INTRODUCTION
Allergic diseases often require the use of a high level of health resources. Treatment and control efficiently reduce the incidence of these diseases, by curing or reducing them, thus leading to an improved quality of life for the patient1-3.
Outpatient appointments represent the main access to specialised allergology care. Good outpatient management improves quality of care, and patient and professional satisfaction alike.
The foundation for introducing any improvement plan lies in two basic tools: standard criteria for action and a reliable information system to control the impact of improvement measures.
These measures will reduce long waiting times for appointments, which is a long sought objective that has yet to be attained in full.
We understand a scheduled appointment as one that is arranged after an agreement between the professional and the patient; it is one of the basic tools in Outpatient Appointments (OA) management4. The objectives of outpatient appointments are: diagnosis, follow-up and control of chronic processes, the latter being the case of many allergic processes such as allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, etc.
Furthermore, compliance, observance or adherence is defined as the extent to which a patient accepts the instructions or advice given by the professional, with regard to changes in life style, taking of prescribed medication, attending appointments, etc.5. It should be noted that compliance with appointments is one of the aspects that has been subject to least study to date, despite the fact that patients who miss appointments are deprived from receiving health care, disrupt the service to other health care users and harm the doctor-patient relationship, take potential time away from other patients and increase health costs6, and are an indicator of lack of quality.
The objective of this study is to analyse the degree of compliance with appointments amongst patients scheduled to be seen at our Allergology Service in 2005, after implementing the corrective measures derived from our group's previous studies7-9.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The study population consisted of patients with appointments scheduled throughout 2005 at the Allergology Service of "Virgen de la Arrixaca" University Hospital, Murcia, who had been referred through the normal route and were being monitored according to the clinic programme. Patients were excluded from the study if, despite having an appointment at the Allergology Clinic, they had not been referred through the normal route because of problems in attending the clinic, because of being referred as a result of adverse reactions to immunotherapy, or for any other different reason.
We considered subsequent appointments as those that were agreed to by the professional and the patient at the previous appointment, and were scheduled on the Allergology Clinic's computerised agenda and on the patient's appointment card (OA Card). The following appointment details were recorded: medical appointment, and time and date, using the method proposed by some authors10-13.
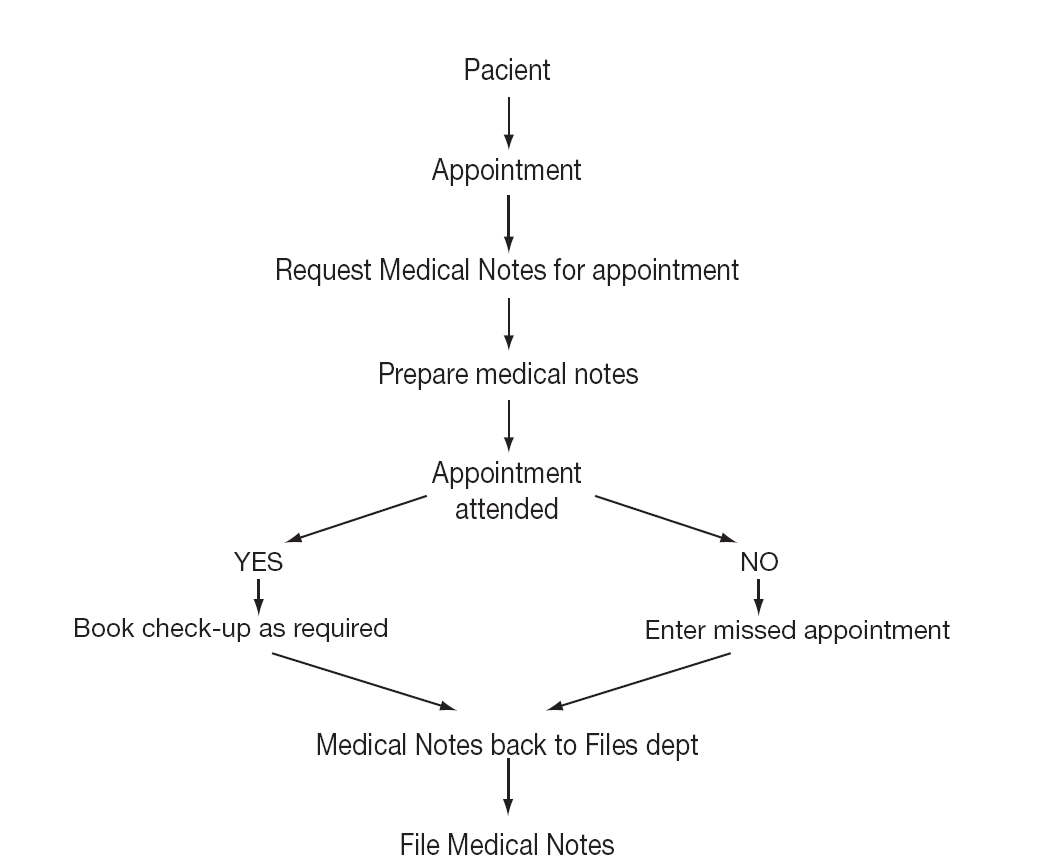
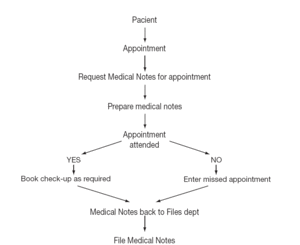
The frequency of control visits and the professional who was to see the patient at each visit were defined according to the Allergology Clinic programme14. Figure 1 shows the algorithm used in the patient appointment process.
