(I) Servir de modelo para aquellos Servicios de ORL que se encuentren en proceso de creación de una Unidad de Voz. (II) Exponer los resultados que hemos obtenido en nuestra Unidad de Voz a lo largo de los últimos 12 meses.
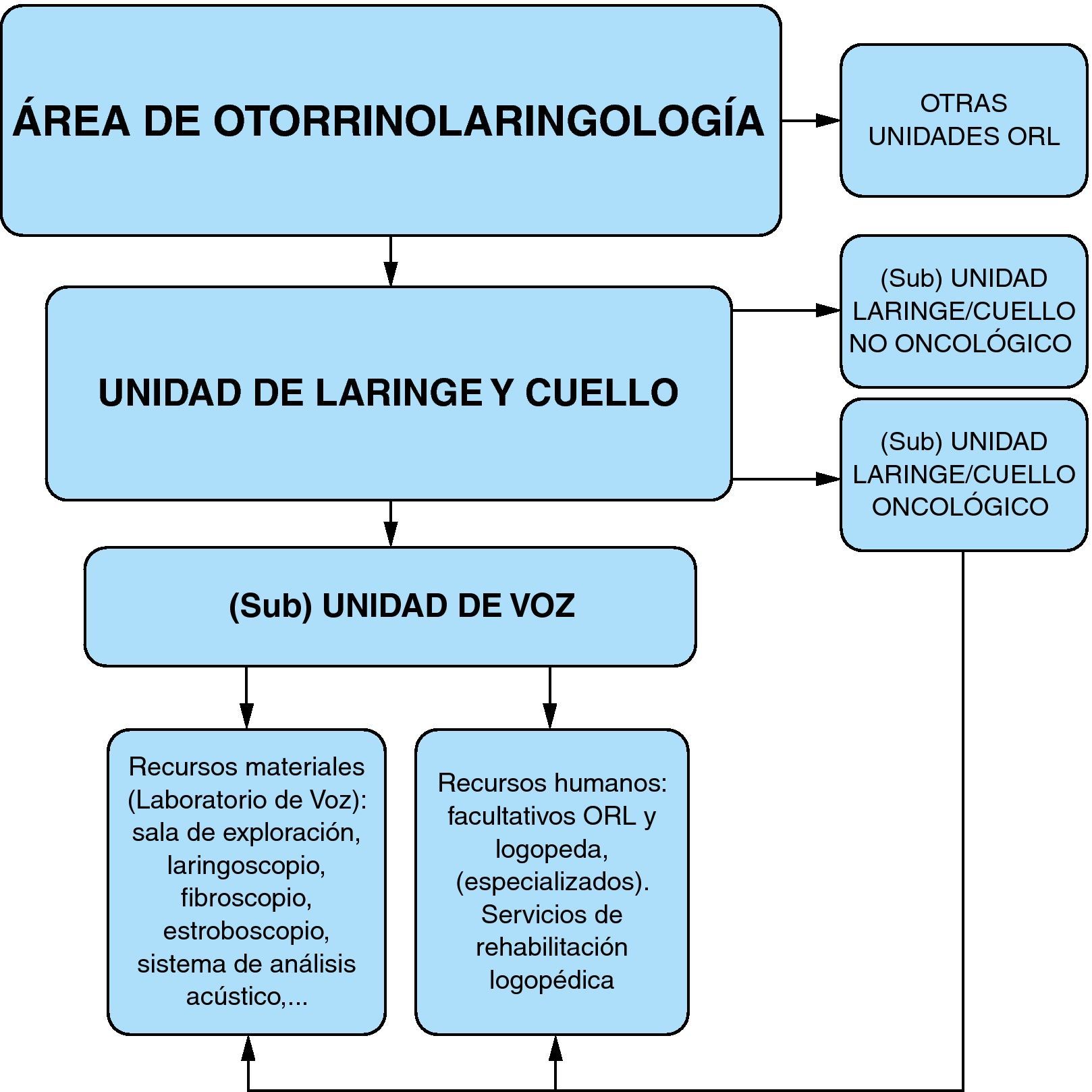
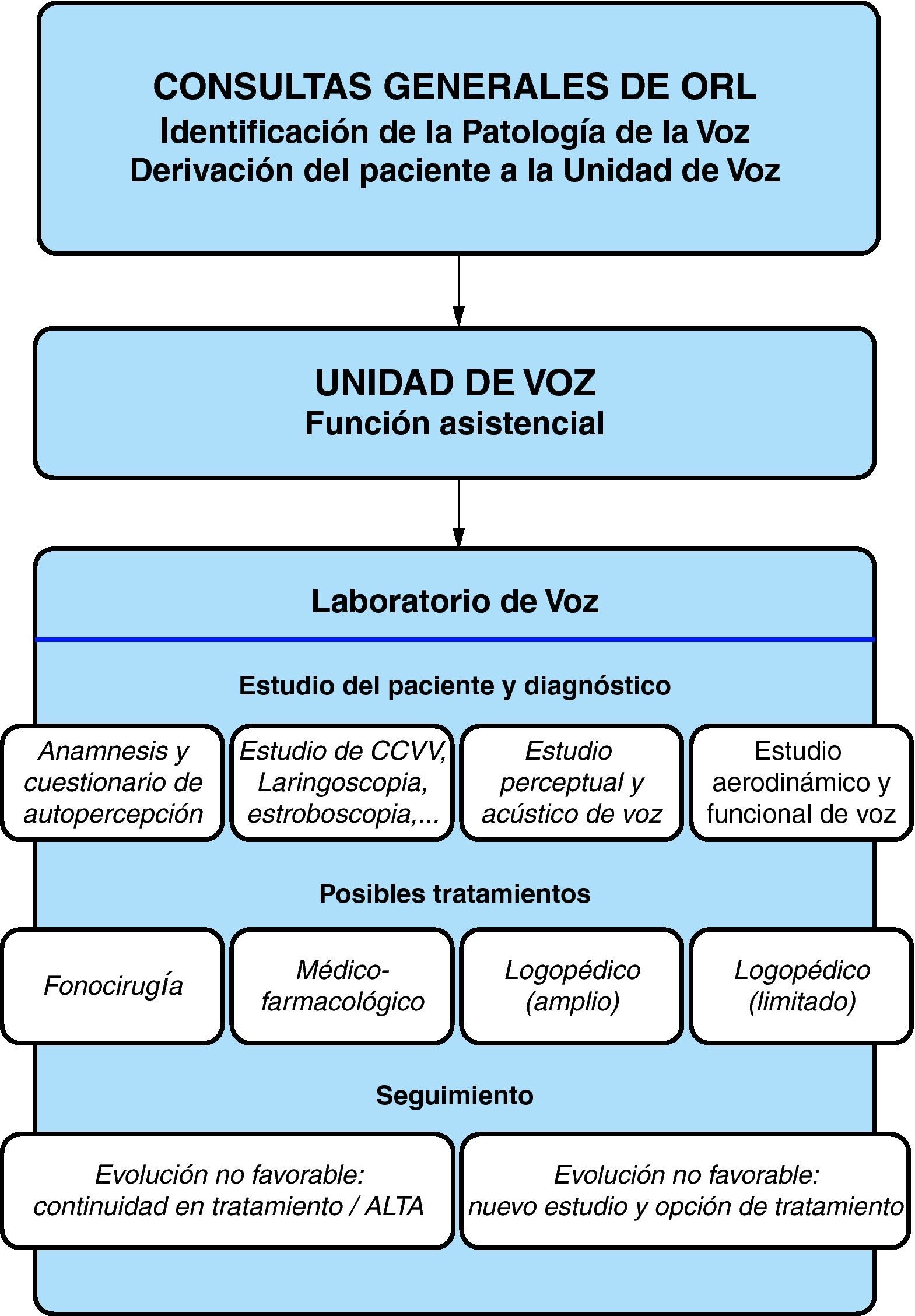
Material y métodoSe desarrollan los apartados: Funciones de la Unidad de Voz; Organización de la Unidad de Voz y Procedimientos de la Unidad de Voz. Se han estudiado 122 pacientes: valoración de autopercepción mediante el Índice de Incapacidad Vocal, categoría diagnóstica, diagnóstico de la Unidad, tratamientos previos y tratamientos propuestos por la Unidad.
