Tuberculosis is a principal mortality causes in world, and vaccination with BCG is a key for your prevention.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the effect of studies plan from Medicine Bachelor's Degree of Universidad Guadalajara LAMAR about the knowledge about immunization against tuberculosis.
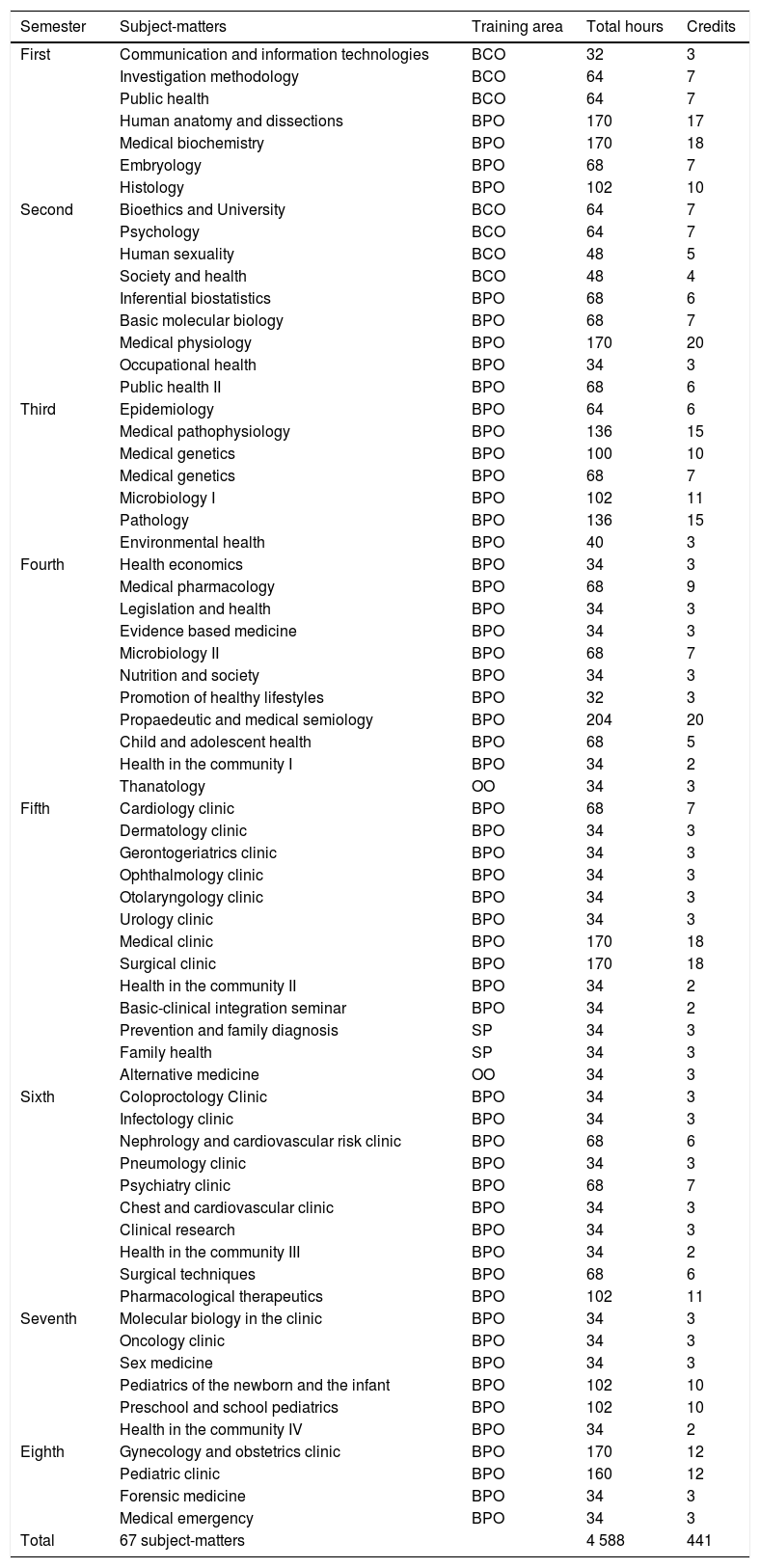
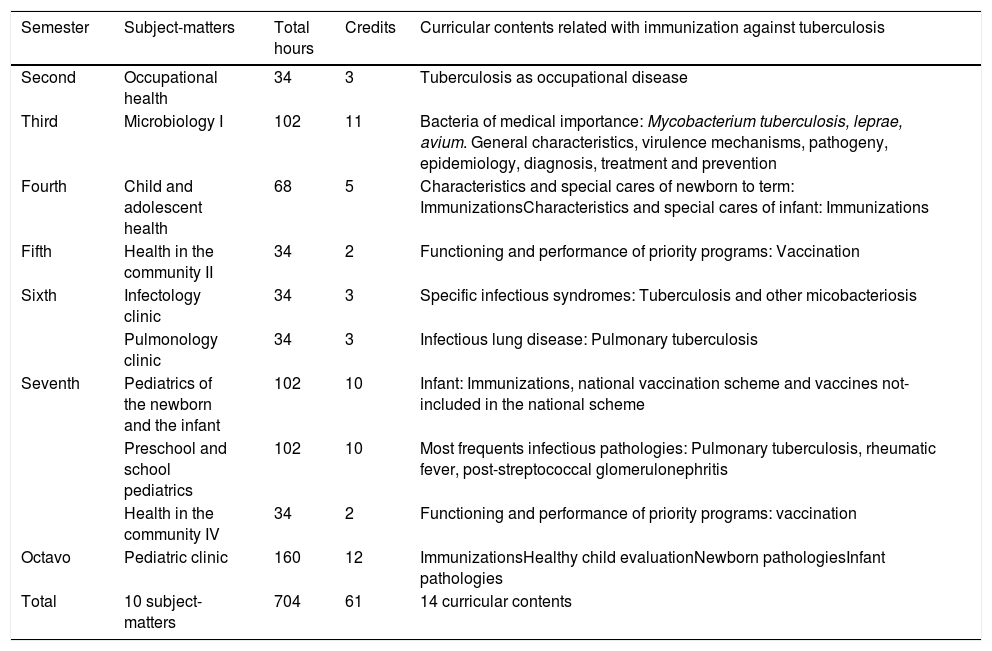
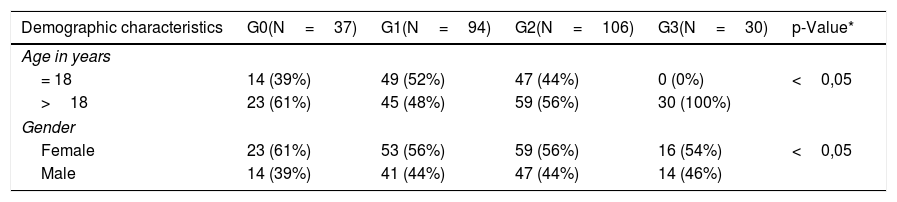
Material and methodsQuasi-experimental study type pre-experimental of comparison with a static group. Emplacement: Vallarta's Campus. Temporality: January-May 2018. Universe: 267 students. Sample: Non-randomized, n=230 students, 94 from 1st semester (G1, intervention moment “A”), 106 from 4th semester (G2, intervention moment “B”) and 30 from 7th semester (G3, intervention moment “C”) from Medicine Bachelor's Degree, more 37 students from 1st semester from Bachelor's Degree not related with health sciences (G0, control). Sampling: Propositive. Selection criteria: Any age and gender and answer the instrument. Variables: Age, gender and knowledge about management of immunization against tuberculosis. Instrument: Written test collegiate. Analysis: Comparison by mean of statistics non-parametric (p = 0,05).
ResultsLevels “high” and “very high” of knowledges: G0 0%, G1 0%, G2 32% and G3 37% (?2, p <0,05). Levels “poor” and “none” of knowledges: G0 100%, G1 89%, G2 58% y G3 63% (?2 p <0,05). The knowledge level was higher to be expose to studies plan and increase your exposition time (?2 p <0,05 in all cases).
ConclusionThe studies plan showed develops high knowledges about management of immunization against tuberculosis. There is a significant gap in this knowledge that does not vary substantially in advanced semesters.
La tuberculosis es una de las principales causas de mortalidad en el mundo, y la vacunación con BCG es una de las claves para su prevención.
ObjetivoEvaluar el efecto del plan de estudios de la Licenciatura en Medicina de la Universidad LAMAR de Guadalajara sobre el conocimiento del manejo de la inmunización contra la tuberculosis.
Material y métodosEstudio cuasiexperimental tipo preexperimental de comparación con grupo estático. Emplazamiento: Campus Vallarta. Temporalidad: enero-mayo de 2018. Universo: 267 estudiantes. Muestra: no probabilística, n=230 estudiantes, 94 de 1er. semestre (G1, intervención momento «A»), 106 de 4.o semestre (G2, intervención momento «B») y 30 de 7.o semestre (G3, intervención momento «C») de Medicina, más 37 estudiantes de 1er. semestre de licenciatura no relacionada con salud (G0, control). Muestreo: propositivo. Criterios de selección: cualquier edad y sexo, y responder instrumento. Variables: edad, sexo y conocimiento del manejo de la inmunización contra la tuberculosis. Instrumento: examen escrito colegiado. Análisis: estadística no paramétrica (p = 0,05).
ResultadosNiveles «alto» y «muy alto»: G0 0%, G1 0%, G2 32% y G3 37% (?2 p <0,05). Niveles «pobre» y «ninguno»: G0 100%, G1 89%, G2 58% y G3 63% (?2 p <0,05). El nivel de conocimiento fue mayor al exponerse al plan de estudios, y aumentó a mayor exposición (?2 p <0,05).
ConclusiónEl plan de estudios demostró desarrollar conocimientos elevados sobre el manejo de la inmunización contra la tuberculosis. Existe un vacío importante en estos conocimientos que no varía sustancialmente en semestres avanzados.