Interleukin-1 (IL-1) seems to have an important role in early reactions towards microbes, while its genetic variability could affect this role in atopic patients who have a distressed immunity towards dermatological infections.
MethodsEighty-nine patients with atopic dermatitis (AD), who were referred to a main referral paediatric hospital, were enrolled in this study. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) of the following IL-1 cluster genes were assessed in this group of patients: IL-1α −889, IL-1β −511, IL-1β +3962, IL-1R Pst-I 1970, and IL-1RA Mspa-I 11100. The results were compared with a group of 140 healthy subjects from the same region.
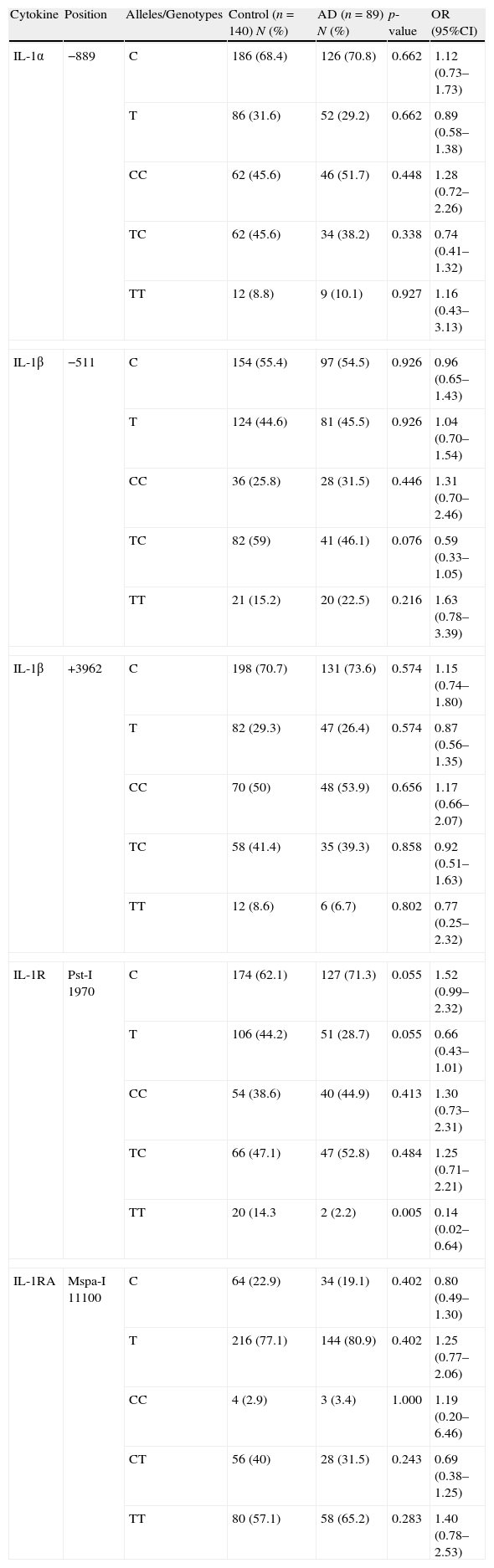
ResultsFourteen percent of the controls had TT homozygous genotype in IL-1R at position Pst-I 1970, while only 2% of the patients with AD had this genotype (p=0.005, OR: 0.14, 95%CI: 0.02–0.64). The CC homozygous genotype was the most common genotype in IL-1α position −889 and IL-1β at position +3962 in both groups of patients with AD and the controls, while the TC heterozygous genotype was the most common genotype in IL-1β at position −511 and IL-1R at position Pst-I 1970, with no significant difference between the two groups.
ConclusionsThis study showed a significant negative association in the IL-1R Mspa-I 11100 TT homozygous genotype in the patients with AD.
Several studies on genetic polymorphisms of cytokines, including pro-inflammatory cytokines, have been conducted in different immunological disorders during the last decade, showing some association between some positions and a number of diseases.1–6 However, it seems that there is no distinct genetic cause for some diseases, including atopic dermatitis (AD), which is considered a multi-factorial disease.7,8 In spite of several studies on the genetics of AD, there is no single response to explain the pathogenesis of disease, while single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) seem to have a role in susceptibility or protectivity of individuals to the disease.7 It seems that particular genotypes/haplotypes of the interleukin (IL)-1 could influence cytokine production,9 while this cytokine seems to have an important role in early reactions towards microbes. However, its genetic variability could affect this role in atopic patients who have a distressed immunity towards dermatological infections.
This study was aimed to analyse the SNPs of IL-1 family in a group of paediatric patients with AS to see if any allele or genotype could either predispose or protect the individual from atopy.
Materials and methodsIn this study, 89 Iranian patients with a diagnosis of AD, from the Children's Medical Centre Hospital, a main referral paediatric hospital in Tehran, Iran, were enrolled. One hundred and forty unrelated healthy subjects without any evidence of atopy were also selected as the control group.10 This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Written informed consent was obtained from all the parents of enrolled individuals.
Polymerase chain reaction with sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP assay kit, Heidelberg University, Germany) was the method for typing of the cytokine genes, which were previously explained in details.10 The frequencies of alleles and genotypes of the following IL-1 cluster genes were verified: IL-1α −889, IL-1β −511, IL-1β +3962, IL-1R Pst-I 1970, and IL-1RA Mspa-I 11100. After counting the allele frequencies, the comparison was made via χ2 test; and the odds ratios (OR), 95% confidence intervals (CI) and p-value (p) were calculated for each allele and genotype.
ResultsThe allele and genotype frequencies of each SNP are presented in Table 1. The CC homozygous genotype was the most common genotype in IL-1α position −889 and IL-1β at position +3962 in both groups of patients with AD as well as in the controls. However, there was no significant difference between frequencies of the alleles and genotypes for these cytokines between the two study groups.
IL-1 family allele and genotype polymorphisms in the atopic and normal population.
| Cytokine | Position | Alleles/Genotypes | Control (n=140) N (%) | AD (n=89) N (%) | p-value | OR (95%CI) |
| IL-1α | −889 | C | 186 (68.4) | 126 (70.8) | 0.662 | 1.12 (0.73–1.73) |
| T | 86 (31.6) | 52 (29.2) | 0.662 | 0.89 (0.58–1.38) | ||
| CC | 62 (45.6) | 46 (51.7) | 0.448 | 1.28 (0.72–2.26) | ||
| TC | 62 (45.6) | 34 (38.2) | 0.338 | 0.74 (0.41–1.32) | ||
| TT | 12 (8.8) | 9 (10.1) | 0.927 | 1.16 (0.43–3.13) | ||
| IL-1β | −511 | C | 154 (55.4) | 97 (54.5) | 0.926 | 0.96 (0.65–1.43) |
| T | 124 (44.6) | 81 (45.5) | 0.926 | 1.04 (0.70–1.54) | ||
| CC | 36 (25.8) | 28 (31.5) | 0.446 | 1.31 (0.70–2.46) | ||
| TC | 82 (59) | 41 (46.1) | 0.076 | 0.59 (0.33–1.05) | ||
| TT | 21 (15.2) | 20 (22.5) | 0.216 | 1.63 (0.78–3.39) | ||
| IL-1β | +3962 | C | 198 (70.7) | 131 (73.6) | 0.574 | 1.15 (0.74–1.80) |
| T | 82 (29.3) | 47 (26.4) | 0.574 | 0.87 (0.56–1.35) | ||
| CC | 70 (50) | 48 (53.9) | 0.656 | 1.17 (0.66–2.07) | ||
| TC | 58 (41.4) | 35 (39.3) | 0.858 | 0.92 (0.51–1.63) | ||
| TT | 12 (8.6) | 6 (6.7) | 0.802 | 0.77 (0.25–2.32) | ||
| IL-1R | Pst-I 1970 | C | 174 (62.1) | 127 (71.3) | 0.055 | 1.52 (0.99–2.32) |
| T | 106 (44.2) | 51 (28.7) | 0.055 | 0.66 (0.43–1.01) | ||
| CC | 54 (38.6) | 40 (44.9) | 0.413 | 1.30 (0.73–2.31) | ||
| TC | 66 (47.1) | 47 (52.8) | 0.484 | 1.25 (0.71–2.21) | ||
| TT | 20 (14.3 | 2 (2.2) | 0.005 | 0.14 (0.02–0.64) | ||
| IL-1RA | Mspa-I 11100 | C | 64 (22.9) | 34 (19.1) | 0.402 | 0.80 (0.49–1.30) |
| T | 216 (77.1) | 144 (80.9) | 0.402 | 1.25 (0.77–2.06) | ||
| CC | 4 (2.9) | 3 (3.4) | 1.000 | 1.19 (0.20–6.46) | ||
| CT | 56 (40) | 28 (31.5) | 0.243 | 0.69 (0.38–1.25) | ||
| TT | 80 (57.1) | 58 (65.2) | 0.283 | 1.40 (0.78–2.53) | ||
n=total number of examinees; N=absolute number; F%=frequency percentage; OR=Odds ratio; 95%CI=Wald's 95% confidence interval.
Indeed, the TC heterozygous genotype was the most common genotype in IL-1β at position −511 and IL-1R at position Pst-I 1970, with no significant difference between the patients and the controls; however, the TT homozygous genotype in IL-1R at position Pst-I 1970, which was the less frequent genotype, has significantly negative association with AD. While 14.3% of the controls had the TT genotype, only 2.2% of the patients with AD had this genotype (p=0.005, OR: 0.14, 95%CI: 0.02–0.64).
On the contrary, the TT homozygous genotype in IL-1RA Mspa-I 11100 was the most common genotype, but there was no significant difference on allele and genotype frequencies at this position between the patient and the control groups.
DiscussionInterleukin-1 seems to be a potential biomarker for itching in AD,11 while Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2)-mediated IL-1β production by monocytes seems to be selectively impaired in atopic patients; this could be a mechanism involved in the susceptibility of the patients to viral infections.12 A 430kb interval on chromosome 2q14 is responsible for the IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-1RA (receptor antagonist).13 The results of this study for the IL-1 cluster (IL-1α −889, IL-1β −511, IL-1β +3962, IL-1R Pst-I 1970, IL-1RA Mspa-I 11100), showed no allelic association with AD. Unlike our study, Landeck et al.14 recently indicated a negative association of IL-1α −889 T allele and a possible protective effect of the IL-1α −889 C/T polymorphism in contact dermatitis, which is in contrast with another study by Starvic et al.,15 which showed IL-1α −889 C allele and CT polymorphism could occur in individuals susceptible to AD. Other studies showed neither association between the IL-1α gene −899T/C and AD, nor the IL-1β gene in the positions of −511C/T, 3953T/C, −1418T/C, and 315T/C.16 The only association between the IL-1 cluster genotype polymorphisms and Iranian patients with AD was the IL-1R Pst-I 1970 for the TT genotype. There was a significant decrease in the AD group, compared to the control group. Reich et al.14 reported no associations for cytokine polymorphisms for the IL-1β −511 T/C, +3953 T/C, and IL-1Rα intron 2 in German patients. In the study by Starvic et al., although there was significant association between IL-1β −511 CT genotype and IL-1β +3962 CT genotype, there was no association between IL-1R Pst-I 1970 and AD.15 It should be noted that Filaggrin loss-of-function mutations have recently been shown to be associated with increased expression of IL-1 cytokines in AD.17
In conclusion, this study showed a significant negative association in the IL-1R Pst-I 1970 TT genotype in the patients with AD. Although the protectivity of the SNP in AD might not be as highly penetrative as some other genetic SNPs, further multi-centre studies with large numbers of atopic patients in different ethnicities are needed to confirm the results of this study.
Ethical disclosuresConfidentiality of data. The authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work centre on the publication of patient data and that all the patients included in the study have received sufficient information and have given their informed consent in writing to participate in that study.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the informed consent of the patients and/or subjects mentioned in the article. The author for correspondence is in possession of this document.
Protection of human subjects and animals in researchThe authors declare that the procedures followed were in accordance with the regulations of the responsible Clinical Research Ethics Committee and in accordance with those of the World Medical Association and the Helsinki Declaration.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
This study was supported by grant from Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services (89-04-80-12136).