To analyze the impact of overactive bladder (OAB) symptoms on the work activity of patients in Spain.
MethodAn observational, multicentre cross-sectional study was conducted with 149 urologists and 131 gynecologists of Spain and included patients diagnosed with OAB, according to clinical judgment, who were of working age (18–65 years). We collected sociodemographic, clinical and work activity data. The patients filled out the Bladder Control Self-Assessment Questionnaire (B-SAQ) and the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire-General Health (WPAI-GH). The effect of each symptom on the daily and occupational activity was assessed. The results were stratified according to sex and the presence of urgency and urinary incontinence (UI) according to the B-SAQ.
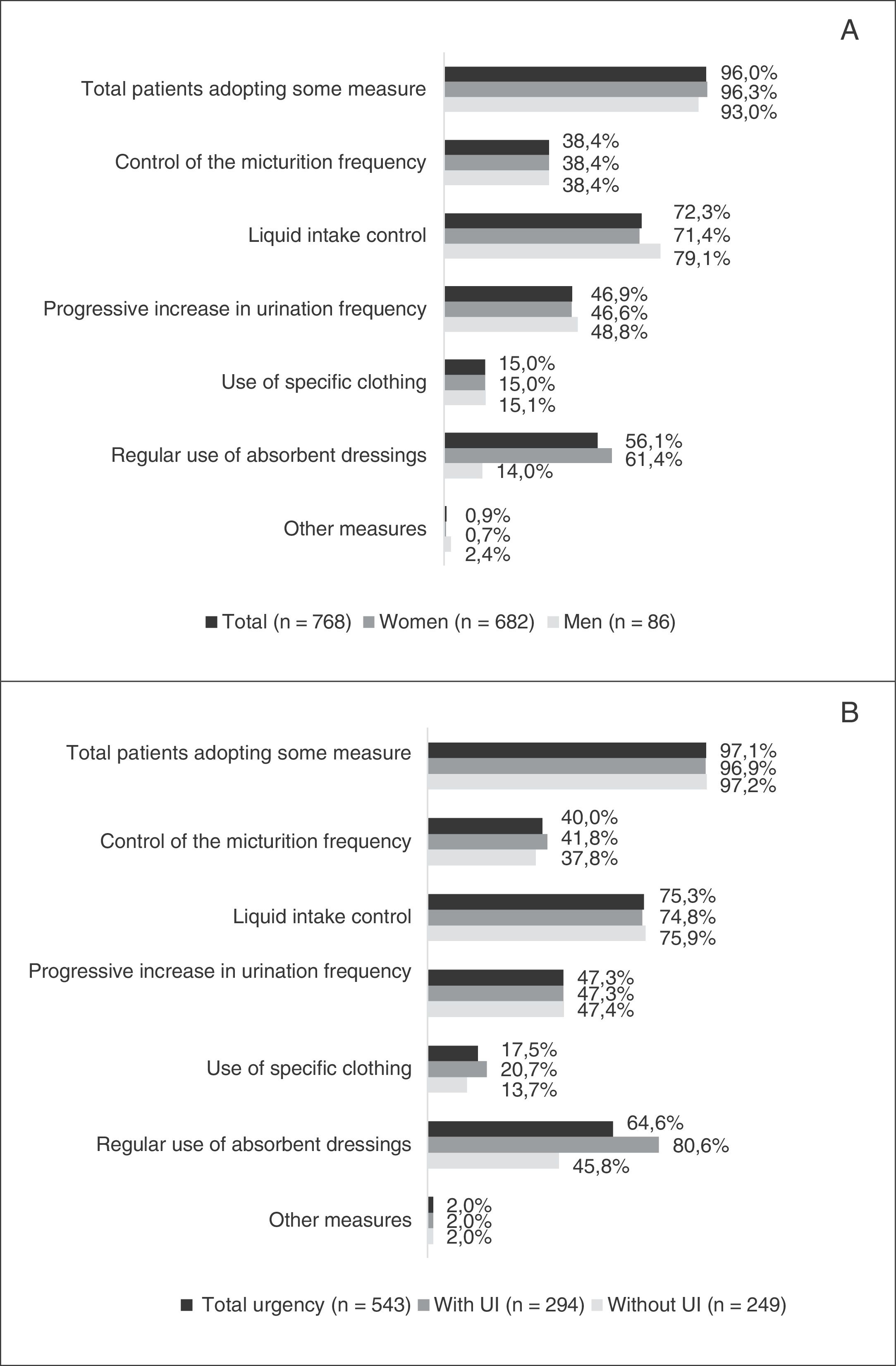
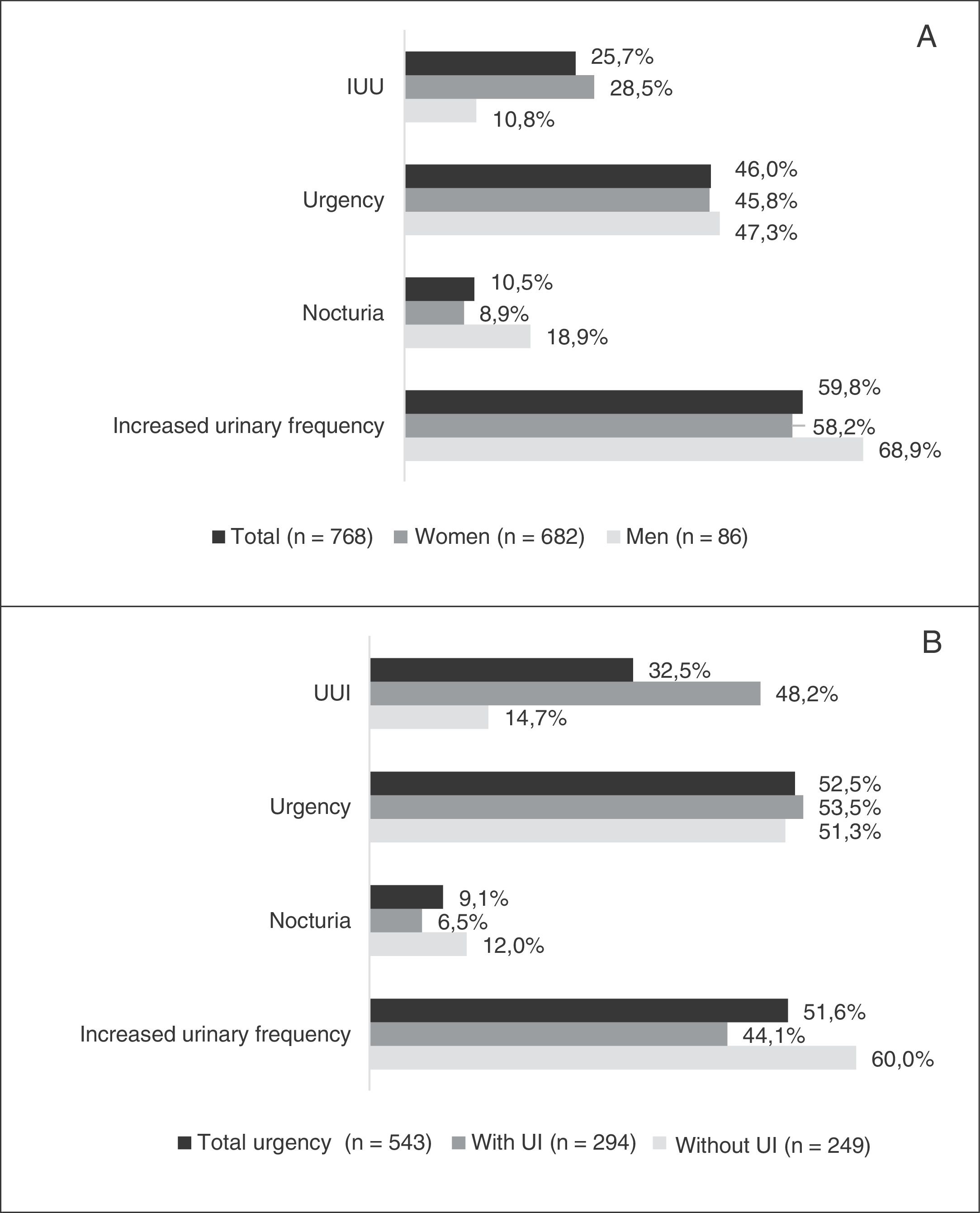
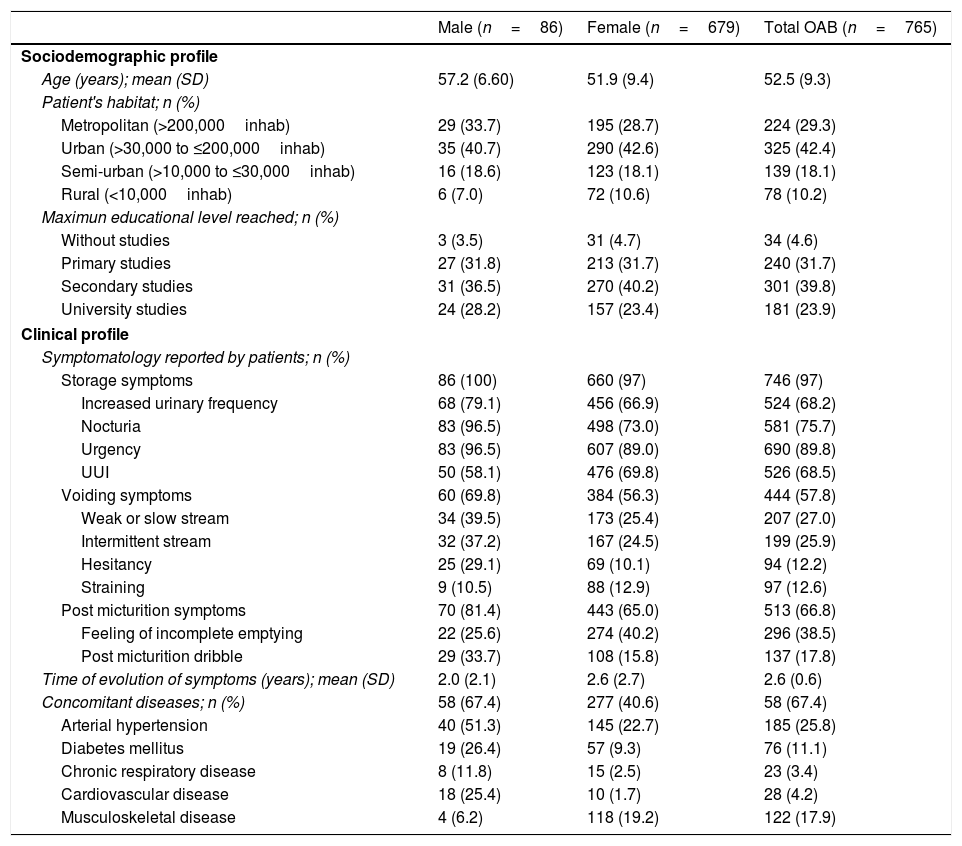
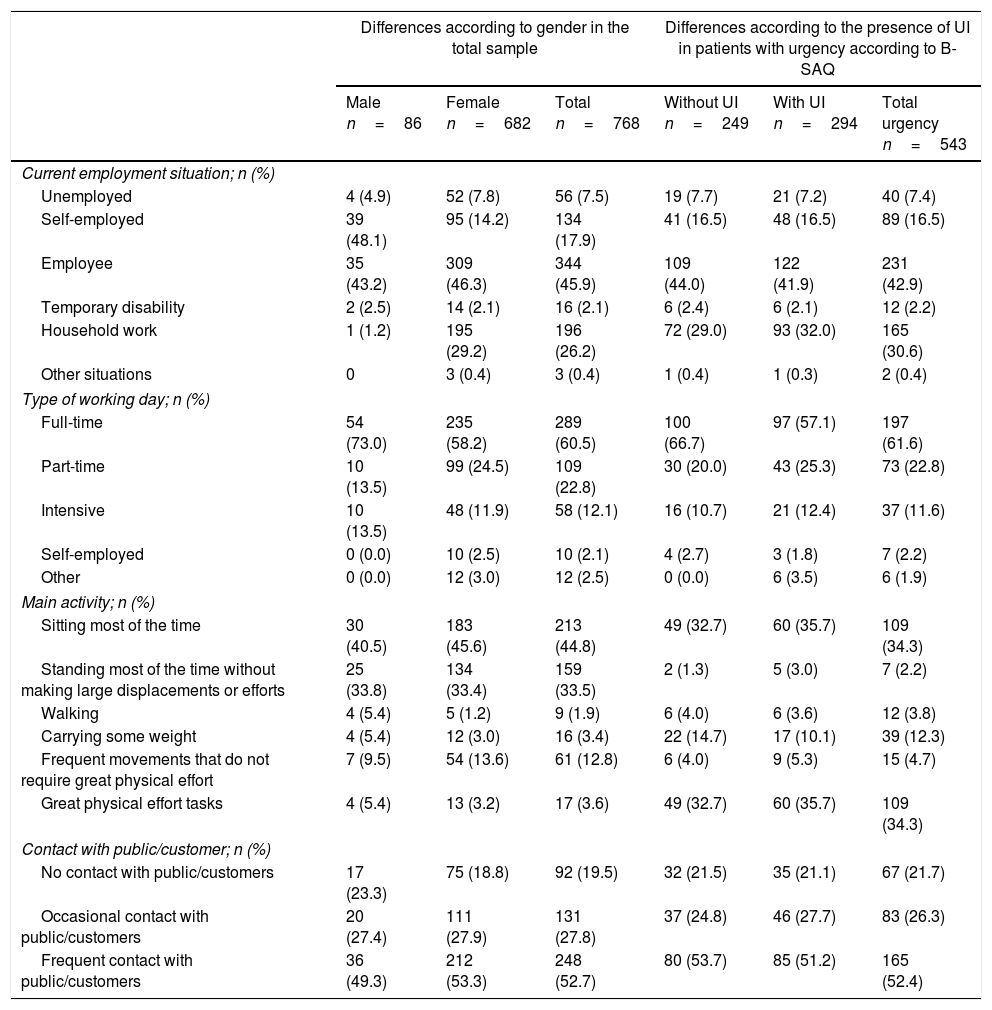
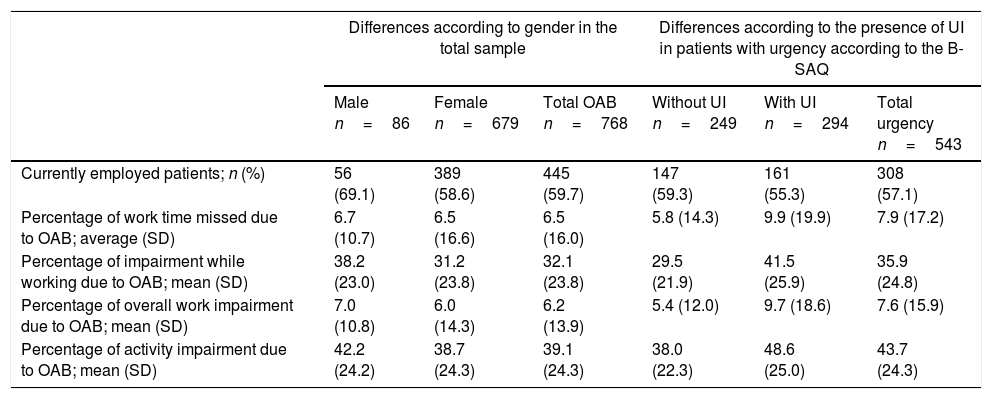
ResultsWe assessed 768 patients (89% women), with a mean (SD) age of 52.5 (9.3) years and 2.6 (2.6) years of OAB progression. The most common symptoms according to the patients urgency (89.8%), nocturia (75.7%), urge urinary incontinence (68.5%) and frequency (68.2%). Ninety-six percent of the patients adopted adaptive measures for their OAB. According to the B-SAQ, 543 patients (71%) presented urgency; of these, 294 (54%) showed UI. The symptom that most affected work activity was frequency (59.8%). According to the WPAI-GH, the patients reported an impact of 32% during the workday (41% in patients urgency and UI) and a work time missed due to OAB of 6.5% (9.9% in patients with urgency and UI).
ConclusionsThe symptoms of OAB negatively affect work activity, especially in patients who have urgent urination and UI.
Analizar el impacto de los síntomas de vejiga hiperactiva (VH) sobre la actividad laboral de pacientes en España.
MétodoEstudio observacional, multicéntrico y transversal con 149 urólogos y 131 ginecólogos de España que incluyeron pacientes diagnosticados de VH según criterio clínico, en edad laboral (18-65 años). Se recogieron datos sociodemográficos, clínicos y de actividad laboral. Los pacientes cumplimentaron el Cuestionario de Autoevaluación del Control de la Vejiga (CACV) y el Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire-General Health (WPAI-GH). Se evaluó el impacto de cada síntoma sobre la actividad diaria y laboral. Los resultados se estratificaron según género y presencia de urgencia e incontinencia urinaria (IU) según el CACV.
ResultadosSe evaluaron 768 pacientes (89% mujeres), con una media (DE) de edad de 52,5 (9,3) años y 2,6 (2,6) años de evolución de VH. La sintomatología más frecuente según el paciente fue urgencia (89,8%), seguida de nicturia (75,7%), incontinencia urinaria de urgencia (68,5%) y frecuencia (68,2%). El 96% adoptaron medidas adaptativas para la VH. Según el CACV, 543 pacientes (71%) presentaban urgencia y de estos, 294 (54%) presentaban IU. El síntoma que más afectaba la actividad laboral fue la frecuencia (59,8%). Según el WPAI-GH, los pacientes refirieron un impacto del 32% durante la jornada laboral (41% en pacientes con urgencia e IU) y una pérdida de tiempo de trabajo del 6,5% (un 9,9% en pacientes con urgencia e IU).
ConclusionesLos síntomas de VH impactan negativamente sobre la actividad laboral, especialmente en pacientes que presentan urgencia e IU.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora