F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose integrated PET-CT scan is commonly used in the work-up of lung cancer to improve preoperative disease stage. The aim of the study was to analyze the ratio between SUVmax of N1 lymph nodes and primary lung cancer to establish prediction of mediastinal disease (N2) in patients operated on non-small cell lung cancer.
Material and methodThis is a retrospective study of a prospective database. Patients operated on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with N1 disease by PET-CT scan were included. None of them had previous induction treatment, but they underwent standard surgical resection plus systematic lymphadenectomy.
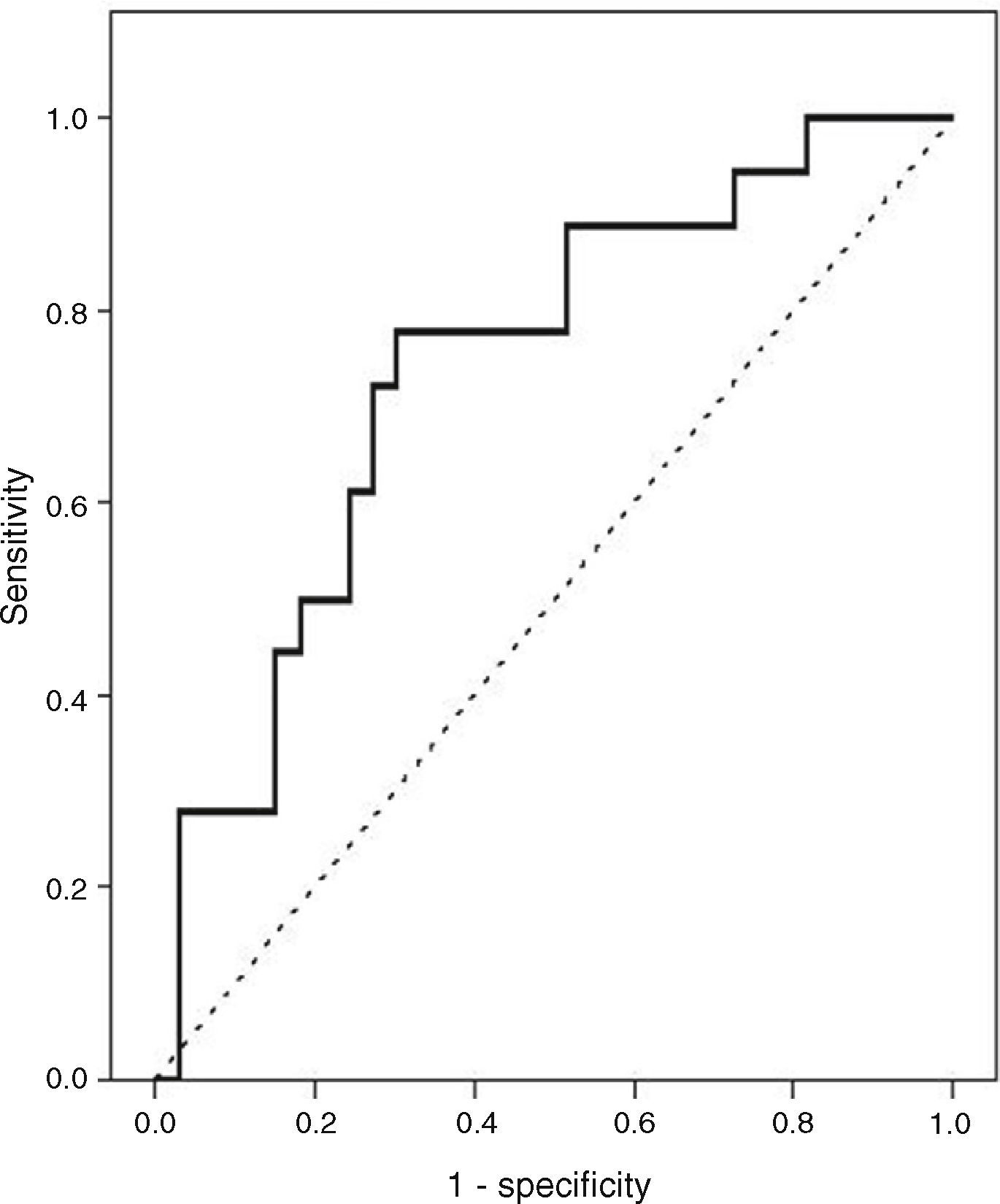
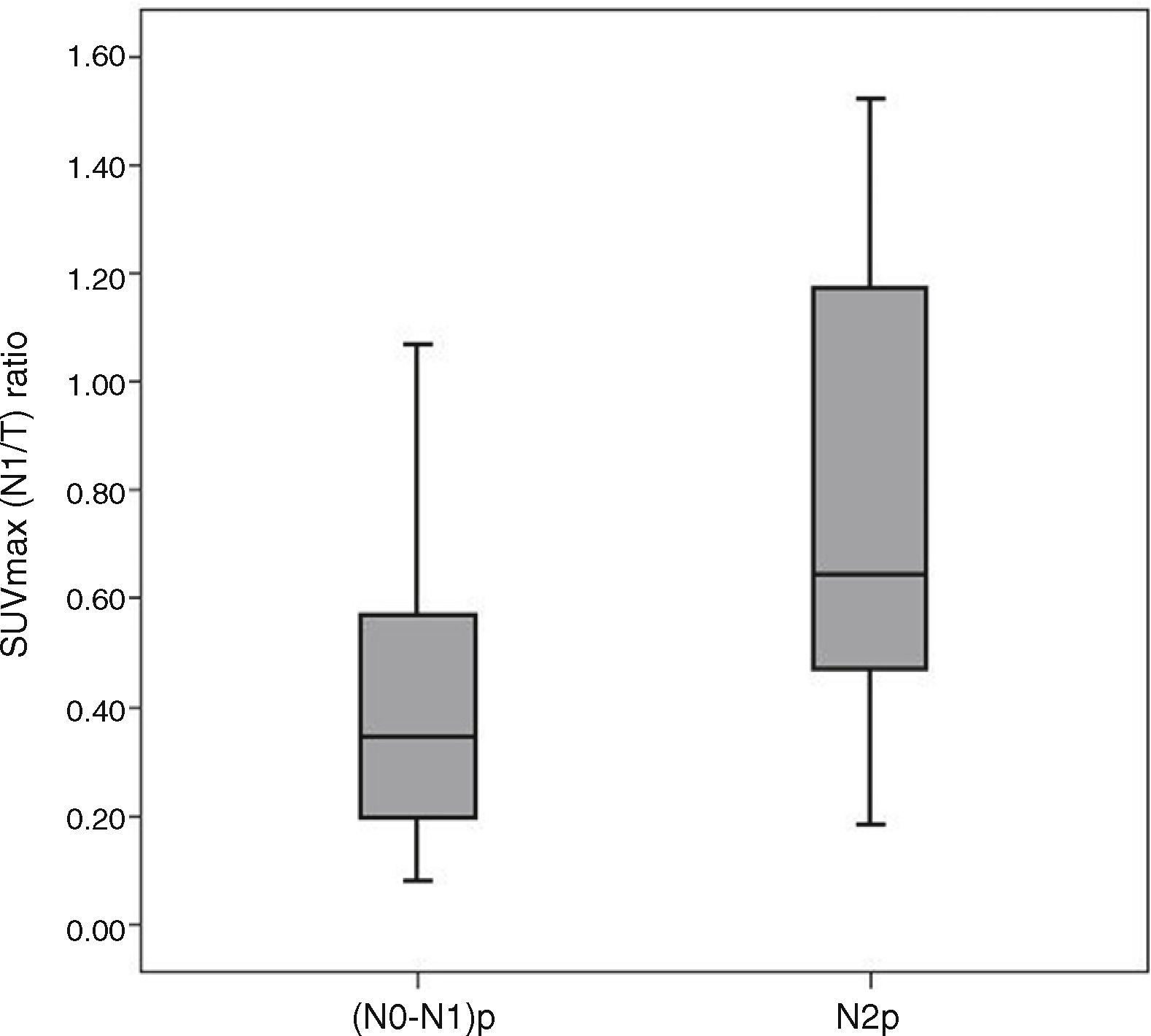
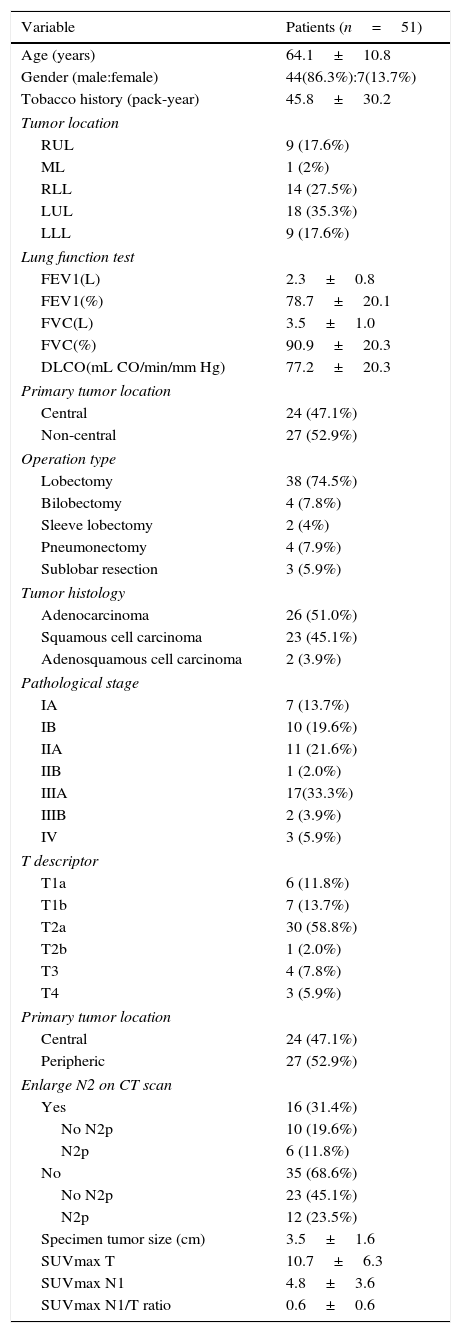
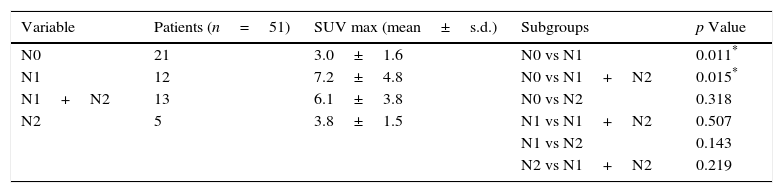
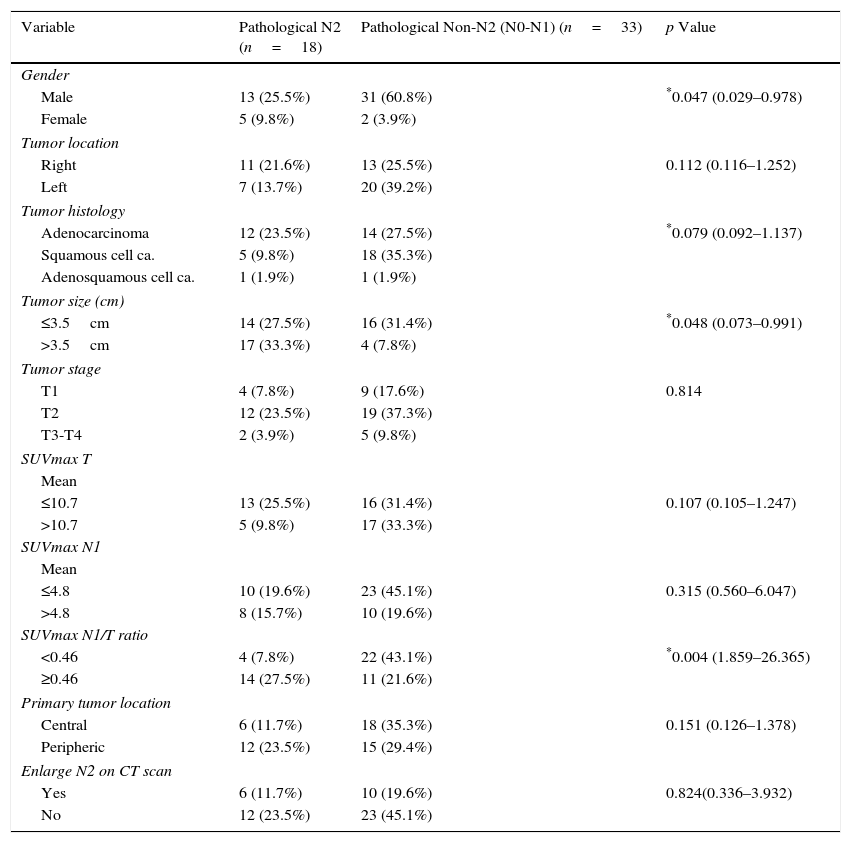
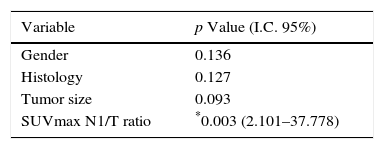
ResultsThere were 51 patients with FDG-PET-CT scan N1 disease. 44 (86.3%) patients were male with a mean age of 64.1±10.8 years. Type of resection: pneumonectomy=4 (7.9%), lobectomy/bilobectomy=44 (86.2%), segmentectomy=3 (5.9%). Histology: adenocarcinoma=26 (51.0%), squamous=23 (45.1%), adenosquamous=2 (3.9%). Lymph nodes after surgical resection: N0=21 (41.2%), N1=12 (23.5%), N2=18 (35.3%). Mean ratio of the SUVmax of N1 lymph node to the SUVmax of the primary lung tumor (SUVmax N1/T ratio) was 0.60 (range 0.08–2.80). ROC curve analysis to obtain the optimal cut-off value of SUVmax N1/T ratio to predict N2 disease was performed. At multivariate analysis, we found that a ratio of 0.46 or greater was an independent predictor factor of N2 mediastinal lymph node metastases with a sensitivity and specificity of 77.8% and 69.7%, respectively.
ConclusionsSUVmax N1/T ratio in NSCLC patients correlates with mediastinal lymph node metastasis (N2 disease) after surgical resection. When SUVmax N1/T ratio on integrated PET-CT scan is equal or superior to 0.46, special attention should be paid on higher probability of N2 disease.