Figure 1.--Algorithm showing patient appointment process.
Demographic characteristics were collected from the Hospital Minimum Basic Data Set (HMBDS) and from Clinical Records. These characteristics were compared with the patient's compliant or non-compliant character. Variables referring to each specific appointment (time of appointment, first/subsequent appointment, time since last appointment, etc.) were collected in the Appointment Agenda Database and were compared with whether or not that specific appointment was kept.
From September onwards, patients who had been given appointments for the first time were reminded of the time and date of the appointment by a telephone call in the days prior to the appointment.
Data collected was recorded in a Microsoft Office XP Professional Excel Spreadsheet.
RESULTS
Of the total 18215 appointments (57.67 % for women and 42.33 % for men) scheduled at the end of the year under study, 13.61 % were not kept. Differences were observed in the degree of non-compliance with appointments according to the type of appointment: there was 14.06 % non-compliance with regard to the 3115 first appointments, and 13.52 % non-compliance in the 15100 subsequent appointments.
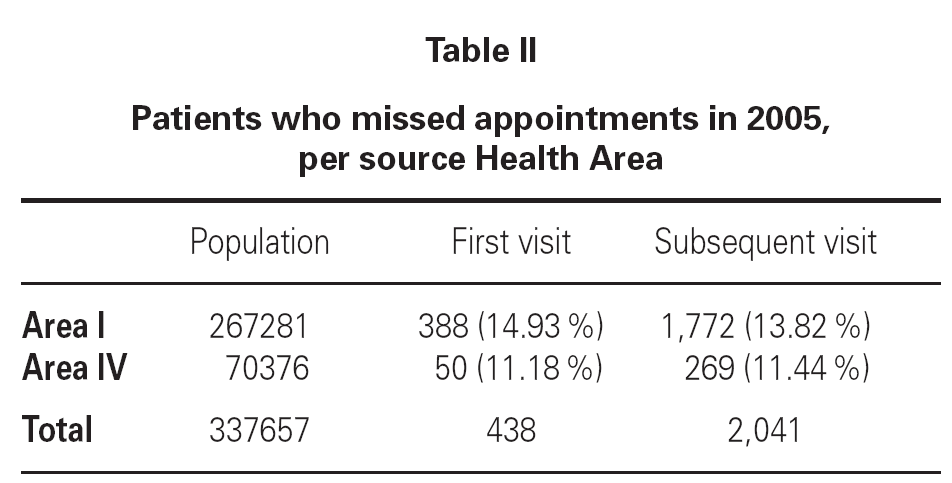
A total of 2479 non-kept appointments were studied (438 first and 2041 subsequent appointments), and of these, 1391 appointments were for women (56.11 %) and 1088 were for men (43.89 %). The missed appointment percentage was 14.11 % for men and 13.24 % for women.
The 2479 missed appointments corresponded to 2215 patients (412 first visits and 1803 subsequent ones), with a mean of 1.12 appointments/patient/year.
The mean age of patients who did not attend appointments was 34.58 ± 14.73 years.
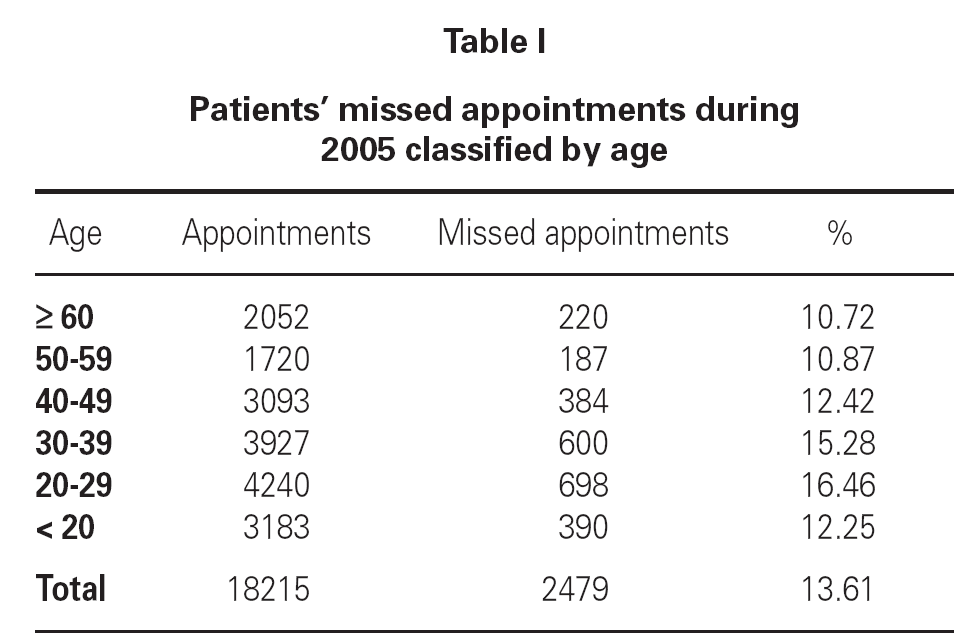
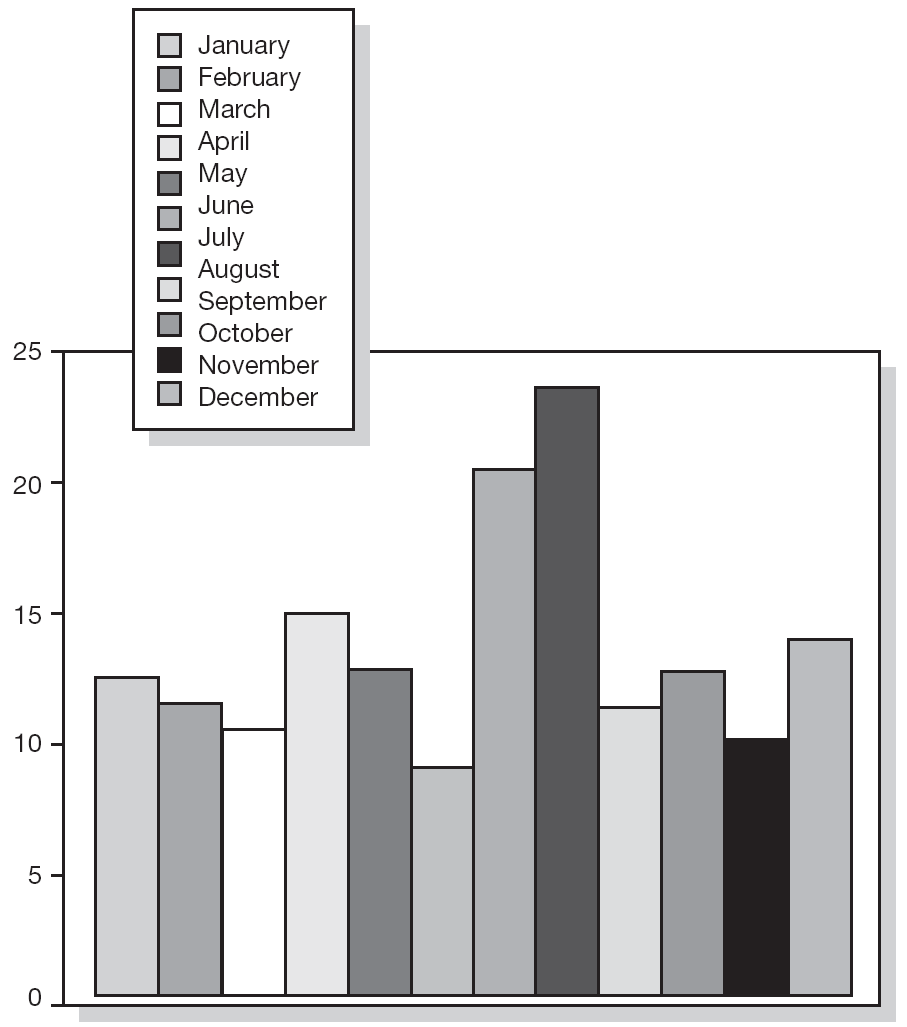
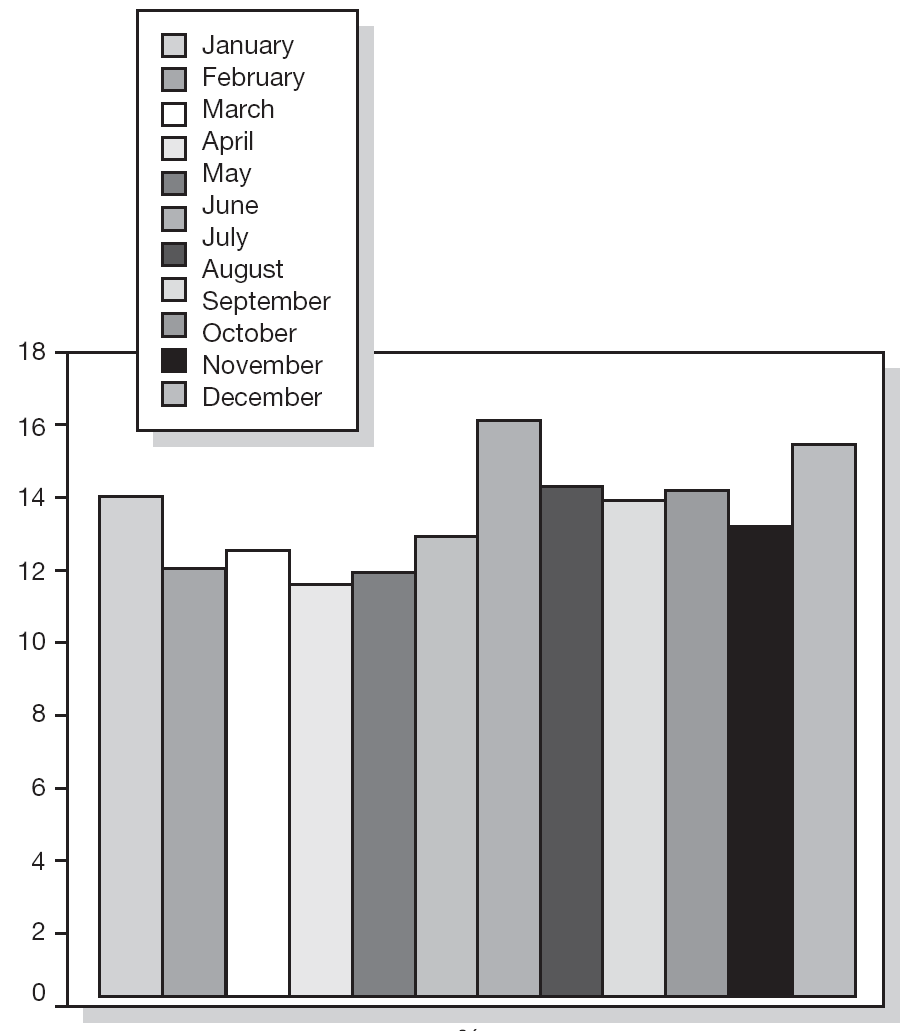
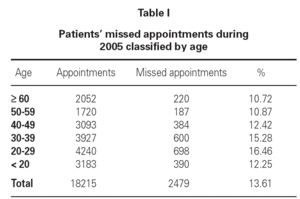
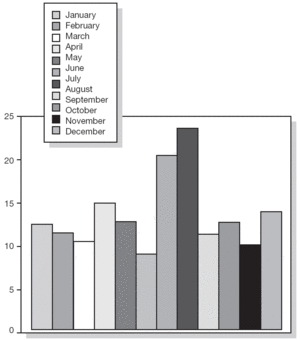
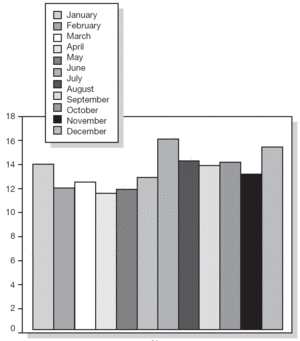
Table I shows the percentage of non-compliance per age group. The age group ranging from 20 to 29 years had the highest percentage of non-compliers (16.46 %). Missed appointments per month of the year are shown in figures 2 and 3; These missed appointments varied from 9.42 % to 23.59 % for first visits and from 11.79 % to 16.14 % for subsequent visits. We observed a significant increase in missed appointments during the summer holidays. July and August showed the highest percentage of missed appointments for both the first visit (20.62 % in July and 23.59 % in August) and subsequent visits alike (16.14 % in July and 14.23 % in August).
