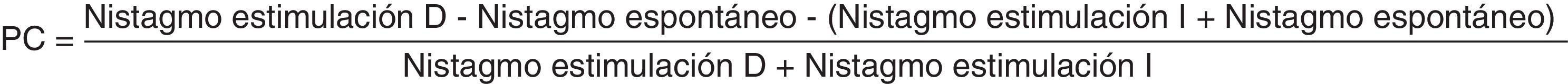Encontrar una forma de estimar el valor de paresia canalicular (PC) a través de la estimulación vestibular calórica monotérmica (EVCM) que pueda utilizarse en cualquier laboratorio, controlando el error que se produce al utilizarla.
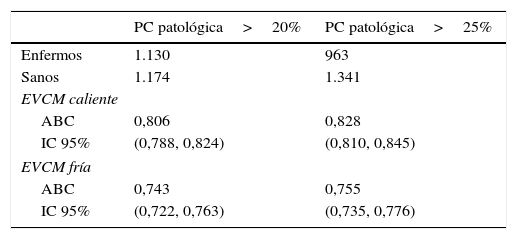
MétodoSe incluyó en este estudio a 2.304 pacientes de nuestro servicio a los cuales se les realizó una videonistagmografía con pruebas calóricas entre 2003 y 2011. El cálculo de la PC se realizó de 3 formas diferentes: utilizando los valores de las 4 estimulaciones calóricas (forma bitérmica) o exclusivamente con los 2 valores de una misma temperatura (formas monotérmica caliente y fría respectivamente). Se estudiaron 3 estrategias para mejorar la precisión de la EVCM: análisis de variables que empeoran la predicción, delimitación de un área gris de predicción deficiente y localización de un punto de separación entre sanos y enfermos de máxima utilidad.
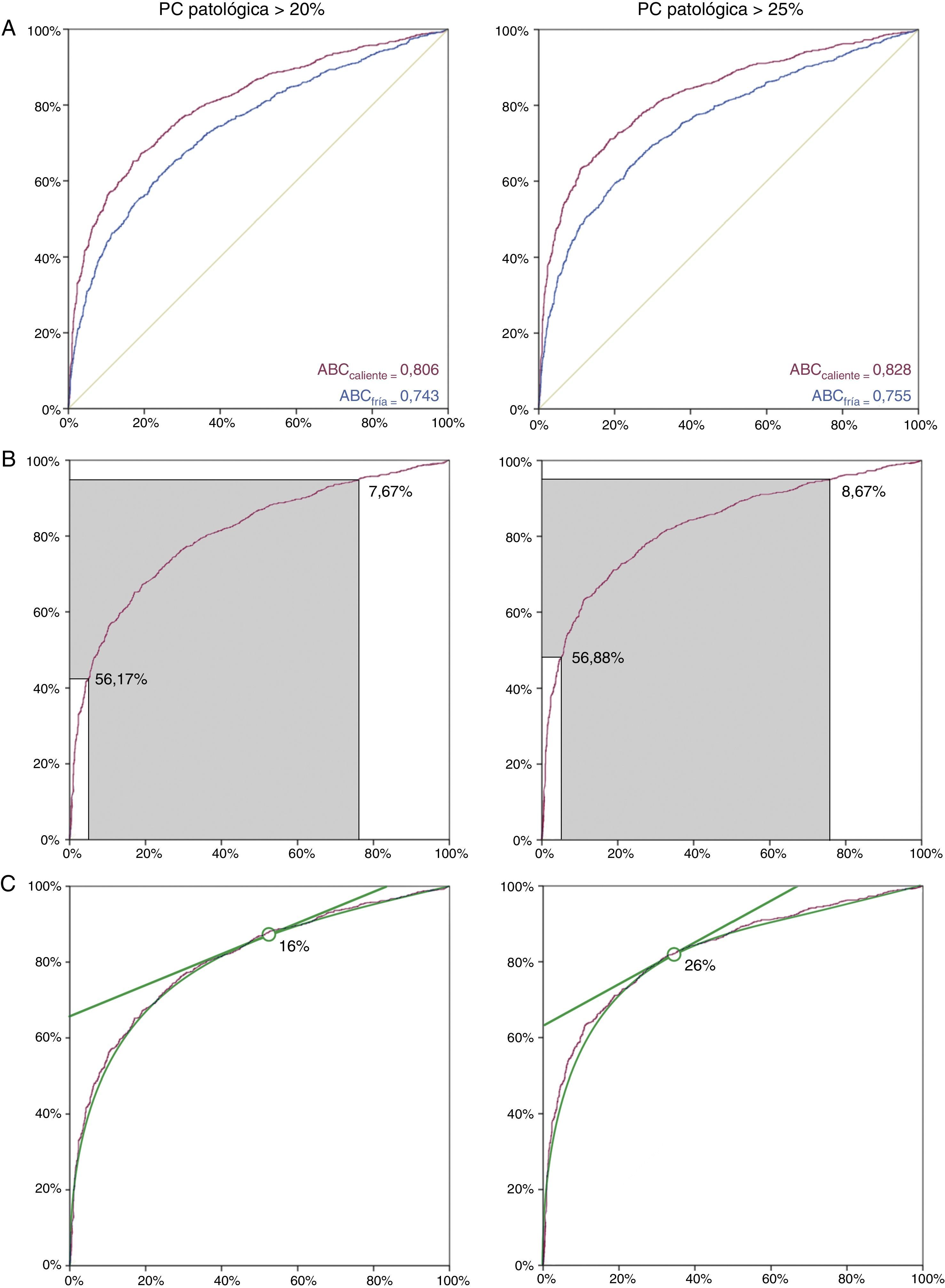
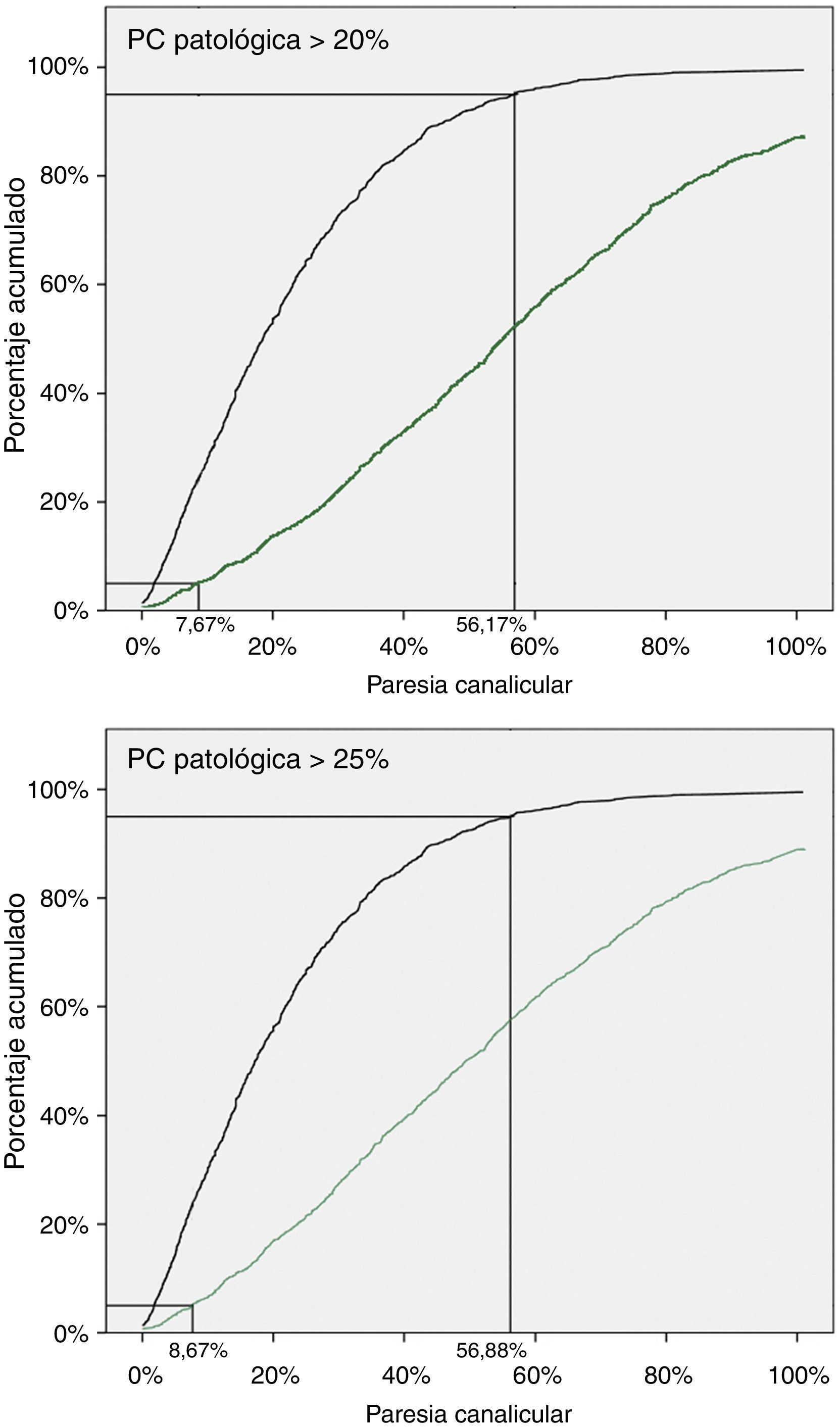
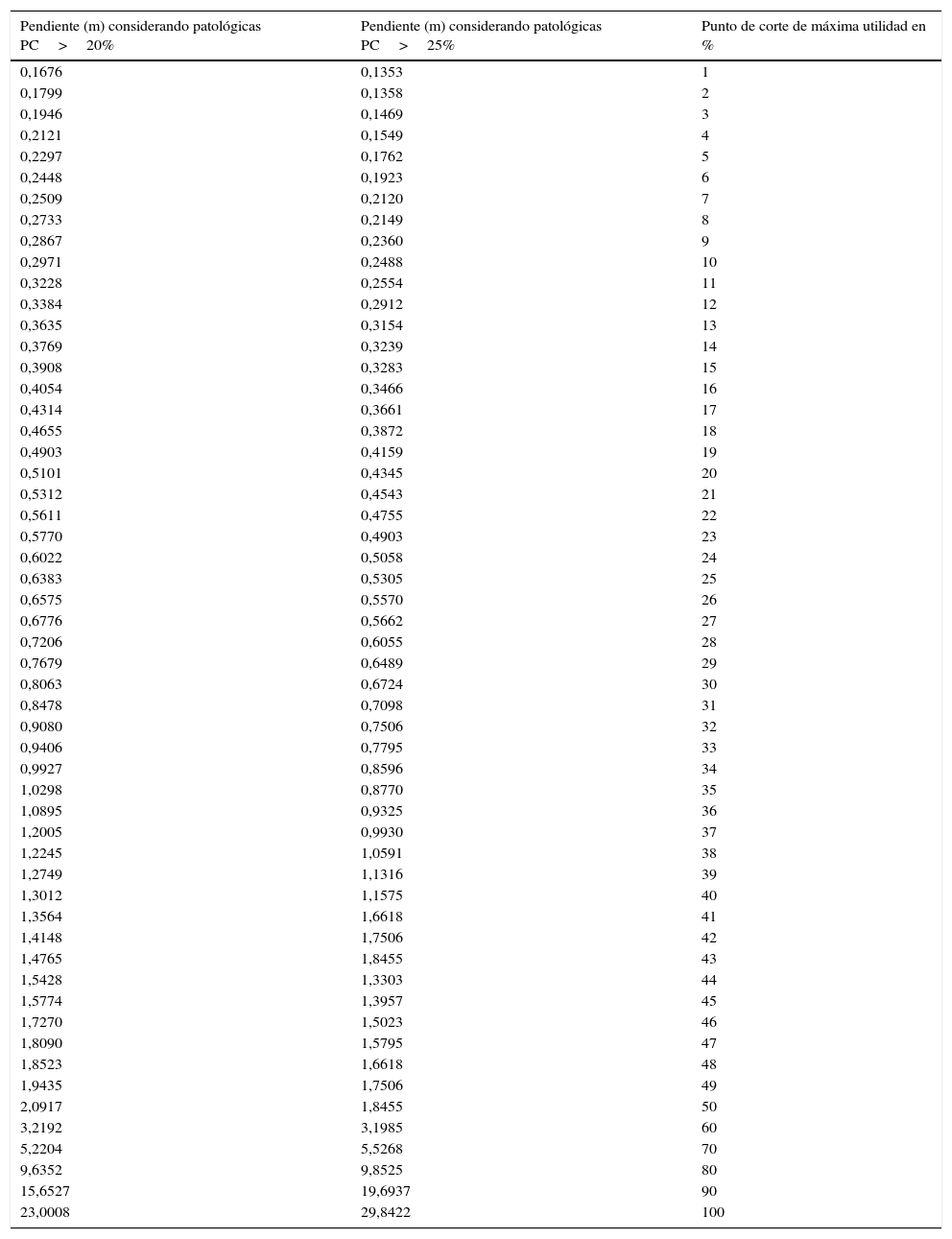
