Laparoendoscopic single site surgery (LESS) has been accompanied by the development of a new generation of purpose-built optics and instruments. Despite all these, suturing still represents a challenge in LESS. The authors describe a technique of urachal cyst excision by LESS, with extramucosal partial cystectomy and cystorrhaphy performed with the SILS™ Stitch instrument. The technique is safe and feasible, offering the advantages of reducing the number of abdominal incisions to one that can be hidden in the umbilicus, with less post-operative pain and improved cosmesis. The extramucosal technique shortens the period of postoperative catheterization and hospitalization.
A cirurgia de porta única (LESS) tem vindo a ser acompanhada pelo desenvolvimento de uma nova geração de óticas e instrumentos adaptados ao efeito. Contudo, a realização de sutura mantém-se um desafio na porta única. Os autores descrevem a sua técnica de excisão de quistos do úraco por LESS, através de cistectomia parcial extramucosa e cistorrafia com o auxílio do SILS™ Stitch instrument. O procedimento é exequível e seguro, reduzindo a uma o número de incisões abdominais, que pode ficar escondida no umbigo, com melhoria da cosmese e redução de dor pós-operatória. A técnica extramucosa reduz o tempo de algaliação e hospitalização.
Laparoendoscopic single site surgery (LESS) represents a progression in laparoscopic surgery and is reported with increasing frequency. However, it defies the most basic laparoscopic concepts, including triangulation of working instruments and external spacing to decrease clashing. To overcome technical limitations related to LESS, industries have also developed a new generation of purpose-built optics and instruments. Articulating instruments have been conceptually developed to allow the surgeon's hands to be positioned farther apart while some triangulation is internally created. Despite all these, suturing still represents a challenge in LESS. The SILS™ Stitch instrument is specially designed to make suturing easier in LESS surgeries.
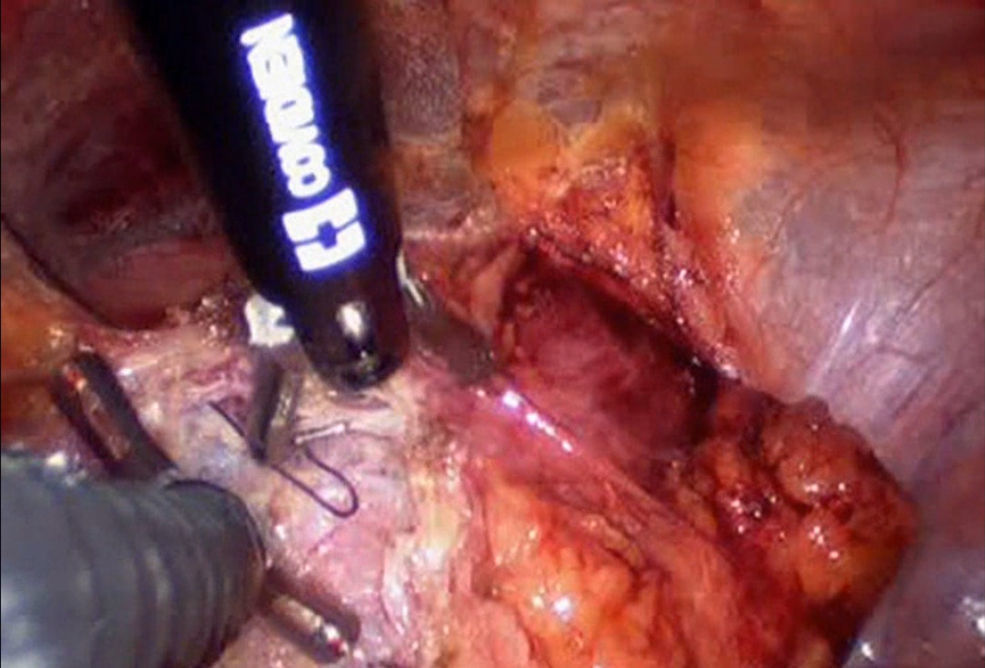
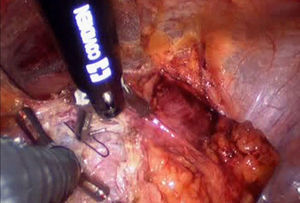
Technique descriptionWe describeour technique of LESS in urachal cyst excision, using a SILS™ port. The patient was placed in the supine, 30° Trendelenburg position during the procedure. With the transumbilical open Hasson technique, a 2–2.5cm vertical intraumbilical skin incision was made. Two tissue forceps were placed to evert both edges of the incision. A vertical midline anterior rectus fasciotomy was made, the abdominal cavity was entered, and a sweep of the finger verified lack of underlying adhesions. The lower edge of the SILS port was grasped via curved artery forceps, and then a lubricant was placed. The port was then deployed and secured in place. The 12mm cannula was placed by its obturator followed by the two 5mm cannulas. These cannulas (ports) were placed at different heights to reduce instruments clashing. The port had an insufflation channel which was connected to the insufflation line to achieve CO2 pneumoperitoneum to a pressure of 12mmHg. A 5mm 30° lens was introduced through the cannula for inspection of the abdominal cavity, followed by the articulating instruments to dissect the urachal remnants and perivesical cyst. Extramucosal partial cystectomy was performed with a 5mm LigaSure™. The cystorrhaphy was performed by the 12mm port with the SILS Stitch instrument, to offer precise access to the surgical site, with distal shaft articulation, needle jaw tip rotation, combined with the instrument's proprietary toggle-activated needle-passing feature (Fig. 1). No drain was placed. The operative time was 50min and vestigial blood loss. The patient was discharged after 24h, catheter-free, with no immediate complications and a 3 months follow-up showed patient satisfaction with good cosmesis. Video available at http://tinyurl.com/nbmuex5.
ConclusionsSILS urachal cyst excision and cystorrhaphy has proved to be safe and feasible, using specially designed ports and instruments. Similar to other procedures, it offers the advantages of reducing the number of abdominal incisions to one that can be hidden in the umbilicus, with less post-operative pain and improved cosmesis. The extramucosal technique shortens the period of postoperative catheterization and hospitalization.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
2nd prize for Best Video at the Congress of the Portuguese Urological Association (APU), 2015, Braga, Portugal.