Figure 2.--Missed first appointments at the Allergology Clinic.
Figure 3.--Missed subsequent appointments at the Allergology Clinic.
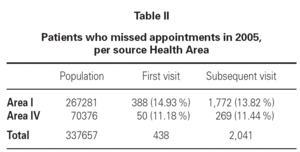
Table II shows non-compliers per source health area. Amongst non-compliers, it was observed that 5.12 % missed appointments on more than one occasion.
DISCUSSION
Improving health care quality has become the principal objective of health systems. Although there is broad consensus amongst health professionals, users and managers regarding the relevance and need to develop strategies to improve quality, there is considerable discrepancy regarding the way to make such improvements.
From our point of view, improving health care quality requires action on a set of related aspects, including an optimisation of actual, proven possibilities in medical science, and patients' perception of the service and human treatment they receive. Both angles capture the defining elements of quality as described in Maxwell's15 classical matrix: effectiveness, efficiency, equity, access, acceptability, and appropriateness.
In our Department, on-going quality improvement has been regarded as a general strategy, structured on patients' needs and preferences, and based on professionals' participation, teamwork, and optimum use of information.
In this Unit we tend to use a single appointment (SA), defined as "an outpatient care service in which a diagnosis is established together with its corresponding treatment, after performing complementary procedures as required, all recorded in a clinical report. All these activities are performed on the same day and within a time that is accepted by the user"16. The aim of the system is to incorporate any specialist consultation into a single visit, including a clinical assessment of the patient (history and physical examination), and any complementary procedures that are required in order to establish the diagnosis and subsequent treatment for the reason that the patient has attended the appointment. The purpose is to try to avoid the delays involved in performing diagnostic tests at a later date, which also means that the patient will not discover his/her diagnosis or commence treatment until later, also entailing more journeys, with their corresponding cost.
This outpatient care service means that patients are scheduled at certain intervals (with 15-20 minute slots per patient) and therefore missed appointments upsets appointment times, which in turn is a determinant factor in reducing waiting lists.
A major problem in the public health system is the large number of patients who require specialist care17. Due to great volume of referrals, the capacity of outpatient appointment management systems is inundated, and inevitably there are waiting lists to see specialists. Waiting lists and delays in receiving care or being informed of a diagnosis are one of the principal causes of dissatisfaction amongst patients, which also has a negative rebound on health professionals18.
The variable of time is no longer used at this clinic as a criterion in waiting list management because, although waiting lists are used to facilitate planning and improve the use of resources, they lose their utility when they become too long, and it is therefore essential to seek other methods of improvement. The normal way to manage waiting lists is to use waiting time as the only criterion for establishing the order of the list, or patients' turns. However, patients' needs do not agree with this order and therefore a patient who waits the longest is not necessarily the one who needs the most care. An advantage of using criteria to decide the order of a waiting list is to remove inappropriate indications, and this significantly reduces erroneous procedures, and in turn increases quality of care. Giving priority according to care needs improves waiting list management, supports the principle of fair access to health services, and increases transparency and trust amongst health system users.
Different authors agree that one of the principal causes of poor control in chronic patients is lack of compliance19-22 and, although it has been demonstrated that appointment compliance does not necessarily correlate with therapeutic compliance in patients with chronic pathologies23-25, some authors have observed that patients who do not attend appointments, rarely heed therapeutic indications26. Some studies have related non-compliance with appointments with the degree of control of chronic pathologies27-29, although no studies on allergies have been found in this respect. Hugues et al30 summarised scientific findings published on the economic impact of non-compliance with pharmacological prescriptions. They observed that economic studies incorporate this variable and concluded that the majority of these studies focused on clinical trials (CT) and therefore on data related to treatment efficacy. Evidence shows that the degree of treatment compliance is always higher in CTs than in normal clinical practice, and non-compliance is a determinant factor in reduced pharmacological treatment efficacy. Authors believe this aspect is an important area that requires a lot of work with regard to studying its economic impact and also in terms of health welfare. Also, missed appointments pose a major obstacle to the efficacy of health interventions.
In 1999 there was a 9.1 % rate of suspended outpatient appointments at public hospitals. This figure does not only include missed appointments, and therefore it is reasonable to imagine that the latter is notably lower than the figures that we observed in three previous studies conducted by our research group, of 15.72 %, 13.06 % and 14.36 %, in comparison with the 13.61 % of appointments in the period that is under review in this study. Of the 70 hospitals that assessed this indicator, 57 analysed the commonest causes for suspension31. The commonest cause in 27 of these hospitals was caused by the hospital itself (suspended appointments due to schedule organisation problems: holidays, conferences, time-off for on-call doctors, and other justified absences on the part of the doctor). In 22 of these hospitals, patients were the commonest cause (cancellation or forgetting the appointment), and in 8 hospitals there were diverse causes. This is not the case of our Clinic, where all these aspects have already been taken into consideration. We did not find any studies in our bibliographic search in similar countries to Spain in order to conduct a comparative study. The only work that we found was conducted in Saudi Arabia32, and it reported a much higher degree of non-compliance, of about 30 %, in that country.
The percentage of non-compliers and non-compliance with specific appointments that we have found in our studies falls within the range of values obtained by other authors of studies conducted in Primary Health Care33-40 and in Specialist Care alike, as is the specific case of study at a gastroenterology outpatients clinic41. However, it should be noted that this comparison has to be made with great care, since the studies are not homogenous with regard to definition of non-compliance (some only consider non-compliance when observed in over 50 % of appointments), follow-up time (the majority are clinical protocols evaluated over 6 months), characteristics of the appointments (specific hypertension appointments in the majority of cases), etc. It should be noted that the doctor-patient relationship is a significant factor in appointment compliance42, and this also limits comparability.
We believe that there is not just one underlying factor responsible for non-compliance. We need to consider such aspects as doctor-patient relationship, cultural factors related to certain pathologies, accessibility to the public health system, characteristics of treatment and adverse effects, and the patients' physical, mental and socio-economic characteristics, which may help to explain the causes of non-compliance.
According to some studies, erroneous appointments scheduled by the admissions department may account for 10 % of cases43. Although we did not quantify this situation, some appointments were scheduled to inform patients of test results, when these tests had not even been performed. This increased the number of appointments, and in some cases the number of appointments missed by a certain patient.
Some authors have suggested that patients have a shared responsibility in public health service waiting lists, as a result of non-compliance with appointments that are not actually cancelled, thus preventing other patients from filling these appointments44.
After implementing the corrective measures proposed in our previous studies7,8, the results from this study make us think that current accessibility to health services may possibly contribute to some extent to non-compliance.
The reasons behind non-compliance are not well known, but there are several theories45-47 It is therefore extremely interesting to evaluate missed appointments and the factors that play a part in them. Several authors have observed that non-compliers do not have a definite general profile48,49, although there are some studies, like ours, that have found greater non-compliance amongst young patients50,51. This may be due to lack of motivation towards illness in this age group. As we observed in our previous study, men were more non-compliant that women, and this difference may be explained by the fact that as yet more men have jobs than women, and therefore women in the non-working sector are able to attend appointments without interfering with working hours.
Patients who have already missed previous appointments show a higher percentage of non-compliance, and other authors have already described this52. This may be due to the fact that the primary causes of non-compliance described by patients are lack of interest and forgetfulness. It could therefore be suggested that patients who have complied well for a long period of time may offer a reasonable guarantee on a long-term, although some authors have observed that non-compliance tends to be higher on a long-term53. Unlike that observed by other authors of studies on chronic pathologies54, in this study and in our previous ones, we have not found major differences in compliance with regard to the time that has passed since the last appointment or visit. This may be because the majority of our patients have rhinitis and/or extrinsic asthma, and therefore after prescribing symptomatic treatment and allergy vaccines, the majority are given appointments one year after for a check up.
In one study conducted by our group on patient satisfaction55, 113 patients completed questionnaires and 28 of them (24.78 %) offered suggestions in the section "How can we improve?" The commonest suggestions were related to improving the appointment system, reducing the waiting list and the long time spent in the waiting room before being seen. Amongst these suggestions, the most commonly repeated phrases were, "less time in the waiting room before the appointment", "be punctual" "wait less time to get an appointment". The time spent in a waiting room is partly due to our objective of achieving single appointments and we feel that so far this has not been sufficiently explained to our patients, who in general accept this wait better at private clinics.
Despite the percentage of non-compliance at appointments, we should not forget that scheduled appointments for chronic pathologies have shown to be more effective and are better accepted by patients than appointments on demand56-58. It has been demonstrated that some measures are effective in increasing the degree of compliance with appointments59-61. When it is decided that a patient needs to be seen again, the ideal situation is to give the patient the time and date of his/her next appointment as they leave the clinic. This gives patients the opportunity to choose the best time for them from the times that are available on the allergology specialist's agenda. At present, we are at a phase of solving this problem. Up to date, administrative clerks check patients' addresses and request that if they cannot attend the appointment or if they have already been seen, to telephone the Clinic on the number provided in order to be given a new time and date, so that the old appointment can be filled by another patient. If an appointment cannot be given at that moment, the administrative department is responsible for notifying patients of the time and date of the appointment as soon as possible by other means.
Having confirmed the high percentage of patients who do not attend their first appointment (14.06 % in this study and 13.29 % in the previous one), often because patients cease to worry once the acute phase of basic processes has been completed, we again are faced with the need to emphasise the Consensus action amongst Primary Health Care and Specialist Allergology Care, which lays down guidelines for allergology referrals. The Consensus was drawn up by representatives of Sociedad Española de Alergología e Inmunología Clínica (Allergology and Clinical Immunology Spanish Society), Sociedad Española de Medicina Familiar y Comunitaria (Family and Community Medicine Spanish Society), Sociedad Española de Medicina General (General Practice Spanish Society), Sociedad Española de Medicina Rural y Generalista (Rural and Family Medicine Spanish Society), and Sociedad Española de Pediatría Extrahospitalaria (Extra-Hospital Paediatrics Spanish Society). In this respect, there is an increasing call for a single management system in order to solve the lack of communication between different health care levels. In the last 25 years there has been a negative split between the two health care levels; the Primary Health Care has grown and in fact increased its scientific and professional level. But a negative aspect has occurred at the same time: there is a manager for each level in the same health area. A single management system would lead to integral care, and primary health care would act as a speciality of its own, and, amongst other things, this would avoid opposing interests such as primary health care aiming to make rapid referrals to specialist areas, and hospitals aiming for primary health care to make less use of its services.
It is also important to understand so called "emergency" situations at hospital A&E departments, in order to provide an appropriate clinical response to every case. Clinical guidelines should be drawn up for shared care at A&E departments, and there should be someone responsible for the coordination of this type of demand every day, using a rotation system. This "emergencies" should be minimal, for after patients are seen in A&E they should be then referred to their primary health care doctor. Taking all this into account we insist on the advantages of regular check-ups, and updating of current protocols, based on scientific evidence, aiming at designing clinical action guidelines that are the subject of frequent debate but little action.
In the case of patients in area IV, travel distance (approximately 50 to 130 km) may play a role in missed appointments to a certain extent. Therefore, in view of the population in that area, the creation of a post for an Allergologist there, this would not only contribute to reducing the waiting list at our Service, but it would also improve patients' attendance in this geographical area, avoiding the need for long distance travel and missing unnecessary hours at work and school.
There is no specific profile of non-compliant patients, although this study does confirm what we had already found in our previous studies, that it would probably be useful to be aware of young patients and those who have previously missed appointments, in order to take measures such as telephone reminders to prevent non-compliance, and for this purpose, hospital management should provide resources as required. Also, when patients miss an appointment, it is advisable to ring them, find out the reason, and offer a new appointment. Although we have already suggested this measure, we have not been able to carry out it out because of lack of human resources. If a telephone call is not possible, patients should be called for an appointment by post, and at the next appointment, the reason for not attending the previous one should be noted, and the regular appointment process should be re-started. We repeat that if a patient misses several appointments and then asks for another appointment, of if he keeps postponing appointments, the patient should be referred to their Primary Health Care Doctor who should decide whether they need to be seen by an allergology specialist.
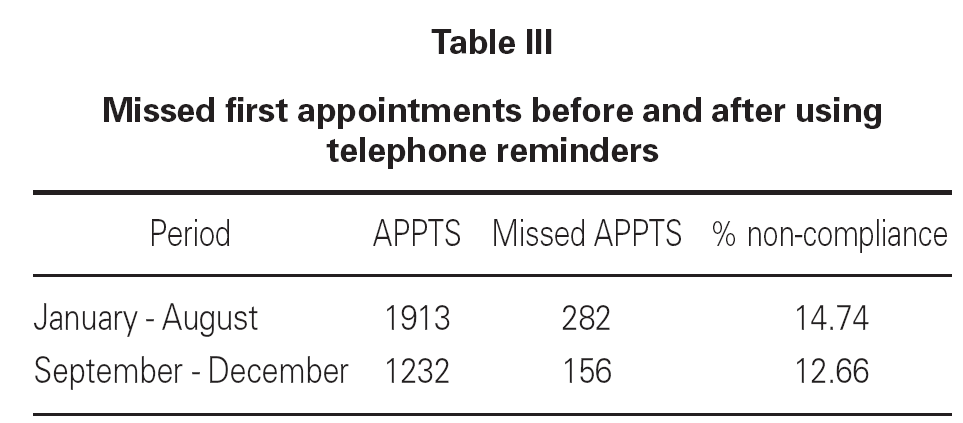
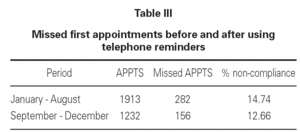
Another important aspect to be considered is the economic cost of non-compliance. Using an approximate calculation of costs at our clinic by means of analytical accountancy, as described in a recent study62, the cost of the doctor's time is 47.40 € at a first visit and 31.60 € at subsequent visits. This means that the cost of missed appointments stands at 85,256.80 €. This figure provides sufficient grounds to put measures into practice that will reduce non-compliance, such as reminding patients of the time and date of their appointment by phone (table III). This measure was carried out from September onwards in all first-time patients. The number of missed appointments fell from 14.74 % to 12.66 %, accounting for an estimated saving of 1185 € in doctors' time during this period. This system did not only serve to confirm attendance; 25 patients also asked for the appointment date to be changed for different reasons, as described in a poster presented by Campuzano López et al63 at the "VIII Jornadas de Gestión y Evaluación de Costes Sanitarios" ("VIII Conferences on Health Cost Management and Evaluation"). It showed that of the 1451 telephone calls made over a 6-month period, 37 patients (2.55 %) asked for the appointment date to be changed as they could not come on that day, and this represents a possible estimated saving in doctors' time of 1753.80 €, in addition to the cost that would have been incurred from patients who had forgotten about their appointments.
CONCLUSIONS
1.Possibly as a result of applying some of the corrective measures proposed earlier, we observed a slight reduction in missed appointments in comparison with previous years' studies (14.36 % from July 2002 to June 2003, 15.72 % from July 2003 to June 2004 and 13.61 % in 2005). However, the relation between non-compliance with first and subsequent appointments varied, showing higher non-compliance with first appointments (14.06 % in 2005 vs. 13.29 % in the previous period) and lower non-compliance with subsequent appointments (13.52 % in 2005 vs. 16.11 % in the previous period).
2.The degree of non-compliance is a quality indicator, because it reduces the yield of appointments, and it evidences a lack of cohesion of patients with Primary Health Care Units for first appointments, and with Specialist Care Units for subsequent appointments. Once certain levels of attendance have been attained, it is difficult to achieve an effect on this point in order to improve attendance rates
3.Health administrators should quantify the economic loss derived from this problem and calculate the cost of studies to reduce such losses.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to express our gratitude to M.ª Dolores Carrillo Mercader, M.ª Pilar Cascales Ruiz, M.ª del Tránsito García Lacal and Josefina López García for their collaboration in organising the appointment agenda at our Clinic.
Correspondence:
J.M. Negro Alvarez
C/ Valle n.º 7
30120. El Palmar.
Murcia. Spain.
Tel: 968-369615
FAX: 968-369791
E-mail: jnegroa@meditex.es