To analyze the most frequent causes and resistances of the uropathogens in patients affected by neurogenic bladder.
Materials and methodsA total of 284 patients, in whom a total of 284 urinary cultures were performed, were included. Of these, 106 came from patients with neurological injuries, 28 from a non-neurogenic control group, 75 from patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) of our Hospital and 75 patients who came into the emergency room with the symptoms of an acute urinary tract infection. A quantitative urine culture was performed in a chromogenic media and the resistances of all urine cultures that were positive for one or two micro-organisms were identified and studied.
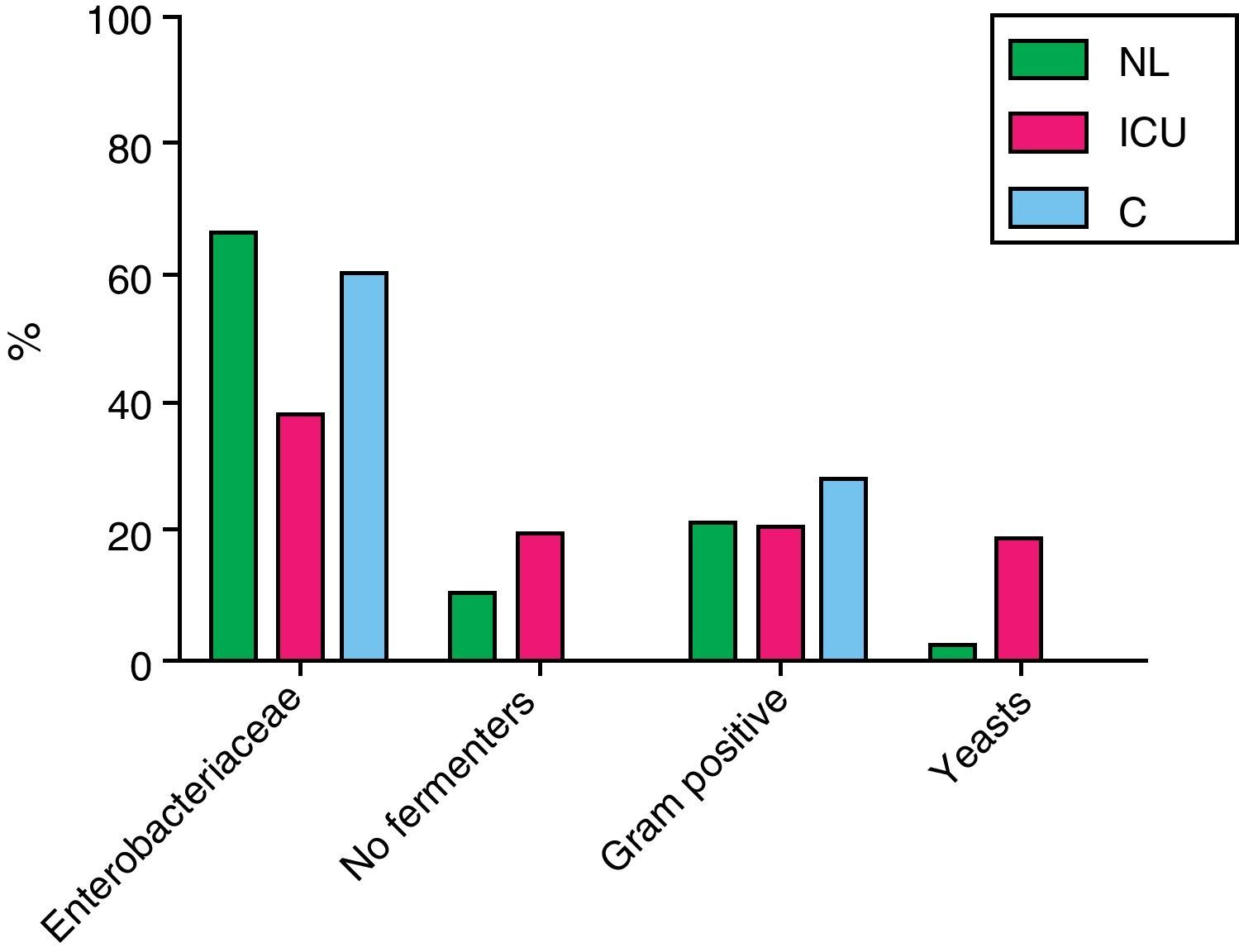
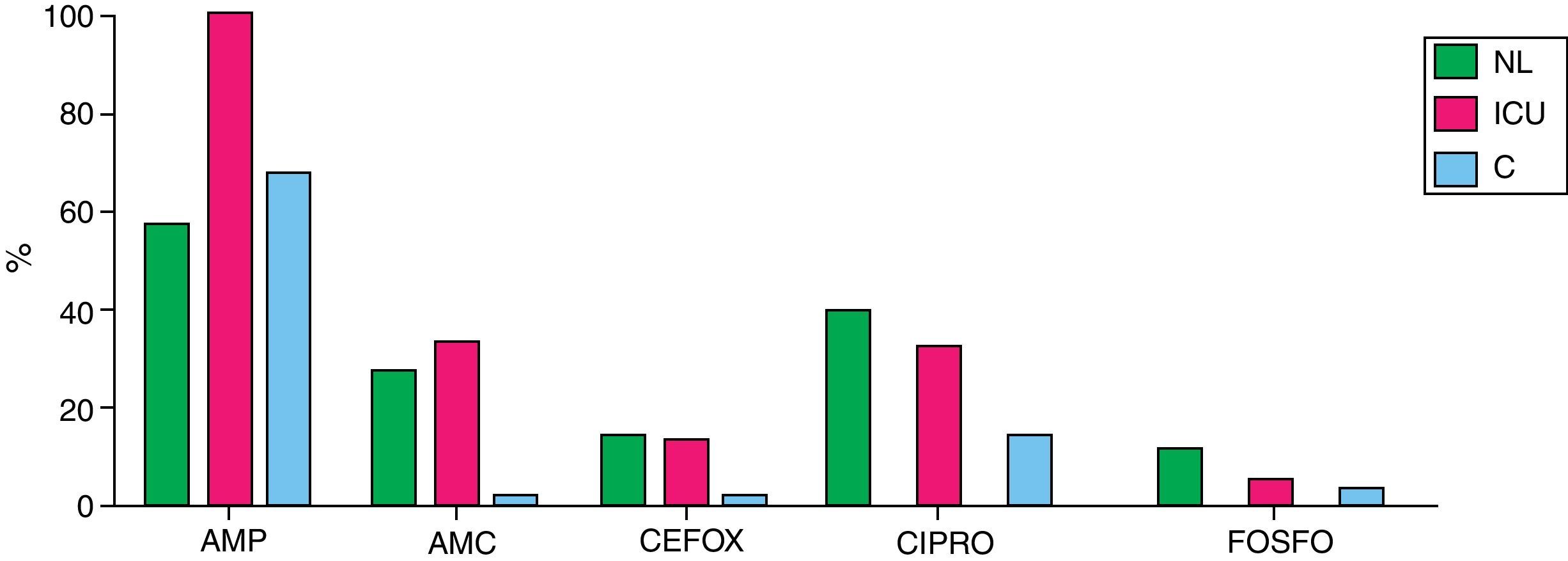
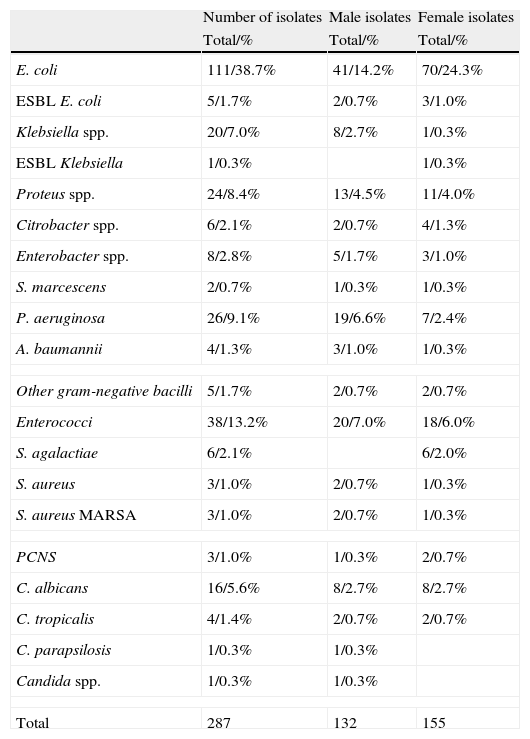
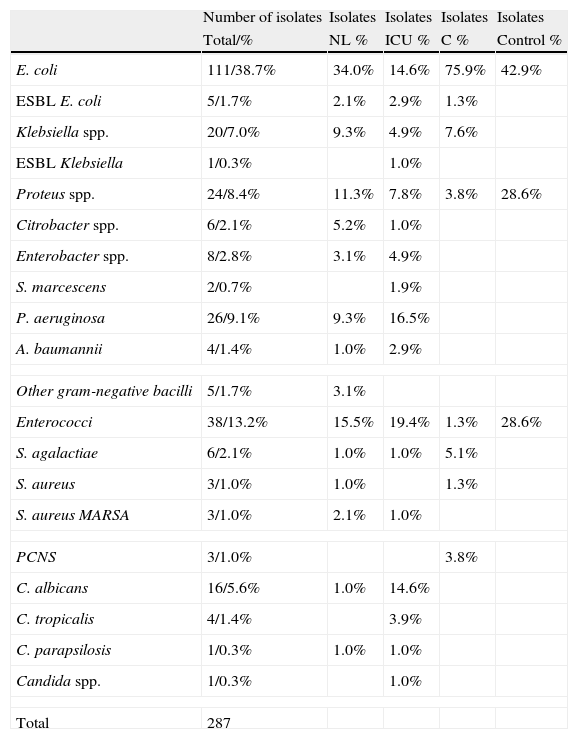
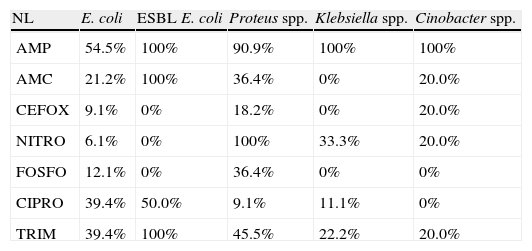
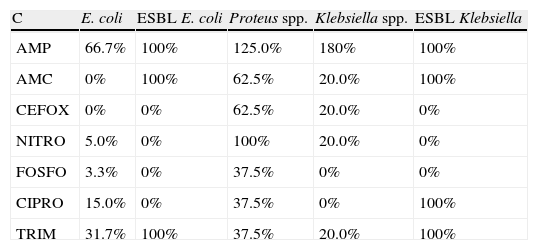
ResultsA total of 67% of the patients with neurological injuries had positive urine cultures compared to 25% of control group patients. The urine cultures of patients admitted into the ICU and those of the Emergency Room group were 100% positive, since the first 75 positive urine cultures were selected for the study. Escherichia coli was the most-frequently microorganism isolated in the group of neurological patients, as well as among the patients from the Emergency Room and from the control group. In the ICU, the most-frequently isolated micro-organism was Enterococcus spp. (19.4%), followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (16.5%). The study of resistances in general E. coli has high rates of resistance to ampicillin and co-trimoxazole and, although to a lesser degree to ciprofloxacin.
ConclusionsE. coli is the micro-organism most frequently isolated among all of the groups except in the ICU, where it is surpassed by Enterococcus spp. and P. aeruginosa. The resistances among the four population groups studied have different features, overall showing a low rate of resistance to nitrofurantoin and especially to fosfomycin, observed in patients from the Emergency Room or admitted to the ICU and neurological patients.
Analizar la etiología y resistencias de los uropatógenos más frecuentes en una pobla-ción con vejiga neurógena.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 284 pacientes a los que se practicaron un total de 284 uro-cultivos. De estos, 106 procedían de pacientes con lesión neurológica, 28 de grupo control no neurógeno, 75 de pacientes ingresados en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos (UCI) y 75 de pacientes que acudieron a Urgencias por sintomatología de infección aguda del tracto urinario. Se realizó urocultivo cuantitativo en medio cromogénico, así como identificación y estudio de resistencias de todos los urocultivos positivos para uno o dos microorganismos.
ResultadosEl 67% de los pacientes neurológicos presentaron urocultivos positivos, frente al 25% de los pacientes control. Los urocultivos de pacientes ingresados en UCI y los del grupo Urgencias fueron positivos al 100%, ya que se seleccionaron los primeros 75 urocultivos positivos. E. coli fue el microorganismo más frecuentemente aislado en el grupo de neurológicos, al igual que en enfermos procedentes de Urgencias y del grupo control. En UCI fue Enterococcus spp. (19,4%), seguido de P. aeruginosa (16,5%). En el estudio de resistencias E. coli presentó altas tasas de resistencia a ampicilina y cotrimoxazol y, aunque en menor grado, a ciprofloxacino.
ConclusionesE. coli es el microorganismo más frecuentemente aislado entre todos los grupos, excepto en UCI, en el que es superado por Enterococcus spp. y P. aeruginosa. Las resisten-cias entre los 4 grupos de población estudiada tienen características diferentes, mostrando globalmente un bajo índice de resistencias a nitrofurantoína y especialmente a fosfomicina, observado en pacientes que provienen de Urgencias o ingresados en UCI y neurológicos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora