To evaluate the psychometric properties of the Spanish version of the ICIQ-Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Questionnaire (ICIQ-MLUTS): feasibility (% of completion and ceiling/ground effects), reliability (test-retest), convergent validity (vs. Bladder Control Self-Assessment Questionnaire [BSAQ] and vs. International Prostate Symptom Score [I-PSS]) and criterion validity (according to presence or absence of symptoms).
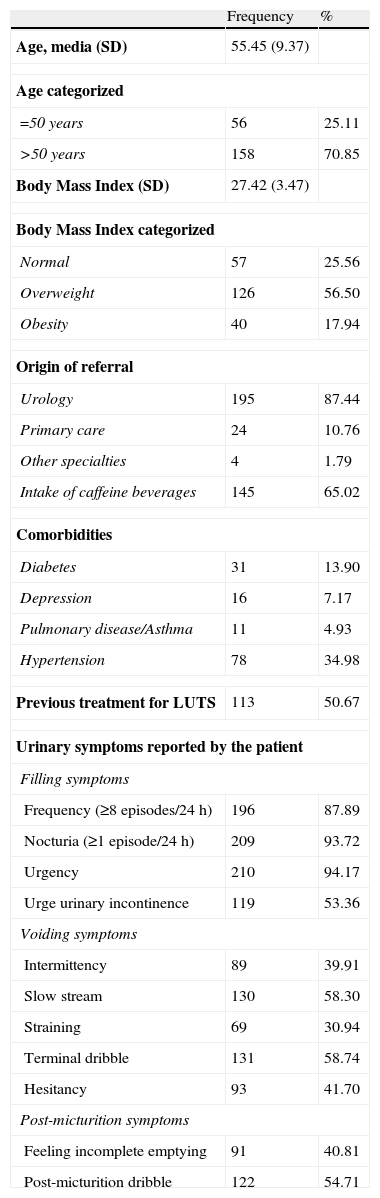
Materials and methodsThis was an observational, non-interventionist and multicenter study. 223 male patients with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), predominantly storage symptoms and aged 18–65, took part in the study. Patients completed the ICIQ-MLUTS (test), I-PSS and BSAQ questionnaires and referred their urinary symptoms in a single visit, with the exception of a subgroup composed by 49 patients who completed the questionnaire again 15 days after initial visit to evaluate test-retest reliability. The questionnaire includes 13 items divided in 2 sub-scales: Voiding symptoms (V) from 0 to 20 and Incontinence symptoms (I) from 0 to 24.
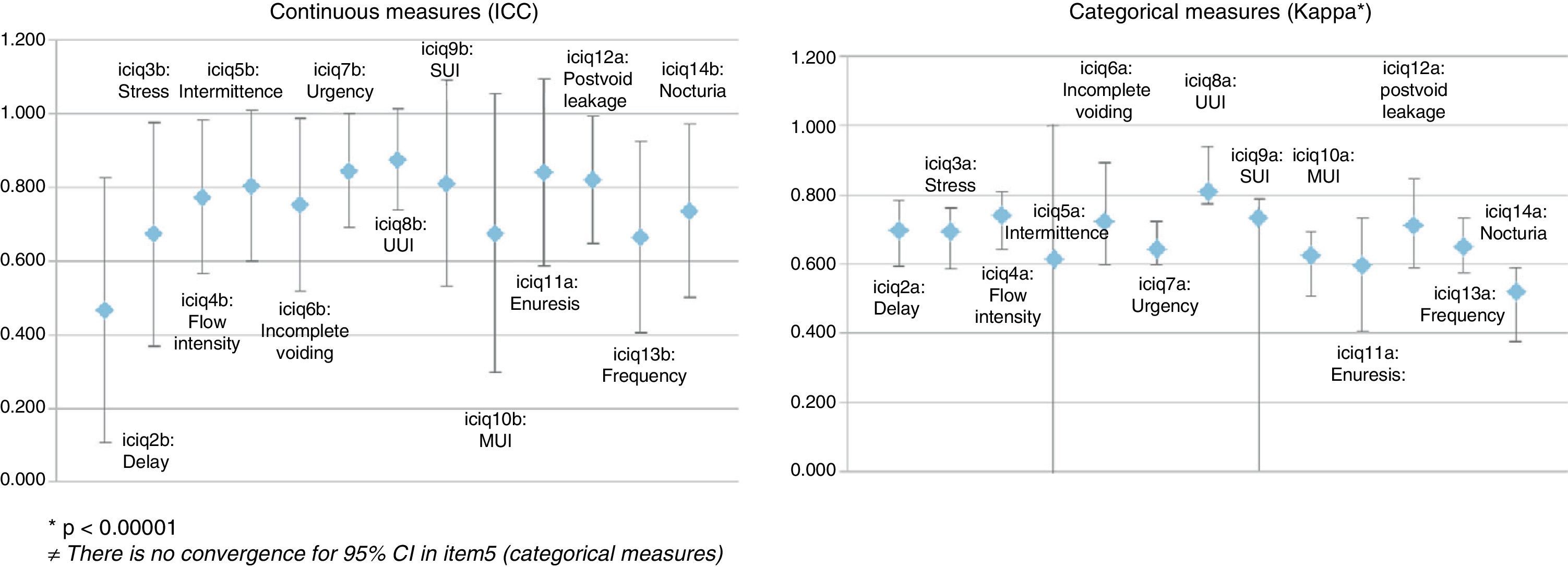
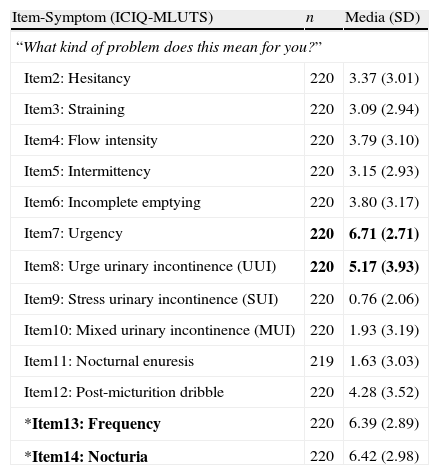
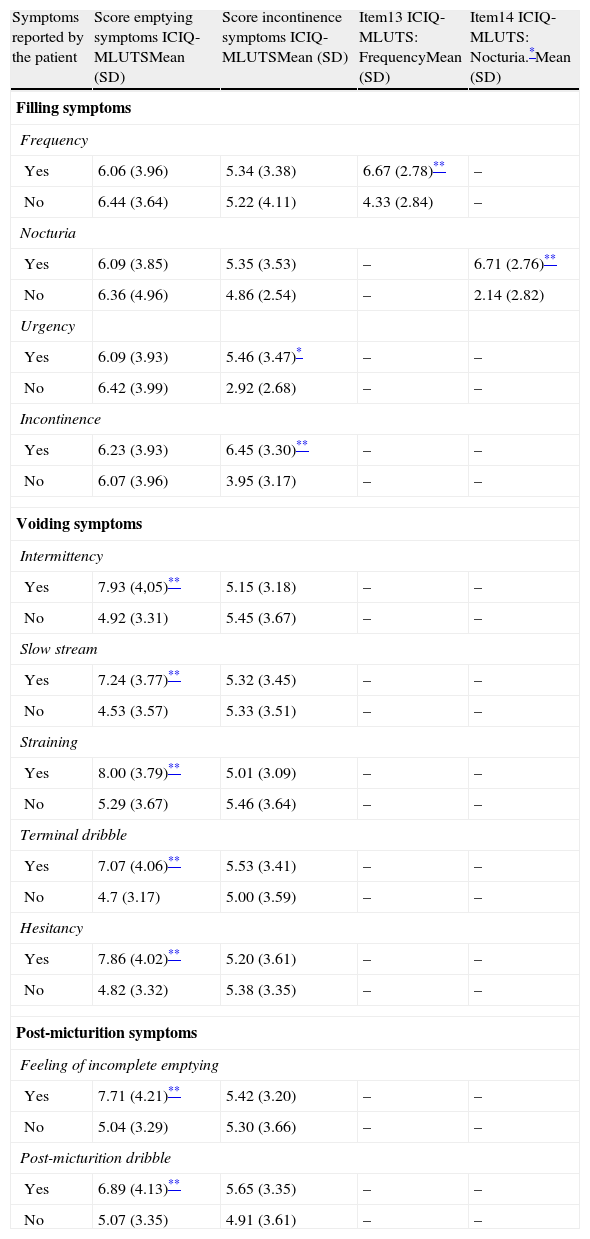
ResultsPercentage of patients who completed all items: 98.84%. Ground effect is 0 and ceiling effect was under 6% in both sub-scales. Test-retest reliability: Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) ranged from 0.68 to 0.88, except on Delay. Kappa shows a good agreement, between 0.60 and 0.81, except for Nocturia. Convergent validity: Correlation (Spearman) between the questionnaire sub-scales scores and the rest of measures is statistically significant (p<.01 and p<.05). Criterion validity: Statistically significant differences (p<.05) between scores on ICIQ-MLUTS, from patients who refer experiencing symptoms and those who do not.