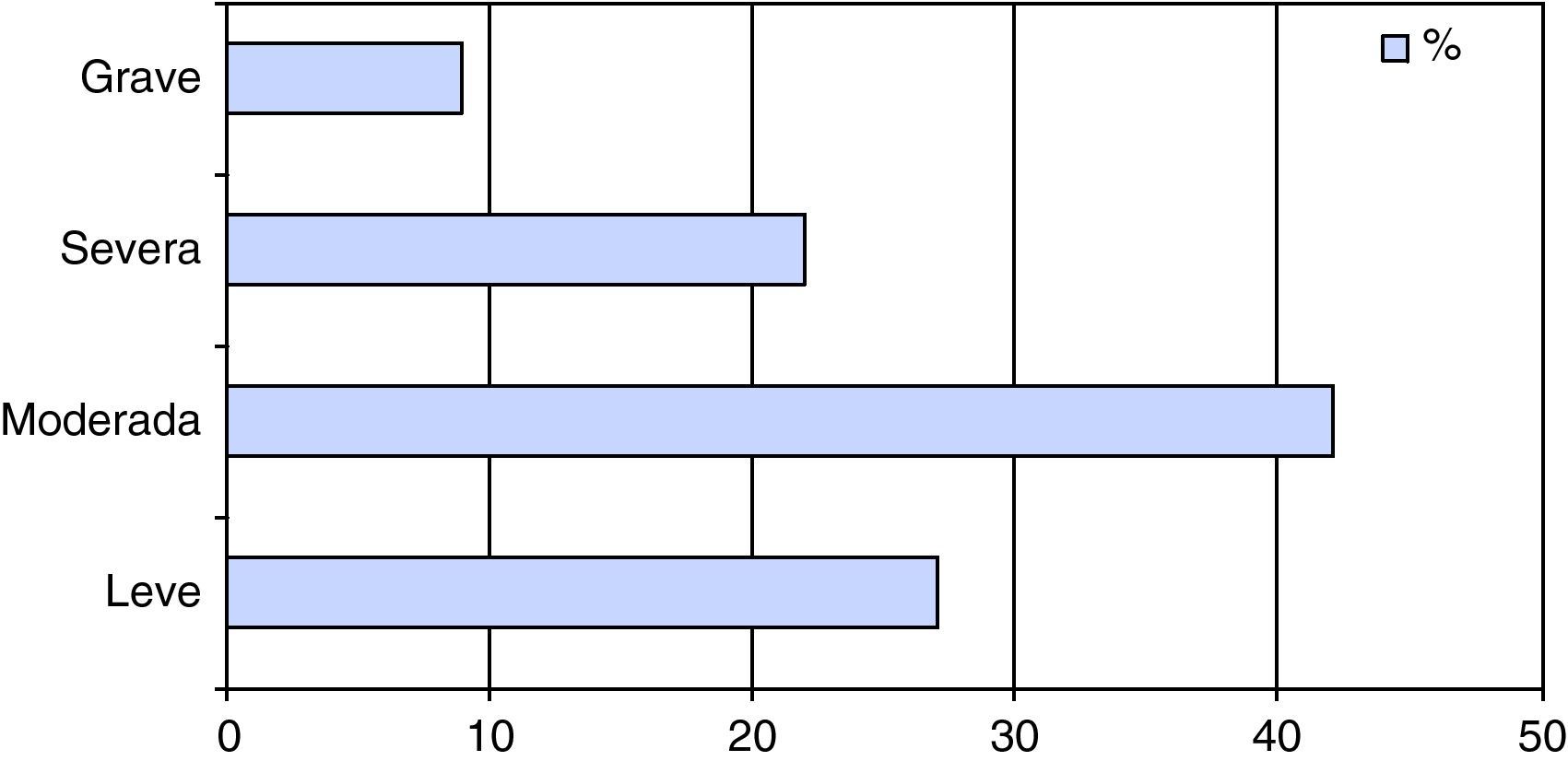
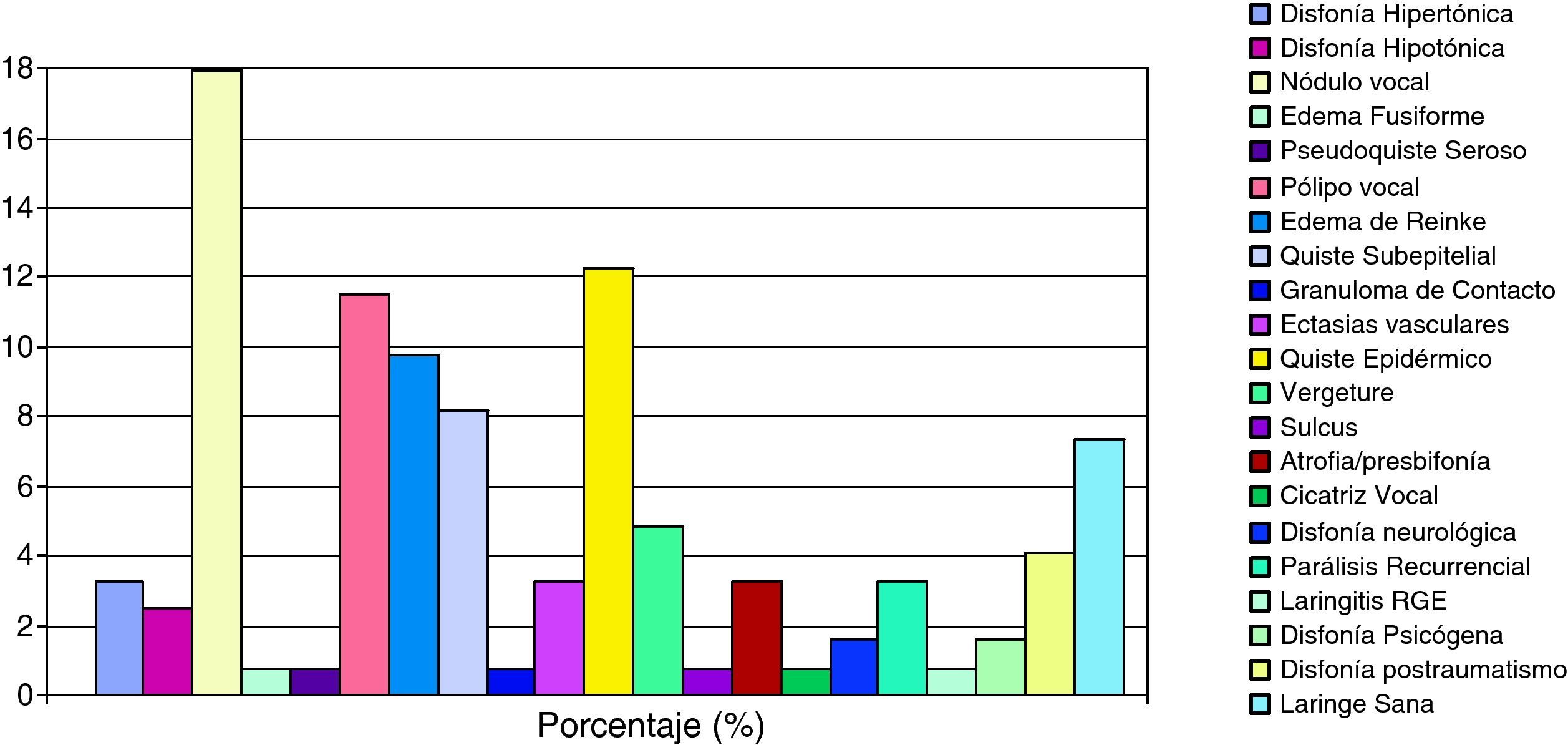
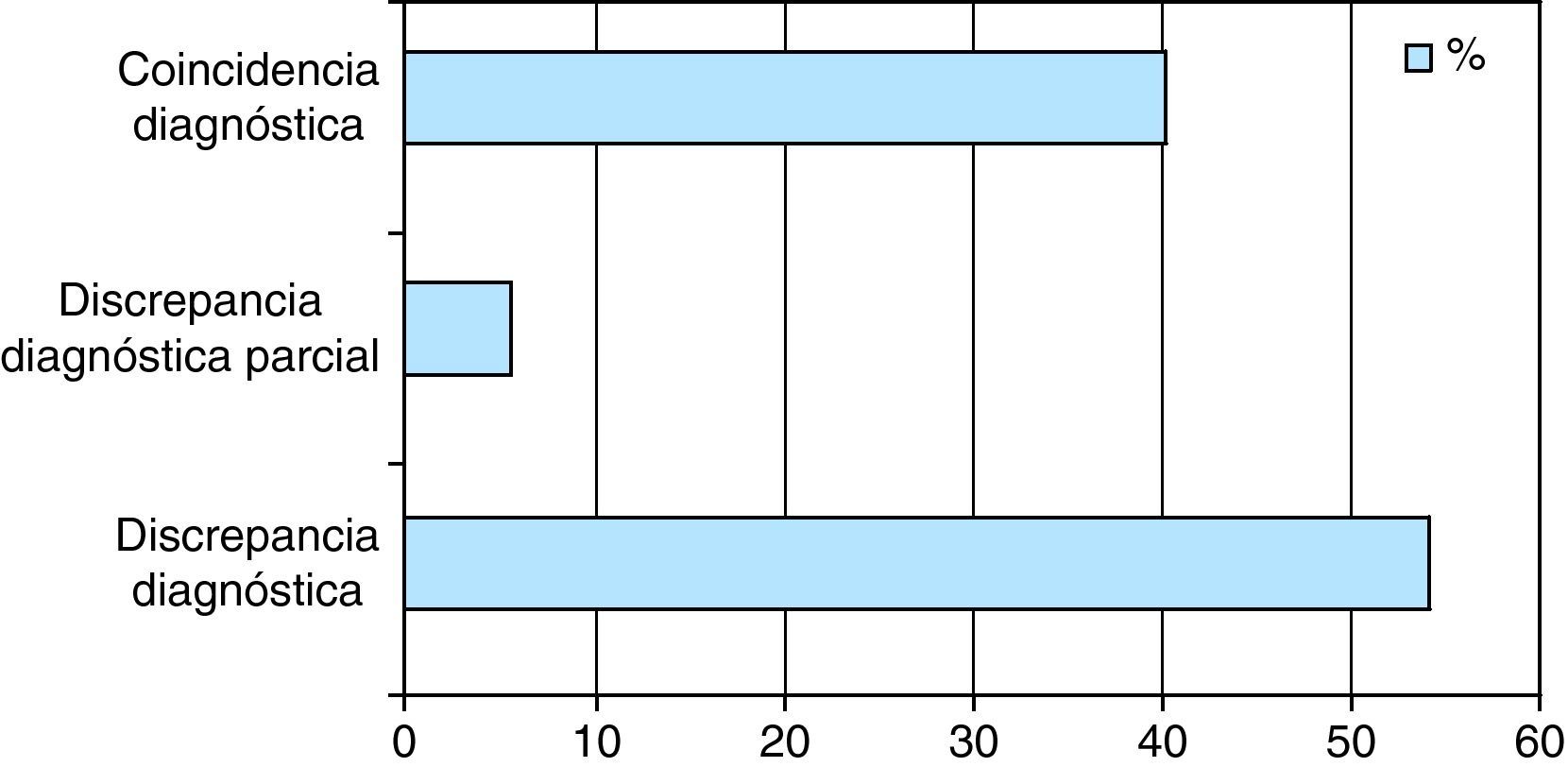
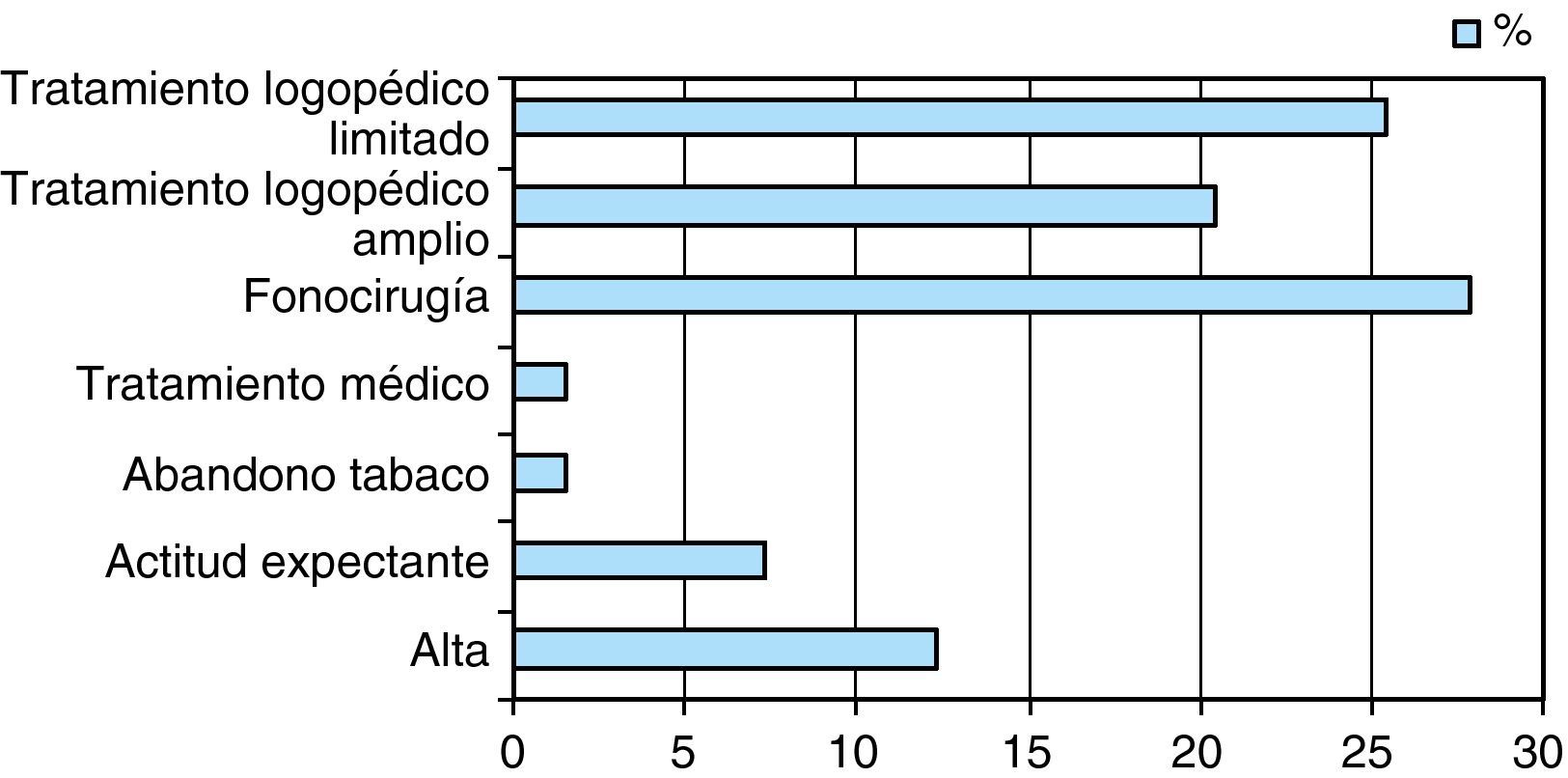
ResultadosEntre los resultados destacamos: tendencia en las puntuaciones del Voice Handicap Index a valoración leve y moderada; el grupo patológico más frecuente son las lesiones exudativas del espacio de Reinke; la existencia de más de un 50% de discrepancias diagnósticas entre las Consultas de ORL Generales y la Unidad de Voz; la terapia más habitual es el tratamiento logopédico (45%) seguido de la fonocirugía con un 28%.
ConclusionesEl objetivo principal de la Unidad de Voz será obtener la máxima efectividad y calidad en sus diferentes funciones. Un diagnóstico y tratamiento correcto aumenta la efectividad y permite un mejor aprovechamiento de los recursos. Para alcanzarlo se requiere un equipamiento mínimo e imprescindible: laringoestroboscopio, protocolo multidimensional y trabajo interdisciplinar.
(I) To serve as a model for ENT services in the process of creating a voice unit and (II) to show the results obtained in our Voice Unit over the past 12 months.
MethodsSections on Voice Unit Functions, Organisation and Procedures are presented, as well as the study of 122 patients: an assessment of patient self-perception using the Voice Handicap Index, diagnostic category, Voice Unit diagnosis, previous treatments and treatments proposed by the Unit.
ResultsThe results highlight that Voice Handicap Index scores tend towards mild and moderate evaluations; that the most frequent pathological group are exudative lesions affecting Reinke's space; that there are diagnostic discrepancies of more than 50% between the general ENT consultations and the Voice Unit; and that the most common treatment is speech and language therapy (45%), followed by phonosurgery (28%).
ConclusionsThe main aim of the Voice Unit is to achieve maximum effectiveness and quality in its various functions. Correct diagnosis and treatment increases effectiveness and allows better use of resources; achieving this requires a minimal, essential setup: laryngostroboscope, a multidimensional protocol and interdisciplinary work.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora