By May 5 2023, WHO announced the end of the pandemic due to declining COVID-19 cases and deaths, coupled with high levels of immunity from vaccination and previous infections. However, the virus remains a global health threat with potential for new variants. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique, has shown promise in treating various conditions, including respiratory infections. This review investigates acupuncture's impact on acute COVID-19 infection and its potential as a complementary therapy.
MethodologyA comprehensive literature search was conducted using PubMed, Science Direct, Scielo, and CNKI, focusing on the impact of acupuncture on COVID-19 patients.
ResultsThe search yielded 35 studies, with five meeting the inclusion criteria. These included two randomized clinical trials and three case reports, all incorporating acupuncture alongside conventional treatments.
Case reports and clinical trials indicated that acupuncture improved symptoms such as shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, and cough in COVID-19 patients. Acupuncture was associated with elevated SpO2 levels, reduced heart rate, and an anti-inflammatory effect. Studies highlighted that acupuncture may activate neuro-immune pathways, leading to modulation of immune responses.
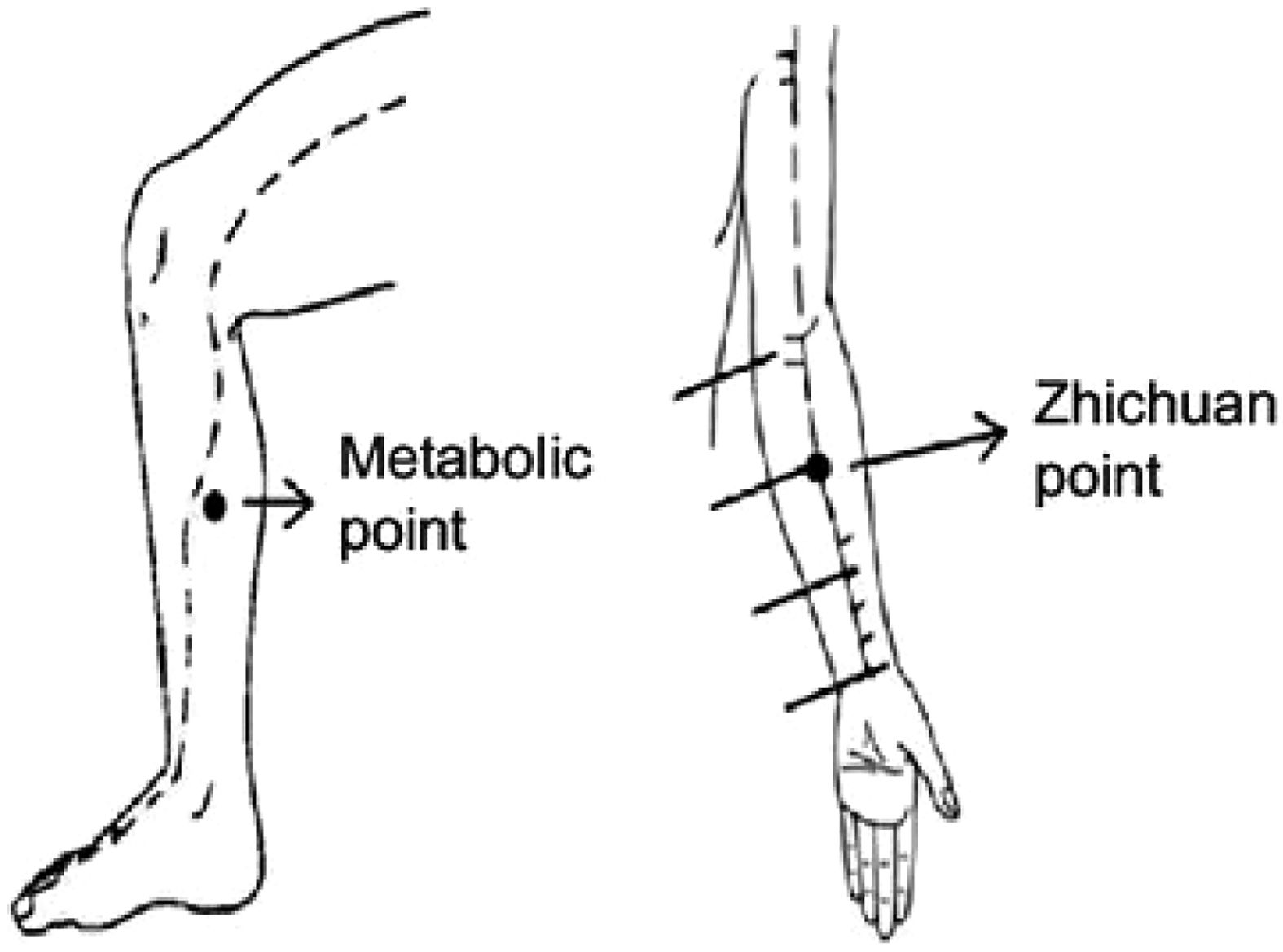
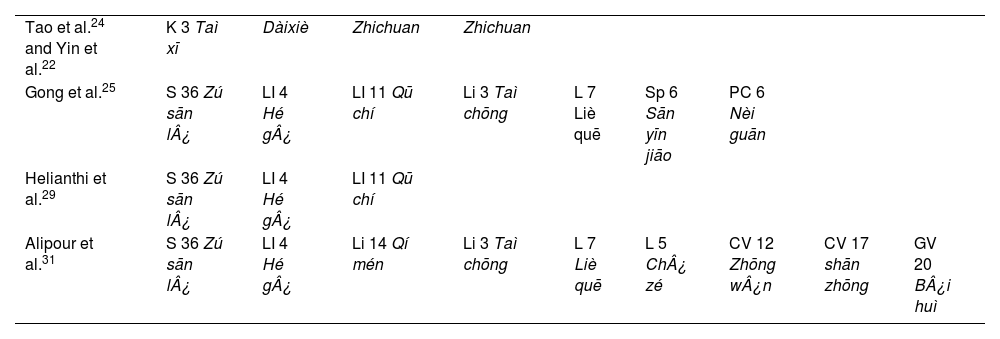
Common acupuncture points used included S 36 Zú sān l¿, and LI 4 Hé g¿. Techniques involved inserting needles at specific depths and angles to achieve the Deqi sensation, with treatments lasting 20–30 min per session.
ConclusionAcupuncture appears to be a valuable complementary therapy for managing acute COVID-19 infection. It enhances clinical outcomes by alleviating symptoms and reducing recovery time. Further research is warranted to fully integrate acupuncture into standard COVID-19 treatment protocols.
El 5 de mayo de 2023, la OMS anunció el fin de la pandemia debido a la disminución de casos y muertes por COVID-19, junto con altos niveles de inmunidad por vacunación e infecciones previas. Sin embargo, el virus sigue siendo una amenaza para la salud global con potencial para nuevas variantes. La acupuntura, una técnica de la medicina tradicional china, ha mostrado potencial en el tratamiento de diversas condiciones, incluidas las infecciones respiratorias. Esta revisión investiga el impacto de la acupuntura en la infección aguda por COVID-19 y su potencial como terapia complementaria.
MetodologíaSe realizó una búsqueda exhaustiva de literatura en PubMed, Science Direct, Scielo y CNKI, centrándose en el impacto de la acupuntura en pacientes con COVID-19.
ResultadosLa búsqueda arrojó 35 estudios, de los cuales cinco cumplían con los criterios de inclusión. Estos incluían dos ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y tres informes de casos, todos incorporando la acupuntura junto con tratamientos convencionales.
Los informes de casos y los ensayos clínicos indicaron que la acupuntura mejoró síntomas como dificultad para respirar, frecuencia cardíaca rápida y tos en pacientes con COVID-19. La acupuntura se asoció con niveles elevados de SpO2, reducción de la frecuencia cardíaca y un efecto antiinflamatorio. Los estudios destacaron que la acupuntura puede activar vías neuro-inmunes, lo que lleva a la modulación de las respuestas inmunitarias.
Los puntos de acupuntura comunes utilizados incluyeron S 36 Zú sān l¿ y LI 4 Hé g¿. Las técnicas involucraron la inserción de agujas a profundidades y ángulos específicos para lograr la sensación Deqi, con tratamientos de 20–30 minutos por sesión.
ConclusiónLa acupuntura parece ser una terapia complementaria valiosa para el manejo de la infección aguda por COVID-19. Mejora los resultados clínicos al aliviar los síntomas y reducir el tiempo de recuperación. Se necesita más investigación para integrar completamente la acupuntura en los protocolos estándar de tratamiento del COVID-19.