To explore the value of otoscopy in diagnosing OME when performed by otorhinolaryngology, pediatrics, and primary care physicians; to evaluate the interobserver and intraobserver agreement of interpretation of otoscopy images.
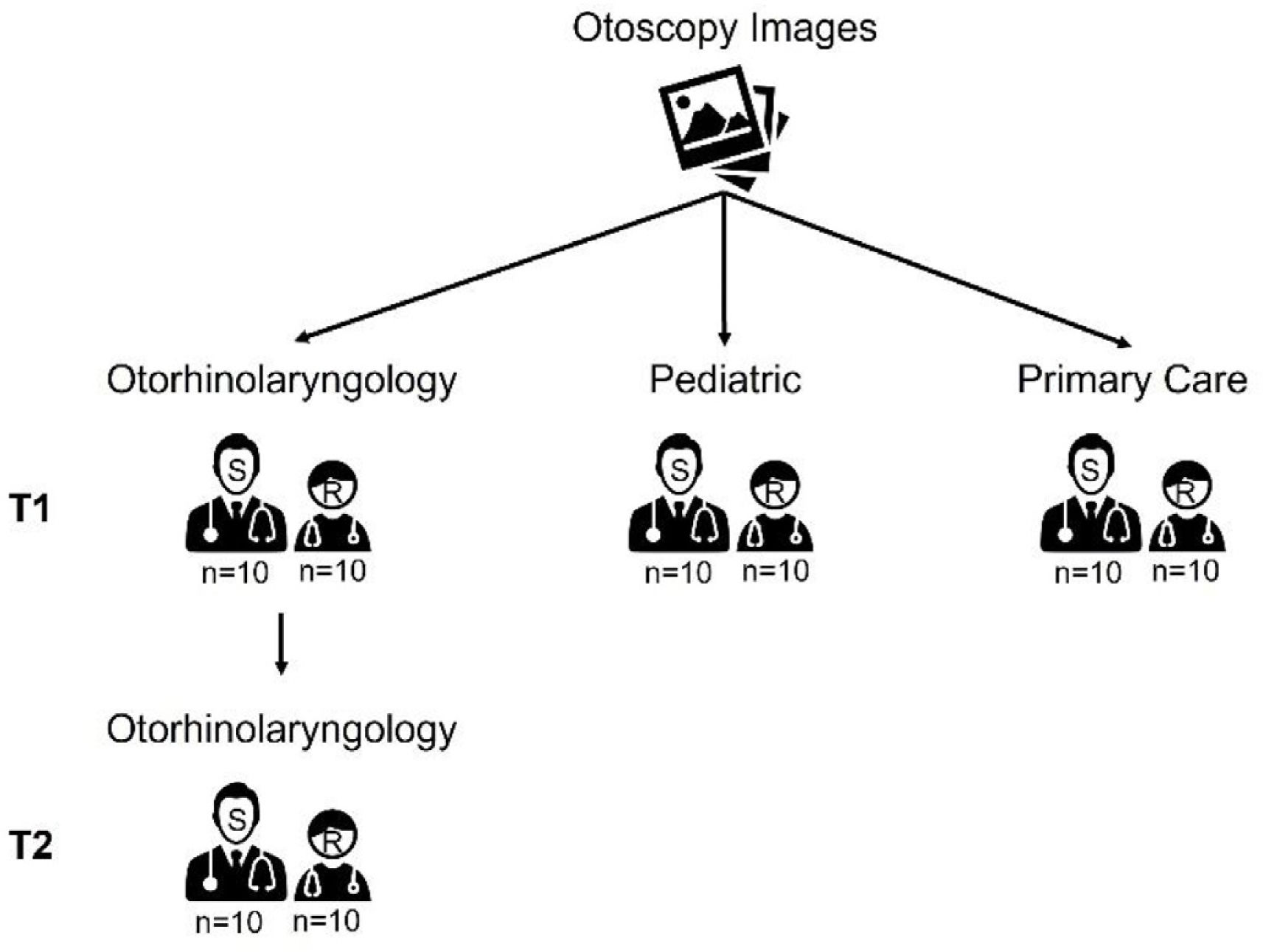
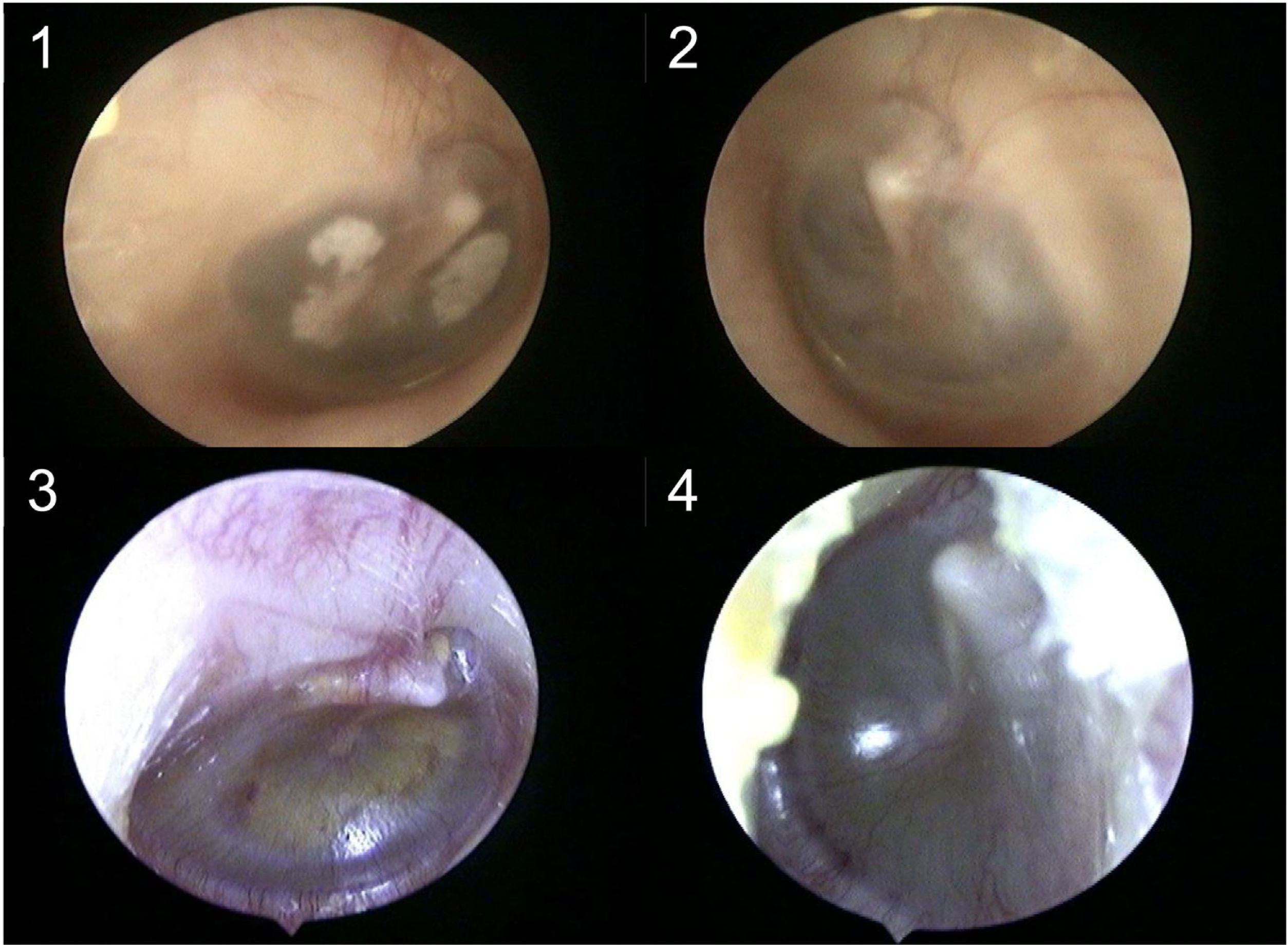
Material and methodsA cross-sectional study using an anonymous mailed survey was used. We presented pre-recorded otoscopy images of pediatric patients to otorhinolaryngology, pediatrics, and primary care physicians (ten volunteer specialists and residents from each medical specialty). All participants had to answer “yes” or “no” if they considered that the image corresponded or not to an OME case, respectively. We considered that the images were positive for OME whenever the respective tympanogram was type B.
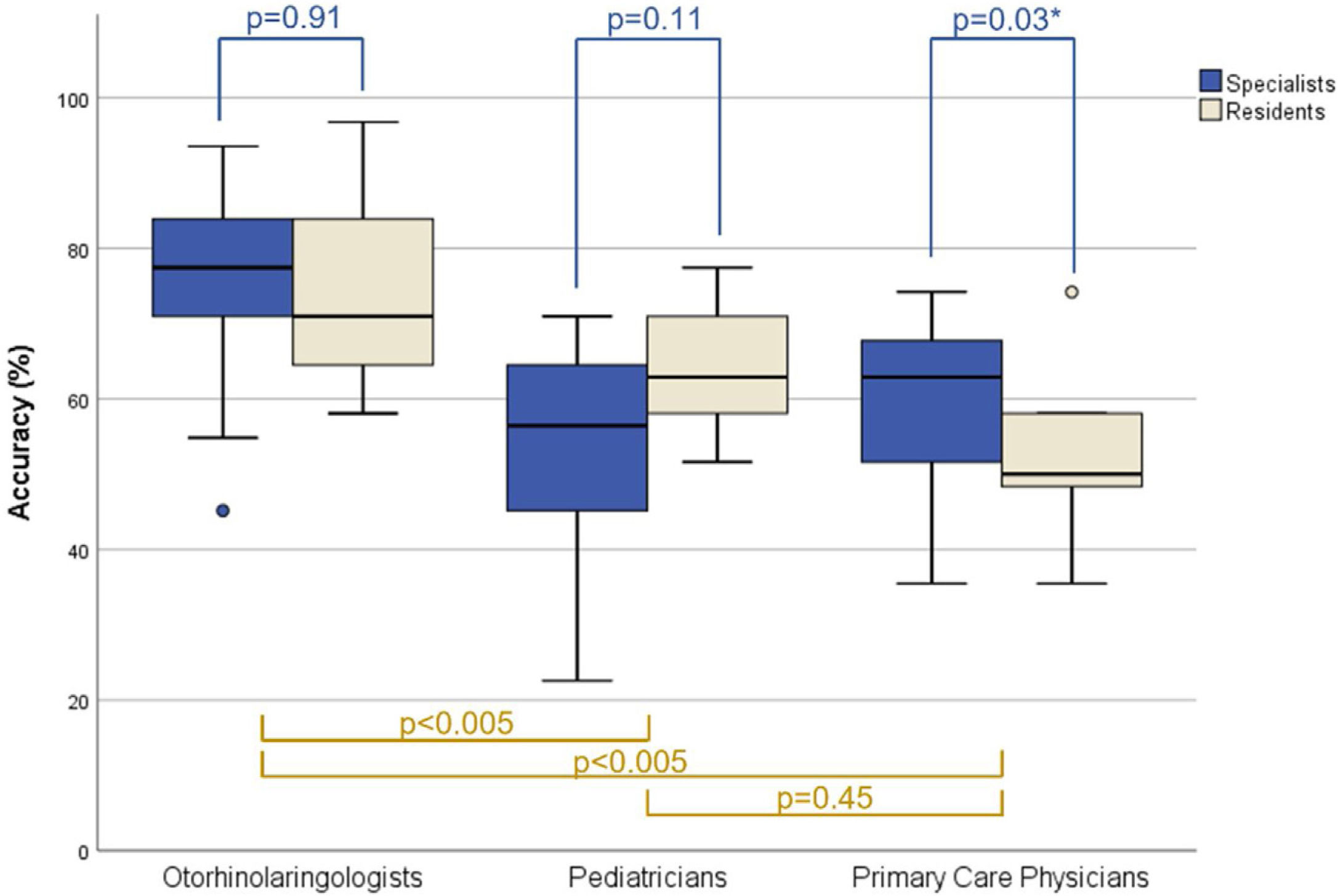
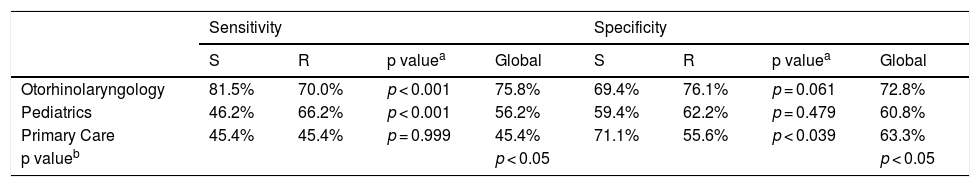
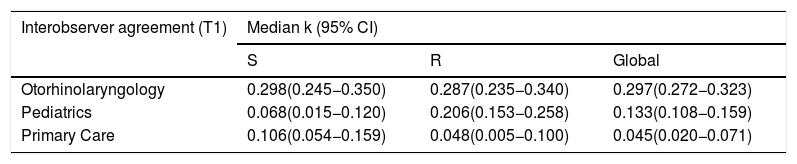
ResultsThirty-one otoscopy images and 1860 responses provided by sixty physicians were analyzed. The accuracy of otoscopy in diagnosing OME was highest in the Otolaryngologists group (mean 74.8%), with the worst rate observed in the primary care residents group (mean 51.3%). Overall sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value of otoscopy for diagnosing OME were significantly higher when performed by otorhinolaryngologists (75.8%, 72.8%, 66.8%, respectively). Fleiss' kappa showed that interobserver agreement was globally weak within each group of specialties, with overall better interobserver agreement observed among otorhinolaryngologists (κ = 0.30; 95% CI 0.27–0.32).
ConclusionAccording to our data, simple otoscopy as a single diagnostic method in pediatric OME is insufficient, even for otorhinolaryngologists. Current recommendations must be followed to improve diagnostic accuracy.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora