Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is essential for preventing recurrence and progression of Non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). The aim of our study was to compare the efficacy and toxicity of the Connaught and Tice strains, as well as the importance of the maintenance schedule.
Material and methodsWe retrospectively reviewed 110 patients with NMIBC who underwent adjuvant endovesical treatment. The patients were distributed into 3 groups, based on whether the treatment was with the Connaught strain, the Tice strain or both sequentially. We calculated the recurrence-free survival rate in each group and compared the patients who completed the maintenance treatments against those who did not. To identify the predictors of recurrence, we performed a multivariate analysis. We also assessed the toxicity by analyzing the onset of BCGitis, urinary urgency, fever, urinary tract infection and treatment withdrawal due to adverse effects.
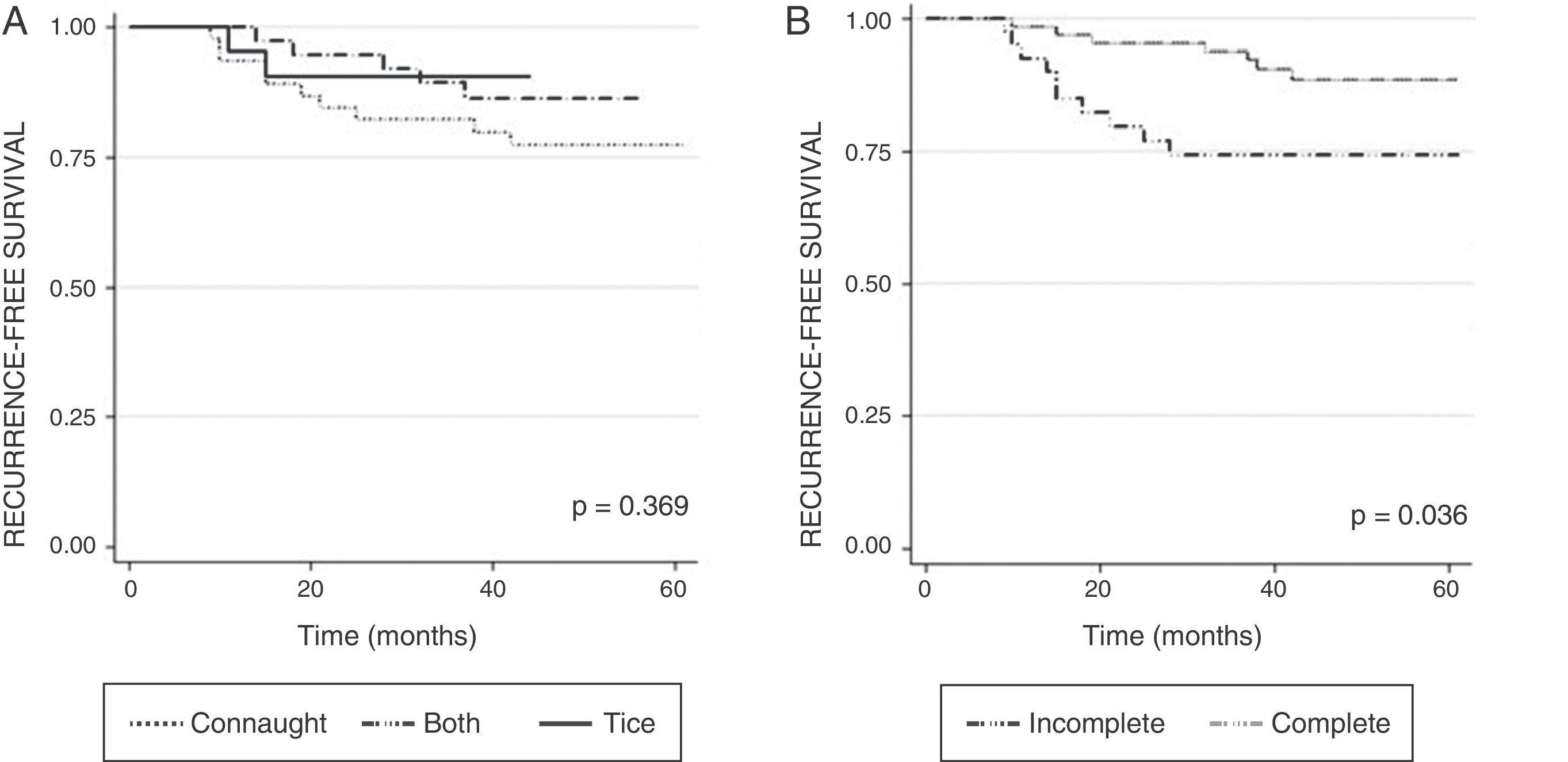
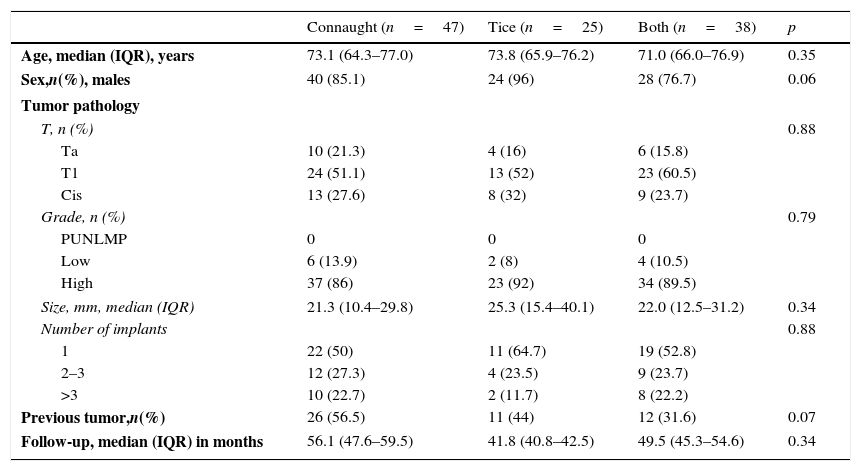
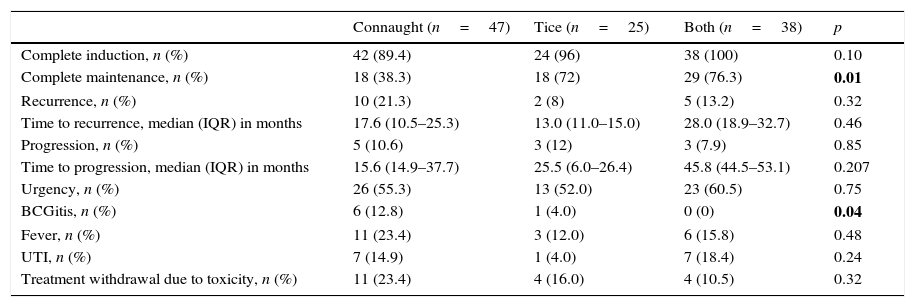
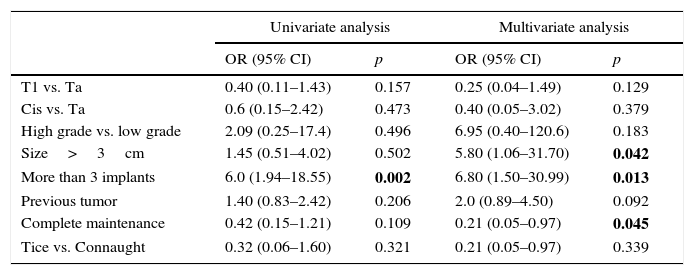
ResultsWe found no differences in the efficacy parameters. The patients in the Connaught group completed the maintenance to a lesser extent (38.4 vs. 72% for the Tice group and 76.3% for both strains group; p=0.010). The patients who completed the maintenance had better recurrence-free survival at 60 months (88.5 vs. 74.2%; p=0.036), regardless of the strain used. The following risk factors of recurrence were identified by multivariate analysis: size larger than 3cm, more than 3 implants and not completing the manteinance. Patients under therapy with Connaught strain had a higher rate of BCGitis, with no differences in the other events studied.
ConclusionCompleting the maintenance phase is essential, regardless of the strain employed. The Connaught strain has a greater risk of BCGitis, and a sequential regimen could be useful in certain scenarios.
El bacilo de Calmette-Guérin (BCG) intravesical es clave en la prevención de recurrencia y progresión de tumor vesical superficial. El objetivo de nuestro trabajo es evaluar comparativamente la eficacia y toxicidad entre Connaught y Tice, así como la importancia del esquema de mantenimiento.
Material y métodosRevisamos retrospectivamente a 110 pacientes con tumor vesical superficial con tratamiento endovesical adyuvante, distribuidos en 3grupos, según el tratamiento fuese con Connaught, Tice, o ambos secuencialmente. Se ha calculado la supervivencia libre de recidiva en cada grupo y también de los pacientes que completaron el mantenimiento frente a los que no lo hicieron. Para identificar factores predictores de recidiva se llevó a cabo un análisis multivariante. Además, se ha valorado la toxicidad analizando la aparición de becegeítis, urgencia miccional, fiebre, infección urinaria y abandono del tratamiento por los efectos secundarios.
ResultadosNo hallamos diferencias en los parámetros de eficacia. Los pacientes del grupo Connaught completaron en menor medida el mantenimiento (38,4 frente a 72% del grupo Tice y frente a 76,3% del grupo ambas; p=0,010). Los pacientes que completaron el mantenimiento tuvieron mejor supervivencia libre de recidiva a 60 meses (88,5 vs. 74,2%; p=0,036), independientemente de la cepa empleada. El análisis multivariante identificó como factores de riesgo de recidiva el tamaño mayor de 3cm, más de 3 implantes y no completar el mantenimiento. Los pacientes de Connaught experimentan mayor tasa de becegeítis, sin diferencias en el resto de los eventos estudiados.
ConclusiónCompletar la fase de mantenimiento es esencial, independientemente de la cepa empleada. Connaught tiene más riesgo de becegeítis y un esquema secuencial puede ser útil en ciertos escenarios.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora