The relation of PET-derived parameters as maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), total lesion glycolysis (TLG), metabolic tumor volume (MTV) with clinical stage in lung cancer and correlation of SUVmax of primary tumor and that of metastatic lesion was studied in lung cancer patients.
Materials and methodsPatients with lung cancer who were referred for FDG PET/CT were included in the study.
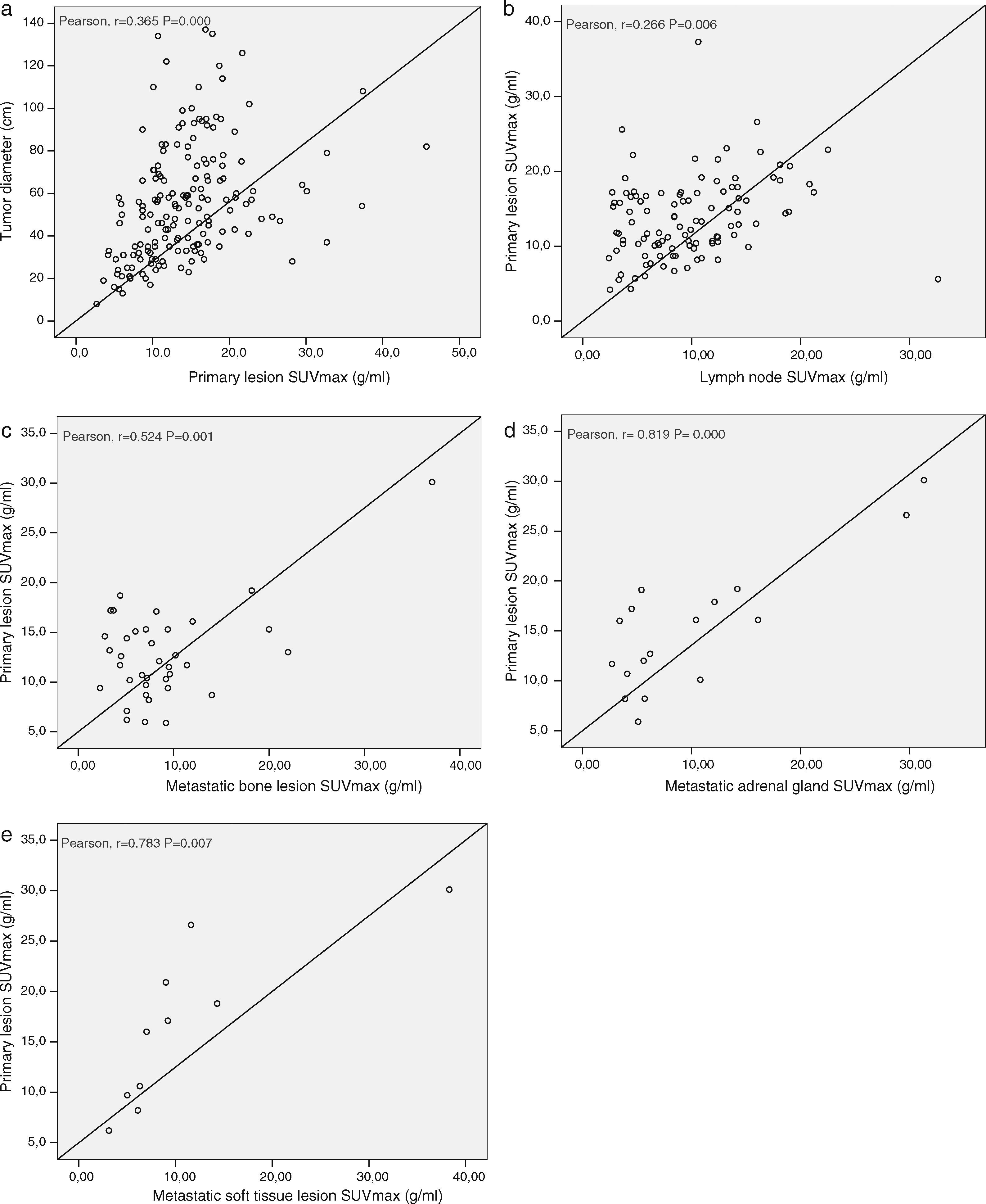
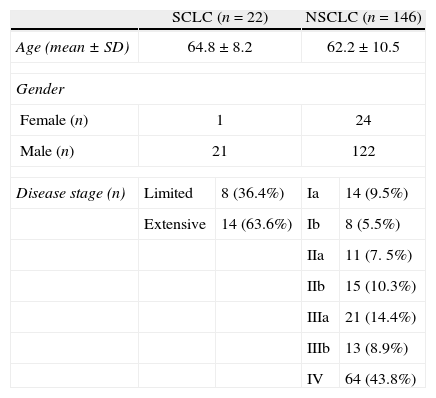
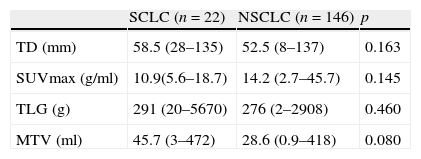
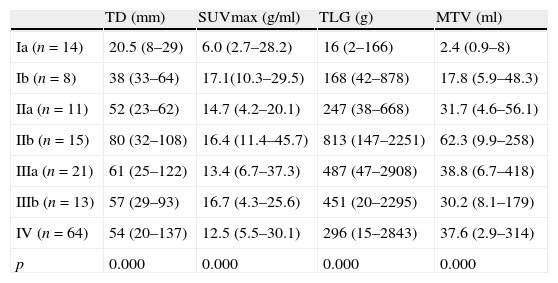
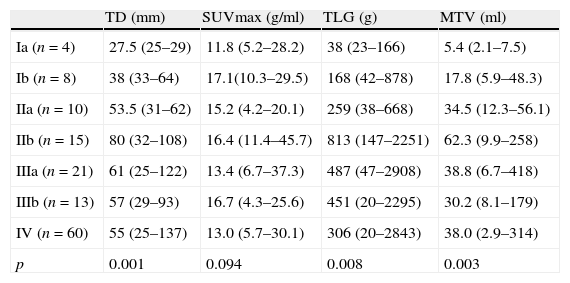
ResultsPET/CT scans and pathology reports of 168 patients were assessed. A total of 146 (86.9%) of these patients had a diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and 22 (13.1%) had small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Metabolic parameters such as SUVmax, TLG and MTV showed significant differences in all the stages in NSCLC patients (p<0.001). However, after tumors sizes <25mm were excluded, no significant differences in SUVmax between stages were observed. No significant differences were found between these metabolic parameters and limited or extended disease SCLC. Tumor diameter correlated with primary tumor SUVmax and significant correlations between primary lesion SUVmax and metastatic lesion SUVmax were found.
ConclusionsAlthough differences were found regarding indices between stages of NSCLC cases, SUVmax differences between stages seem to be caused by underestimation of SUVmax in small lesions. Other glucose metabolism indexes such as MTV and TLG show promising results in terms of prognostic stratification. Future studies are needed for better understanding of their contribution to clinical cases.
En pacientes con cáncer de pulmón hemos investigado la relación de los parámetros PET como el valor máximo estandarizado de captación (SUVmax), la glucólisis lesional total (TLG) y el volumen tumoral metabólico (MTV) con el estadio clínico y la correlación del SUVmax del tumor primario con el SUVmax de las metástasis.
Material y métodosEl estudio incluyó pacientes con cáncer de pulmón enviados para realizar una estadificación con FDG PET/TC.
ResultadosSe estudiaron las imágenes PET/TC y los informes anatomopatológicos de 168 pacientes. De los 168 pacientes, 146 (86,9%) tenían cáncer pulmonar de células no pequeñas (CPCNP) y 22 (13,1%) cáncer pulmonar de células pequeñas (CPCP). En todos los estadios de los pacientes con CPCP se detectaron diferencias significativas (p<0,001) en el SUVmax, la TLG y el MTV. Sin embargo, al excluir los tumores de un tamaño inferior a 25mm, no se encontró una diferencia significativa en el SUVmax de los diferentes estadios. No se encontraron diferencias significativas entre estos parámetros metabólicos y la enfermedad limitada o extendida del CPCP. El diámetro del tumor se correlacionó con el SUVmax del tumor primario y se obtuvieron diferencias significativas entre el SUVmax del tumor primario y el SUVmax de las metástasis en todo el conjunto de pacientes.
ConclusionesAunque se encontraron diferencias en los índices metabólicos entre los distintos estadios del CPCNP, las diferencias de SUVmax en los diferentes estadios parecen ser resultado de una infraestimación del SUVmax en las lesiones pequeñas. Otros índices del metabolismo de la glucosa, como el MTV y la TLG, muestran resultados prometedores de cara a una estratificación pronóstica y se deberían realizar futuros estudios para alcanzar un mejor conocimiento de su contribución clínica.
Article

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)