Resultados1) Corregir la fórmula de Jongkees con el valor del nistagmo espontáneo permite incluir como candidatos a la EVCM a sujetos con nistagmo espontáneo o inversión nistágmica. 2) Establecer una zona gris de predicción deficiente evita aproximadamente el 38% de las estimulaciones bitérmicas realizadas, con una sensibilidad y especificidad del 95%. 3) La máxima utilidad de la EVCM se obtiene al considerar como función vestibular normal la de sujetos con valores de EVCM caliente menores o iguales al 16%, suponiendo patológica una asimetría mayor del 20%.
ConclusiónLas nuevas herramientas estadísticas permiten a los clínicos tomar decisiones que afecten al manejo de sus pacientes basados en los resultados de la EVCM.
The objective was to find a way to estimate the value of inter-ear difference (IED) through monothermal caloric screening testing (MCST) that can be used at any laboratory, controlling and minimising the resulting error.
MethodsWe retrospectively included in this study 2304 patients from our department to whom a videonystagmography with caloric testing was performed between 2003 and 2011. The IED was calculated in 3 different ways: Using the values of the 4 caloric stimulations (bithermal form) and using only the 2 same-temperature values (warm monothermal and cool monothermal forms). We studied 3 strategies to improve the accuracy of MCST: Analysis of variables that could impair the prediction, delimitation of a grey area of insufficient prediction and location of a maximum utility cut-off point.
ResultsCorrecting Jongkees’ formula with the value for spontaneous nystagmus makes it possible to include subjects with spontaneous nystagmus or nystagmus inversion. Establishing 2 cut-off points to classify the subjects avoids approximately 38% of bithermal stimulations performed with a sensitivity and specificity of 95%. Maximum utility was obtained diagnosing as healthy those subjects with IED values lesser than or equal to 16% in warm MCST when the pathological IED was set as greater than 20%.
ConclusionNew statistical tools help clinicians to make decisions that affect their patients based on the results of MCST.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora