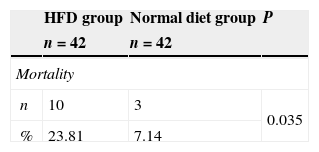We aimed to investigate the role of IGF-1 related pathway in high-fat diet (HFD) promotion of TRAMP mouse PCa progression.
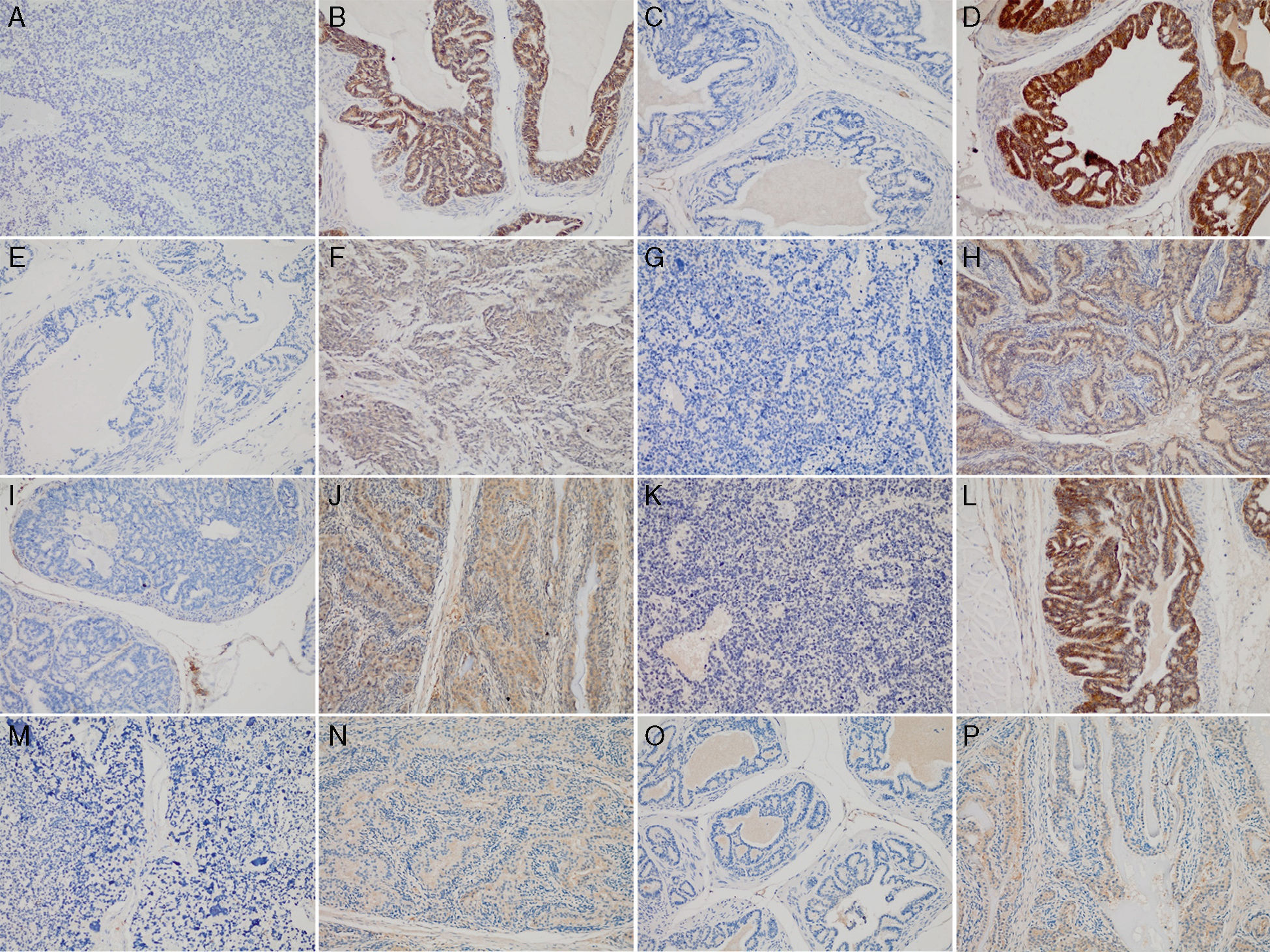
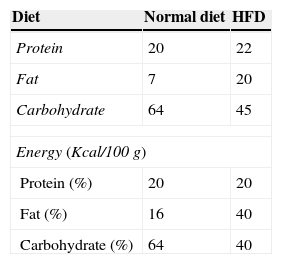
MethodsTRAMP mice were randomly divided into two groups: HFD group and normal diet group. TRAMP mice of both groups were sacrificed and sampled on the 20th, 24th and 28th week, respectively. Serum levels of insulin, IGF-1 and IGF-2 were tested by ELISA. Prostate tissue of TRAMP mice was used for both HE staining and immunohistochemical staining of IGF-1 related pathway proteins, including IGF-1Rα, IGF-1Rβ, IGFBPs and AKT.
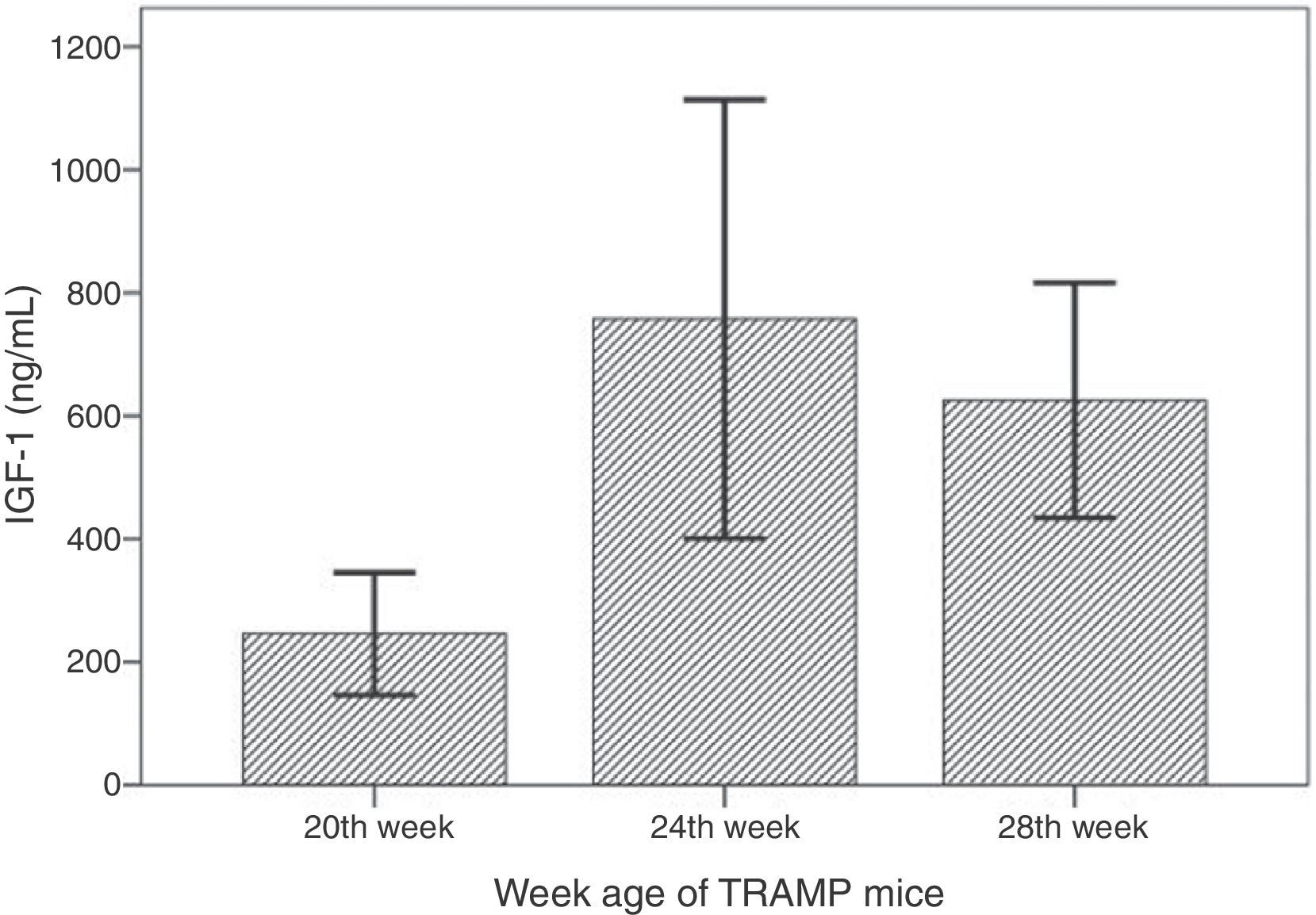
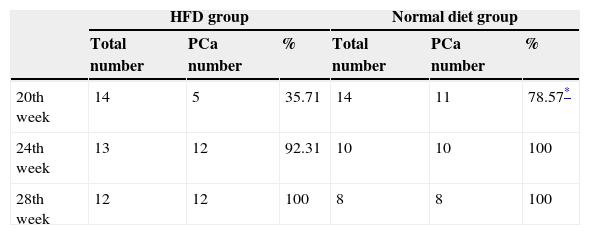
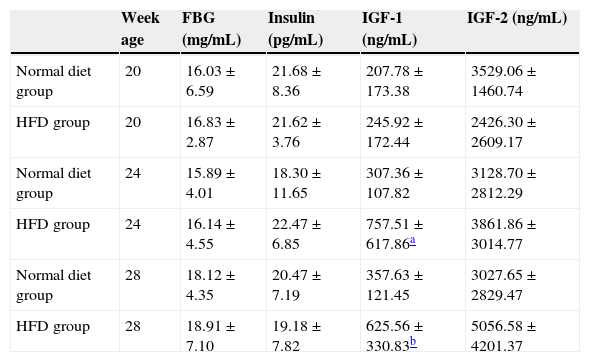
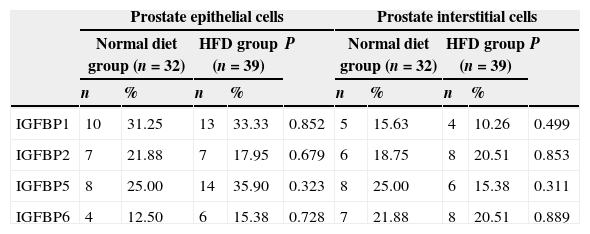
ResultsThe mortality of TRAMP mice from HFD group was significantly higher than that of normal diet group (23.81% and 7.14%, P=0.035). The tumor incidence of HFD TRAMP mice at 20th week was significantly higher than normal diet group (78.57% and 35.71%, P=0.022). Serum IGF-1 level of HFD TRAMP mice was significantly higher than that of normal diet TRAMP mice. Serum IGF-1 level tended to increase with HFD TRAMP mice's age. HFD TRAMP mice had higher positive staining rate of IGF-1Rα, IGF-1Rβ, IGFBP3 and Akt than normal diet TRAMP mice.
ConclusionsIGF-1 related pathway played an important role in high-fat diet promotion of TRAMP mouse PCa development and progression.
Nuestro objetivo fue investigar el papel de las vías relacionadas con IGF-1 en la promoción de dieta alta en grasas (DAG) de la progesión del cáncer de próstata en ratones TRAMP.
MétodosLos ratones TRAMP fueron divididos aleatoriamente en 2 grupos: el grupo DAG y el grupo de dieta normal. Los ratones TRAMP de ambos grupos fueron sacrificados y se tomaron muestras en las semanas 20, 24 y 28, respectivamente. Los niveles séricos de insulina, IGF-1 e IGF-2 se probaron mediante ELISA. El tejido prostático de los ratones TRAMP se utilizó tanto para tinción H-E como para tinción inmunohistoquímica de proteínas de la vía relacionadas con IGF-1, incluyendo IGF-1Rα, IGF-1Rβ, IGFBPs y AKT.
ResultadosLa mortalidad de los ratones TRAMP del grupo DAG fue significativamente más alta que la del grupo de dieta normal (23,81% y 7,14%, p=0,035). La incidencia de tumores de los ratones TRAMP de DAG a la semana 20 fue significativamente mayor que en el grupo de dieta normal (78,57% y 35,71%, p=0,022). El nivel sérico de IGF-1 de los ratones TRAMP de DAG fue significativamente mayor que el de los ratones TRAMP de dieta normal. El nivel sérico de IGF-1 tendió a aumentar con la edad de los ratones TRAMP de DAG. Los ratones TRAMP de DAG tenían una tasa de tinción positiva más elevada de IGF-1Rα, IGF-1Rβ, IGFBP3 y AKT que los ratones TRAMP de dieta normal.
ConclusionesLa vía relacionada con IGF-1 ejerció un papel importante en la promoción de la dieta de alto contenido en grasa del desarrollo y la progresión del CaP de ratón TRAMP.