To evaluate the impact of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) on health related quality of life (HRQoL) and sexual function, in patients with moderate–severe lower tract urinary symptoms (LUTS/BPH) under treatment with alpha-blockers; to study differences associated to age, urinary symptom severity and time under treatment.
Materials and methods1580 patients diagnosed of BPH and LUTS/BPH, and in treatment with alpha-blockers were recruited in urology practices all around Spain. Socio-demographic- and clinic-data together with LUTS/HBP severity assessment (IPSS questionnaire) and responses to EQ-5D and the Sexual Function Index Questionnaire (SFI) were collected. A descriptive statistical analysis was performed, as well as test to contrast the results by age, LUTS/HBP severity and time under treatment; multiple linear regression models were adjusted for the answers to EQ-5D and SFI.
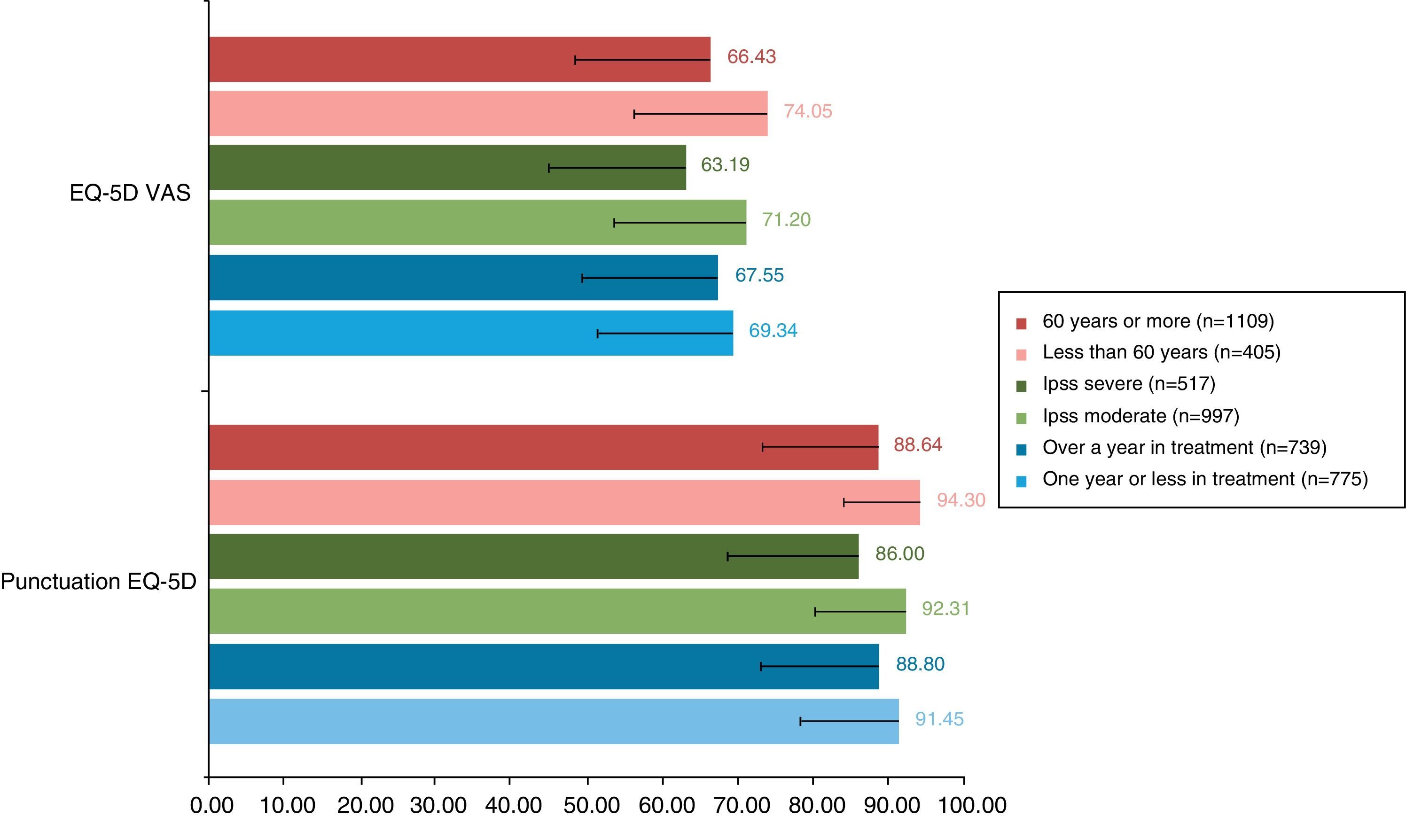
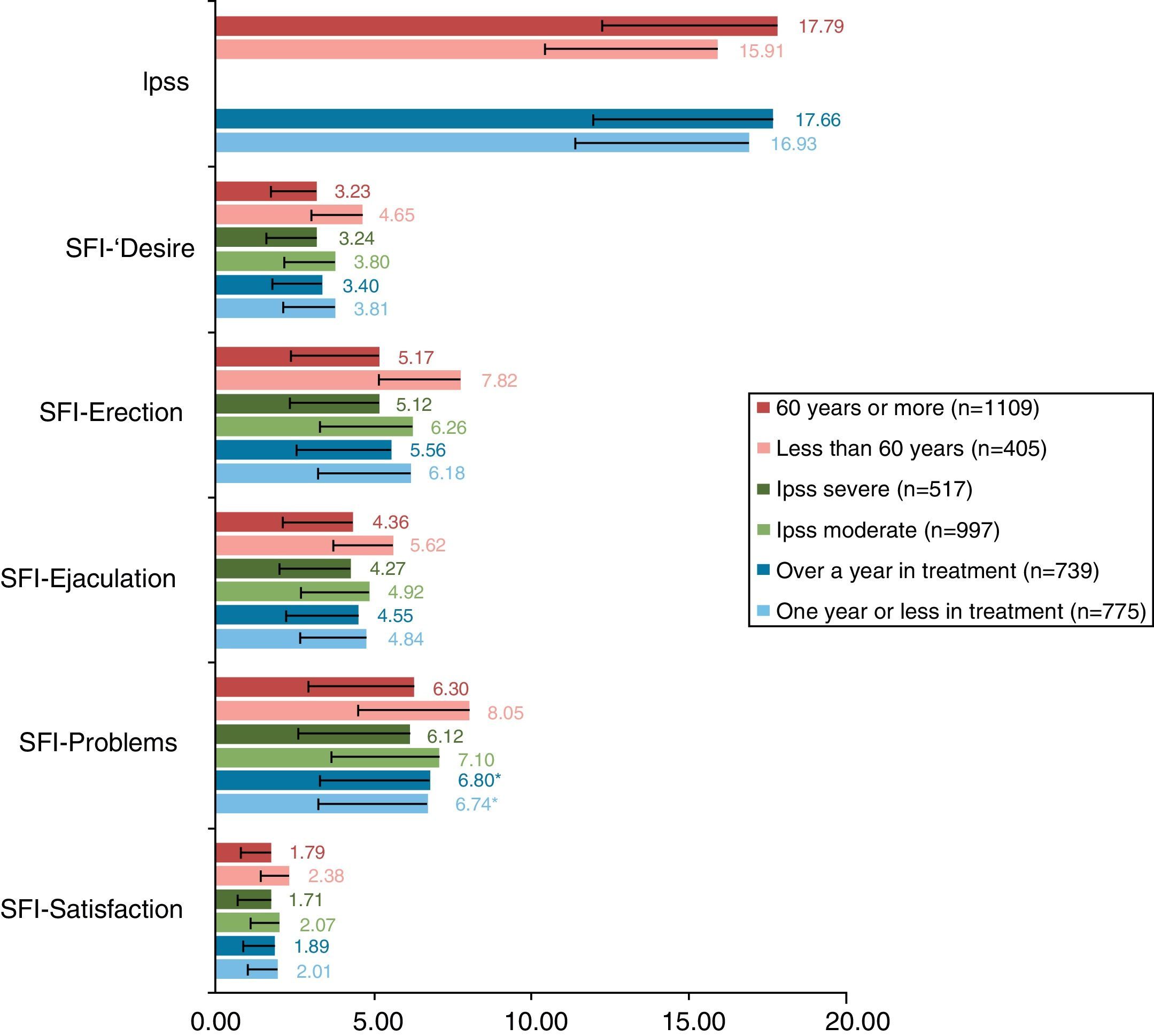
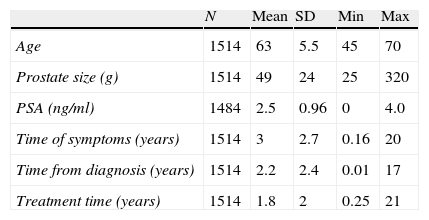
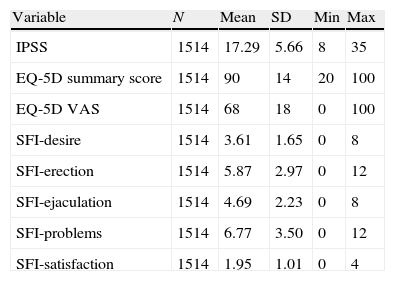
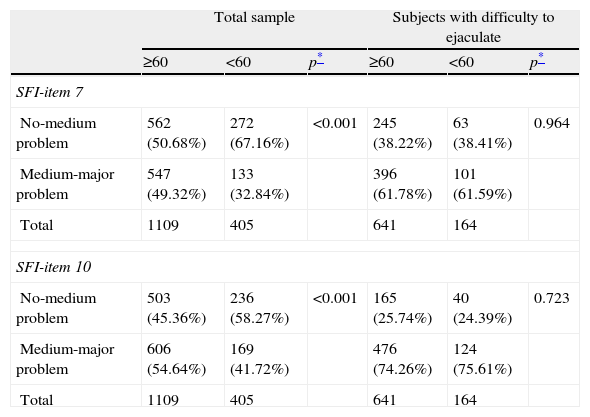
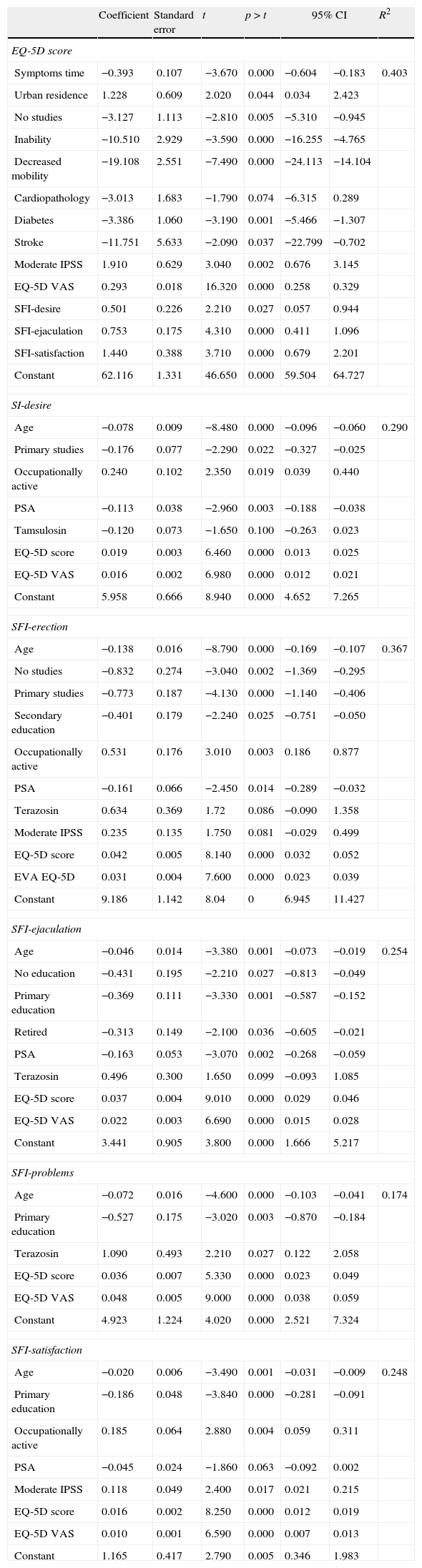
ResultsAnalysis database contained information of 1514 patients. Mean age (SD) was 63 (5.5) years (26.75% under 60 years), mean treatment time 1.8 (2.09) years (51.19% under one year). Mean questionnaire scores were: IPSS 17.29 (5.66) (65.85% moderate symptoms), EQ-5D 90 (14). The SFI-domains with worse scores were satisfaction and sexual drive. 52.58% of patients presented deteriorated HRQoL (IPSS-item 8). Age, symptom severity and time under treatment showed association with HRQoL and sexual function.
ConclusionsBPH and its treatment impact negatively on HRQOL and sexual function, with a more pronounced deterioration in patients with severe LUTS/HBP, in older patients and in patients in treatment over a year.
Evaluar el impacto en la Calidad de Vida Relacionada con la Salud (CVRS) y en la función sexual de la Hiperplasia Benigna de Próstata (HBP) y su tratamiento, en pacientes con síntomas urinarios (STUI/HBP) moderados-graves en tratamiento con alfa-bloqueantes; estudiar las diferencias asociadas a edad, gravedad de síntomas urinarios y tiempo con tratamiento.
Material y métodosSe reclutaron 1.580 pacientes diagnosticados de HBP y con STUI/HBP en tratamiento con alfa-bloqueantes, en consultas de urología de toda España. Se recogieron datos socio-demográficos, clínicos y de gravedad de STUI/HBP (cuestionario IPSS) y las respuestas al cuestionario EQ-5D y el “Sexual Function Index-SFI”. Se realizó un análisis estadístico descriptivo, contrastes por edad, gravedad de STUI/HBP y tiempo de tratamiento y se ajustaron modelos lineales de regresión múltiple para las respuestas al EQ-5D y SFI.
ResultadosSe analizaron datos de 1.514 pacientes. La media (D.E) de edad fue 63 (5,5) años (26,75%<60 años), de tiempo de tratamiento 1,8 (2,0) años (51,19%<1 año), para IPSS 17,29 (5,66) puntos (65,85% síntomas moderados), para EQ-5D 90 (14) puntos. Las dimensiones del SFI más dañadas fueron satisfacción y deseo. El 52,58% de los pacientes mostraron afectación en CVRS (IPSS-ítem 8). Edad, gravedad de síntomas y tiempo en tratamiento mostraron asociación con CVRS y función sexual.
ConclusionesLa HBP y su tratamiento impactan negativamente en la CVRS y en la función sexual, siendo el deterioro mayor en pacientes con síntomas STU/HBP graves, en los de mayor edad y en los que llevaban más de 1 año de tratamiento.