ConclusionThe Spanish version of the ICIQ-MLUTS questionnaire shows adequate feasibility, reliability and validity.
Evaluar las propiedades psicométricas de la versión en castellano del cuestionario ICIQ-Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (ICIQ-MLUTS): factibilidad (porcentaje de cumplimentación y efecto suelo y techo), fiabilidad (test-retest), validez convergente (vs. Cuestionario de Autoevaluación del Control de la Vejiga [CACV] y vs. International Prostate Symptom Score [I-PSS]) y validez de criterio (según presencia o no de síntoma).
Material y métodosEstudio observacional, no intervencionista y multicéntrico. Participaron 223 pacientes varones de 18–65 años con síntomas del tracto urinario inferior (STUI), predominante de llenado. Los pacientes cumplimentaron el ICIQ-MLUTS (test-retest), el I-PSS y el CACV y refirieron sus síntomas urinarios en visita única, a excepción de un subgrupo de 49 pacientes que lo cumplimentaron 15 días después para evaluar la fiabilidad test-retest. El cuestionario contiene 13 ítems en 2 subescalas: Vaciado (V), de 0-20, e Incontinencia (I), de 0-24.
ResultadosPorcentaje de pacientes que responden a todos los ítems: 98,84%. Efecto suelo, 0%, y techo menor de 6% en las 2 subescalas del cuestionario. Fiabilidad test-retest: el coeficiente de correlación intraclase (CCI) osciló entre 0,66 y 0,88, salvo en Retardo. El kappa muestra buen acuerdo, entre 0,60 y 0,81, a excepción de Nicturia. Validez convergente: la correlación (Spearman) entre las puntuaciones de las subescalas del cuestionario y el resto de medidas es estadísticamente significativa (p<0,01 y p<0,05). Validez de criterio: diferencias estadísticamente significativas (p<0,05) entre las puntuaciones en el ICIQ-MLUTS de los pacientes que refieren los síntomas respecto a los que no.
ConclusiónEl ICIQ-MLUTS versión en español muestra adecuada factibilidad, fiabilidad y validez.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora