme (Focus DET). Ictal–interictal SPECT and SISCOM images were analyzed independently by two nuclear medicine physicians (observers 1 and 2). Kappa concordance coefficient was used to evaluate the reproducibility. In sixteen patients, SPECT, SISCOM and PET findings were compared with the resected area during the surgery, and surgical outcome using Engel scale or with the stereo EEG-(SEEG).
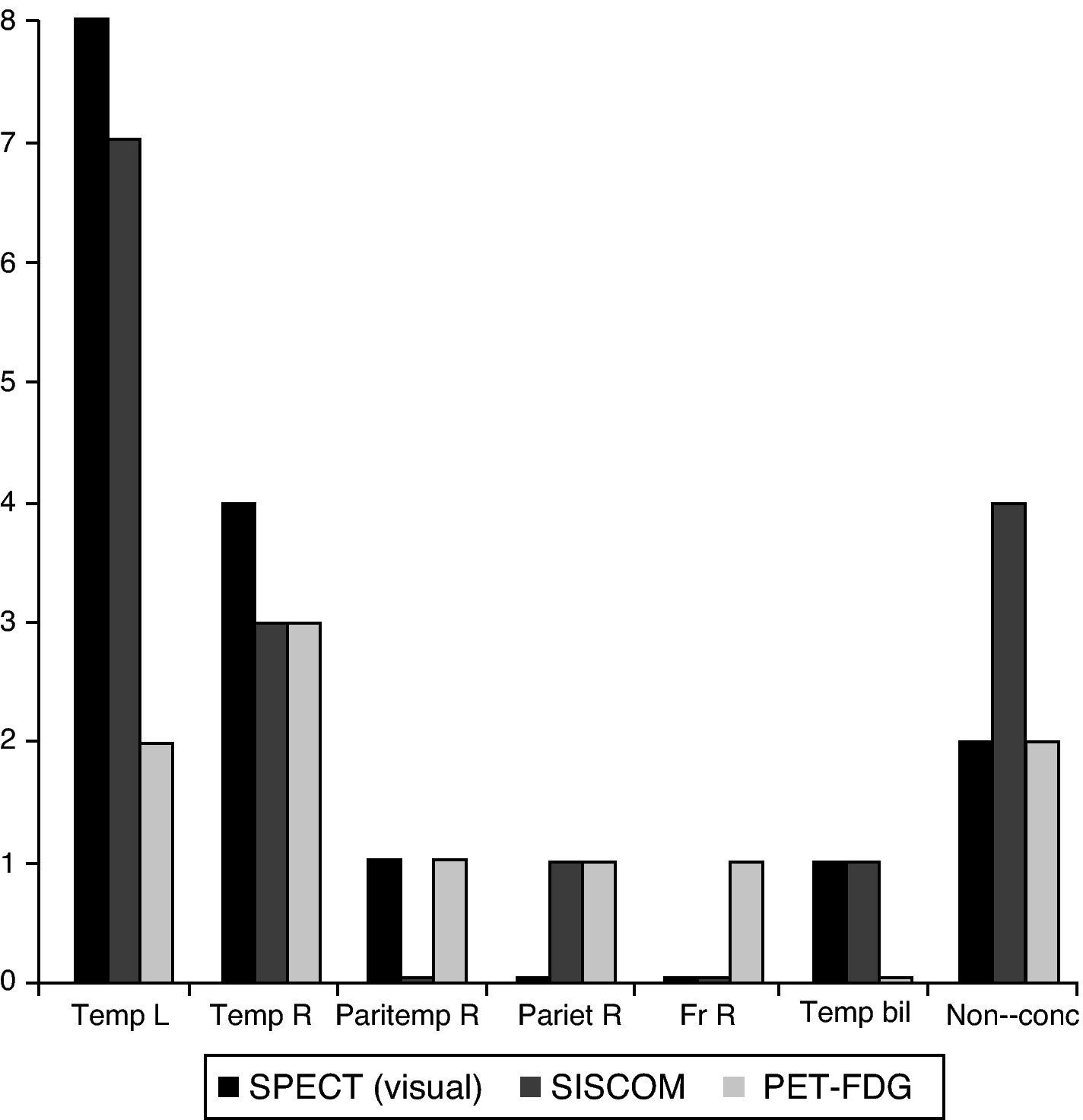
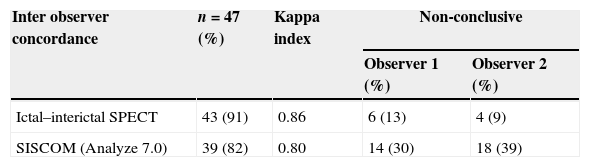
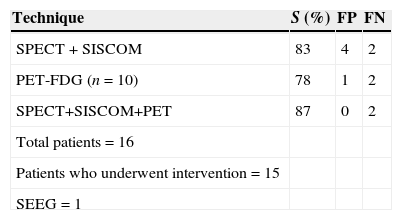
ResultsThe ictal–interictal SPECT interobserver agreement was 91%, Kappa index 0.86, SISCOM (Analyze 7.0) interobserver agreement percentage was 82%, Kappa index 0.80, Analyze 7.0 showed a higher inconclusive results than visual SPECT analysis. SISCOM FocusDET interobserver agreement was 92%, Kappa index 0.87, with lower inconclusive results than Analyze 7.0. SPECT, SISCOM and PET combined findings identified 87% seizure onset zone: 79% temporal, 26% parieto-temporal and 7% frontal.
ConclusionsIctal–interictal SPECT and SISCOM showed a high reproducibility in this sample of patients with drug-refractory epilepsy. SPECT, SISCOM and PET combined findings improved detection of epileptogenic zone in comparison with the individual assessment.
La SPECT de perfusión ictal-interictal, subtraction ictal SPECT coregistered to MRI (SISCOM) y 18F-FDG-PET (interictal), desempeñan un papel fundamental en la valoración prequirúrgica del paciente epiléptico fármaco-resistente.
Los objetivos de este trabajo fueron establecer la reproducibilidad del análisis visual de la SPECT y SISCOM y la capacidad de la SPECT, SISCOM y PET en la identificación del foco epileptógeno.
Material y métodosSe realizó una SPECT 99mTc-HMPAO (ictal-interictal) y SISCOM (Analyze 7.0) en 47 pacientes epilépticos fármaco-resistentes (24M, 19–60 años). En 13 pacientes se repitió el SISCOM utilizando el programa FocusDET. El análisis de las imágenes fue realizado por 2 observadores. Se valoró la reproducibilidad utilizando el índice Kappa. Los resultados conjuntos de la SPECT, SISCOM y PET, en 16 pacientes, fueron comparados con la localización del área resecada y el seguimiento clínico poscirugía (escala de Engel) o con la estereo-EEG.
ResultadosGrado de acuerdo interobservador de la SPECT 91% índice Kappa 0,86. Grado de acuerdo interobservador SISCOM Analyze 7.0 82%, índice Kappa 0,80. El Analyze 7.0 mostró un elevado número de resultados no concluyentes, superior al del análisis visual. El SISCOM FocusDET mostró un grado de acuerdo interobservador 92% con un índice Kappa 0,87 y menor número de resultados no concluyentes que el Analyze. La valoración conjunta SPECT, SISCOM y PET permitió identificar 87% focos epileptógenos: 79% temporales, 26% parieto-temporales y 7% frontales.
ConclusiónLa SPECT ictal-interictal y el SISCOM mostraron una elevada reproducibilidad. La valoración conjunta de la SPECT ictal-interictal, SISCOM y PET permitió mejorar la rentabilidad diagnóstica de la valoración individualizada.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)