La PET-TC integrada con F-18fluorodeoxiglucosa es utilizada frecuentemente en la estadificación preoperatoria del cáncer de pulmón(CP). El objetivo del estudio fue analizar la relación entre SUVmax de los ganglios linfáticos N1 con el tumor pulmonar para establecer un factor predictivo de enfermedad metastásica ganglionar en el mediastino(N2) en pacientes operados de cáncer de pulmón no microcítico.
Material y métodoEstudio retrospectivo de una base de datos prospectiva. Se incluyeron pacientes operados de CP con enfermedad N1 por PET-TC. Ninguno tuvo tratamiento previo. Se realizó una resección pulmonar estándar y linfadenectomía.
ResultadosHubo un total de 51 pacientes con N1 por PET-TC. 44(86,3%) fueron varones, edad media=64,1±10,8 años. Tipo de resección: neumonectomía=4(7,9%), lobectomía/bilobectomía=44(86,2%), segmentectomía=3(5,9%). Histología: adenocarcinoma=26(51,0), epidermoide=23(45,1%), adenoescamoso=2(3,9%). Ganglios linfáticos tras la resección: N0=21(41,2%), N1=12(23,5%), N2=18(35,3%). La relación media entre el SUVmax de los ganglios N1 con el SUVmax del tumor pulmonar (relación SUVmax N1/T) fue 0,60 (rango 0,08–2,80). El análisis de la curva ROC se realizó para determinar el punto de corte óptimo para predecir N2 (metástasis mediastínica). En el análisis multivariante encontramos que una relación de 0,46 o mayor fue un factor pronóstico independiente para N2, con una sensibilidad y especificidad de 77,8% y 69,7%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesLa relación SUVmax N1/T en pacientes con CP no microcítico se correlaciona con la metástasis ganglionar mediastínica (N2) después de la resección quirúrgica. Cuando la relación SUVmax N1/T en la PET-TC es igual o mayor de 0,46 se debería prestar atención especial por la alta probabilidad de enfermedad mediastínica N2.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)